Prevent deleting data in Windows Server 2003 Active Directory
TipsMake.com - It can be said that one of the most 'problematic' issues in managing and working with Active Directory is mistakenly deleting data or objects that are accidentally or incorrectly handled by users. Of course, technically they must have full rights in Active Directory to be able to perform the removal of the internal object . Besides, there is a very easy case, that is, users delete all Organizational Unit - OU with all that inside without paying attention to the next message window.
One of the most frequently encountered problems is moving a single unit of OU with all internal objects to another OU :
Remember, as a system administrator, members of the Domain Admins , Enterprise Admins, or Schema Admins groups are very important locations. If you are not sure whether they can handle the job or not, it is best not to assign them rights. The methods used here are mainly for Active Directory and Windows Server 2003 Domain Controller , and for Windows Server 2008 , there are some more options on the graphical interface.
Theoretically, if you want to avoid deleting the wrong data or internal objects, the administrator must assign the corresponding permissions to each Object or Organizational Unit of Active Directory . Besides, you can use the method below to assign Access Control Entries - ACEs:
- For Organizational Unit components need 'protection', add Deny ACEs to the level of Delete and Delete Subtree of Everyone group.
- For the external Container containing the OU , assign Deny ACE to Delete All Child Objects of the Everyone group.
This will help the administrator prevent OU objects from being mistakenly deleted. In particular, when someone deliberately or unintentionally deletes these protected components, the system will display an error message stating that access and operation is denied.
Method 1: Use Active Directory Users and Computers:
To do so, log on to the Domain Admins group member computer, then open Active Directory Users and Computers from the Start Menu -> Administrative Tools or type DSA.MSC in the Run window. Next, apply the appropriate level of authorization to the OU object to be protected by right-clicking and selecting Properties .
At the object properties window, select the Security and Advanced tabs:
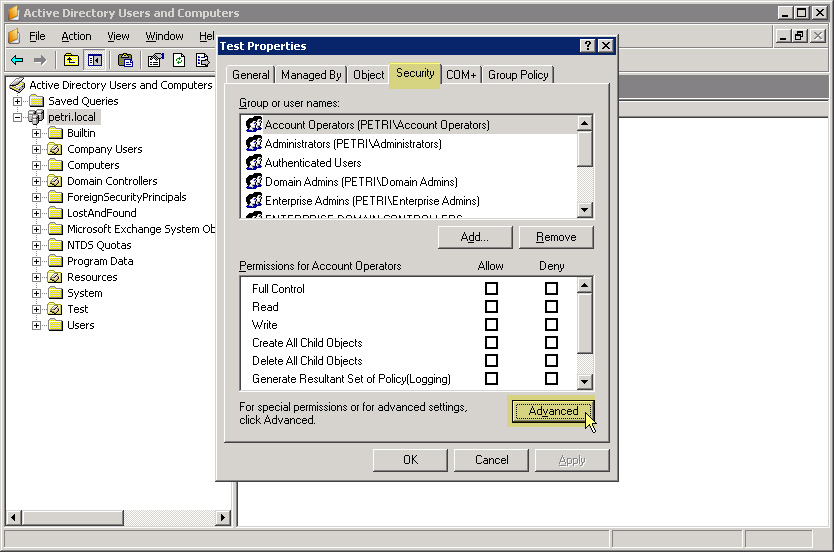
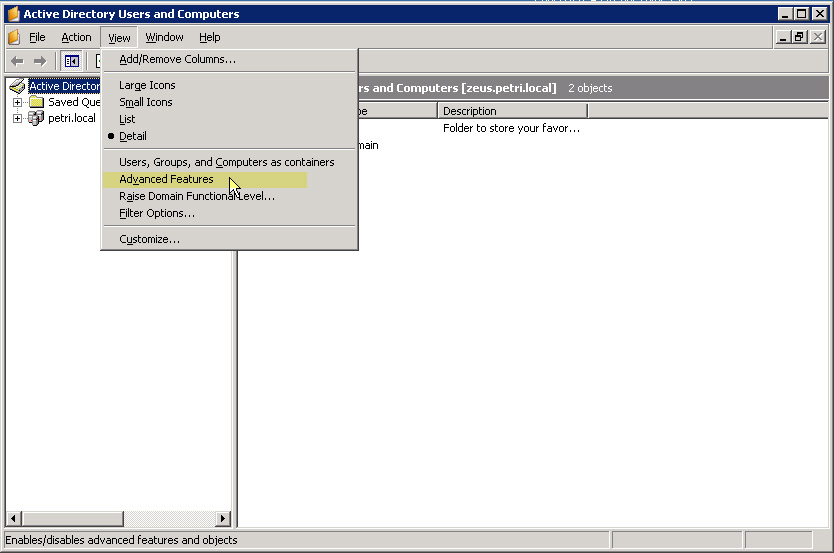
Note that the Security tab is not available in default mode. To open this window, close the Property section and select Advanced Features from ADUC View:
In Advanced Security Settings, click Add , type Everyone then click OK :

In the Permissions section of Permission Entry , check the corresponding Deny checkbox of Delete and Delete Subtree . Check the box Apply these permissions to objects and / or containers within this container only as shown below:

Click OK to close the Permission Entry window :

Click Apply at Advanced Security Settings. Then, review the information when the Windows Security window displays and select Yes to continue:
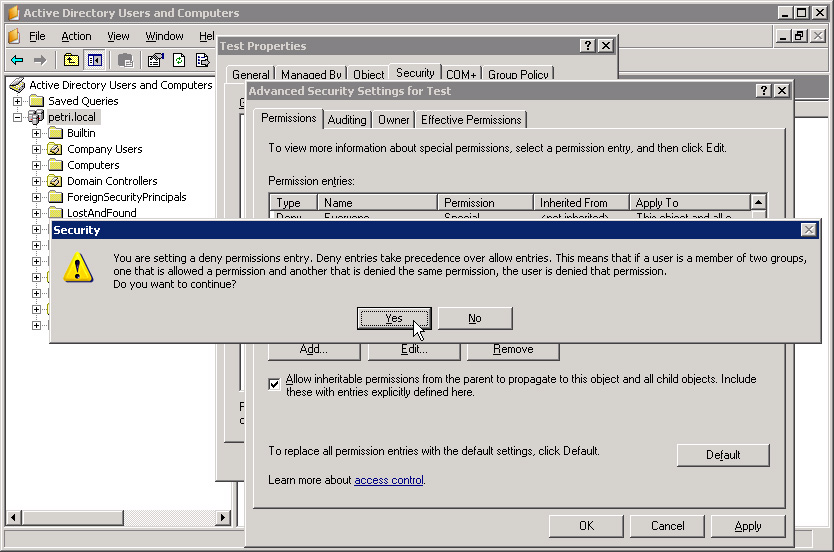
Click OK to close the Advanced Security Settings window and continue OK to close OU Properties .
Next, apply the same level of authorization to the Container section containing the protected OU . To do this, right-click on the Container and select Properties:
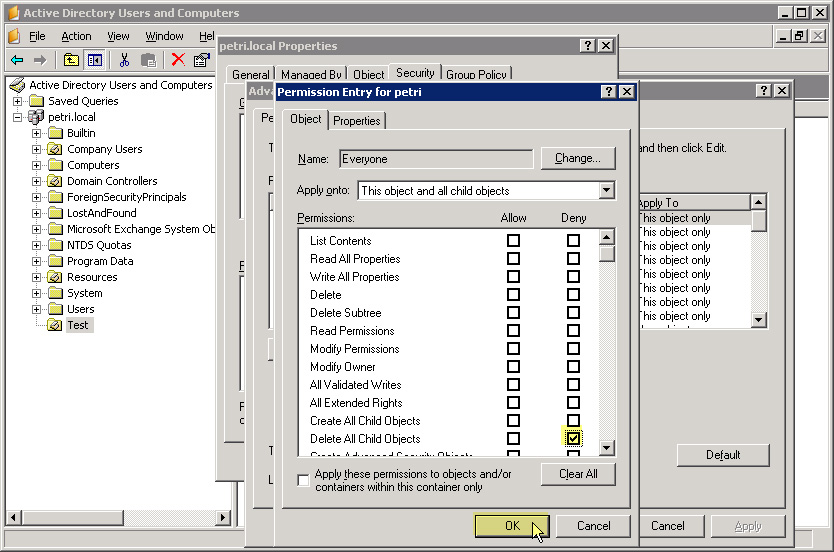
Select the Security tab in the Container Properties window . Then, click Add , type Everyone and OK . In the Permissions for Everyone section , check the Deny checkbox of Delete All Child Objects, then click Apply :
Then close all the windows of this section. When deleting any arbitrary OU , the system will display an error message as shown below:

To remove this protection, delete the Deny ACEs assigned to the Everyone group.
Method 2: use DACLS statement:
On the other hand, if you want to use the DSACLS function to protect the OU object, you can apply:
dsacls "ou = Company Users, dc = mydomain, dc = com" / d Everyone: SDDT
If you want to protect the entire OU structure, you can use the command:
for / f "tokens = *"% i in ('dsquery ou -limit 0') due to dsacls% i / d Everyone: SDDT
Note that the above command will apply to the Organizational Unit EVERY in the Active Directory domain. If you want to apply different security levels, change the dsquery command.
Good luck!