How to troubleshoot Ubuntu problems does not start
You are starting your computer to prepare for some tasks, editing documents or simply playing games. But suddenly there was a problem. Ubuntu does not start.
Sadly, although Linux is very reliable, it sometimes encounters problems, like Windows 10 or macOS. In most cases, you can solve this problem. See how to do this in the article below. (These steps are designed for Ubuntu users, but in general, they can also be applied to other Linux operating systems).
Fix Ubuntu failure to start
- 1. Can you access GRUB Bootloader?
- Fix the GRUB bootloader
- Try a dedicated boot disk
- 2. Restore the GRUB Bootloader menu
- 3. Reinstall Ubuntu
4. Hardware replacement is faulty
1. Can you access GRUB Bootloader?
GRUB is a bootloader to ensure that the selected operating system is booted. On a dual-boot computer, it will include all installed operating systems, including Windows. Installing Windows with Ubuntu may cause the bootloader to be overwritten, resulting in problems starting Ubuntu.
Other problems may also damage the bootloader, such as an unsuccessful upgrade or a power failure. It's not uncommon for an error to interrupt your Linux experience.

To check the GRUB bootloader, please restart your computer, while holding SHIFT. You should now see a list of installed operating systems, a navigable menu using the arrow keys. If not, then the problem you have is that the GRUB bootloader has been corrupted or overwritten. Repairing bootloader is the only solution (if you are booting dual, you can still access Windows).
Note : If you see the GRUB bootloader, skip to the next section.
Fix the GRUB bootloader
If GRUB doesn't load, you can fix it with a disk or USB with Ubuntu installation. Restart the computer with the inserted disk and wait for it to load. You may need to change the boot order of the computer in the system BIOS to make sure that the disk will boot first. Record the boot order before you change it!
When the installation disk is booted into the Live environment , confirm that you have a network connection and then open a Terminal. Enter the following commands:
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:yannubuntu/boot-repair sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y boot-repair boot-repair This will install the boot-repair tool and run it after the last instruction. Wait for the system to be scanned, then select the Recommended Repair option . Note that there is an Advanced view mode , which allows you to choose the default operating system, the default disk or partition, and other settings that may be useful. Click Apply when done. You can now restart your computer and boot into Ubuntu, or treat it as an option in the GRUB bootloader menu.
Try a dedicated boot disk
Another way to run the installation disc is to try a dedicated disk, such as Boot-Repair-Disk, which you can download from Sourceforge. For best results (especially if you are using Windows 8/10), you should write it to a USB device instead of a CD / DVD.
This boot disk is basically a boot-repair program detailed above, but on its own boot media. Therefore, the instructions are the same. That's just a quicker solution.
2. Restore the GRUB Bootloader menu
If you can see the bootloader, then you don't have to do any of the above. There is a recovery tool built into Ubuntu, which you can use to help fix the problem.
In the bootloader menu, find the Advanced options section in Ubuntu, then select the entry connected to recovery mode with the arrow keys. Press Enter to continue and wait when Ubuntu is booted into a stripped down version. If you used Windows' Safe Mode, this is the same.
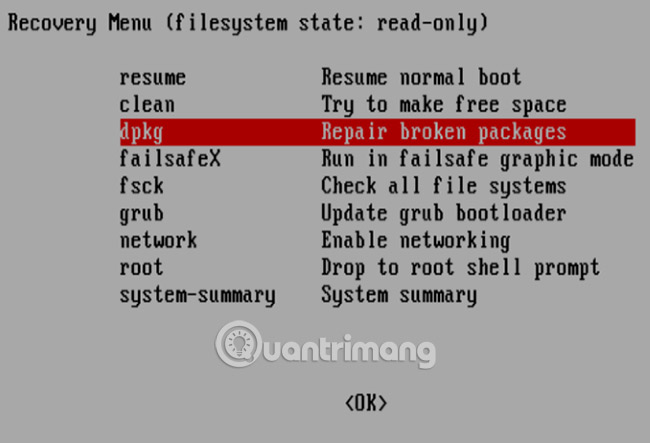
Some options are available here to fix the problem. The three options you should try in order are:
1. fsck - This is a file system checker, scans hard drives and fixes any errors it finds.
2. clean - Use this feature to create free space, useful if Ubuntu fails to boot due to lack of hard drive capacity.
3. dpkg - With this option, you can repair the broken package. Failure to install or update the software may also cause problems when booting Ubuntu. Fixing them can solve this problem.
If Ubuntu has not been started before, you should also try failsafeX. Graphics drivers or problems with the Xorg graphics server can prevent Ubuntu from booting correctly. Please use failsafeX to fix this.
Meanwhile, advanced users can choose the root menu option to fix the problem manually, assuming what the cause is.
3. Reinstall Ubuntu
In the event of a serious problem and it will take a long time to resolve, you can simply reinstall Ubuntu. This can be done without overwriting your existing files and folders.
Again, boot into the Live environment on your Ubuntu CD / DVD or USB drive, and start the installation. The installer will detect the current version of Ubuntu and provide you with the Ubuntu Reinstall option. Search options with notes " Documents, music, and other personal files will be kept . " In most cases, the installed software will also be retained.
Of course, you should have a backup copy of all your Ubuntu data, either manually using a backup utility, or using a disk mirroring tool like dd. You may prefer to synchronize data with the cloud via Dropbox or another open source cloud solution.
After the reinstallation is complete, Ubuntu will be backed up and run.
Note : The Ubuntu and Install Erase option is not recommended, unless other options are not available.
4. Hardware replacement is faulty
Another cause that Ubuntu can't boot may be due to hardware failure. This is often a problem with their hard drives and cables, although problems with motherboards and processors, or even power supplies, may be the source of the problem.
Try Quantrimang 's hard drive diagnostic guide . You can also focus your efforts on diagnosing hardware problems, which can cause your computer to boot and repair them at no cost.
And don't think that just because you're using a laptop you can't fix your problems yourself. Although you are often encouraged to contact the manufacturer for assistance when the warranty period is still available, but if the warranty has expired or you prefer to repair it yourself, you should consult the troubleshooting guide. and repair broken laptop.

When a faulty HDD is replaced, you often need to reinstall Ubuntu from scratch. (Unless you have done a full backup of the previous drive image, in this case, it can be restored.)
If Ubuntu doesn't boot, it won't be easy to make things work again. If GRUB bootloader cannot be repaired, it will take a long time for you to use your computer again. However, another argument favors maintaining regular backups, or at least syncing your valuable data to the cloud!
Is your Ubuntu computer loaded? How do you fix it? Did you fix the bootloader or simply start from scratch? Perhaps the failure caused you to give up Linux and delete Ubuntu from the system? Let us know in the comments section below!
See more:
- How to fix MBR from Ubuntu
- Fix BootLoader error for Ubuntu
- Restore the Ubuntu Bootloader Wubi component