POISSON function - The function returns the Poisson distribution in Excel
In predicting the number of events that occur within a specific time, one cannot help but use the POISSON function. The following article details how to use the POISSON function, the function returns the Poisson distribution.
Description: The function returns the Poisson distribution, which is the basis for determining the number of events occurring over a defined period, for example, with the vehicle density on weekends, the number of vehicles passing through the toll booth in 1 minute. From the anticipation, there will be specific support measures.
Syntax: POISSON (x, mean, cumulative) .
Inside:
- x: Number of events, is a required parameter.
- mean: The value to be estimated (value in the form of numbers), is a required parameter.
- cumulative: A logical value that determines the format of the return value. The following values are available:
+ cumulative = TRUE => function returns the cumulative Poisson probability that 0
+ cumulative = FALSE: function returns the cumulative Poisson probability that the number of events = x.
Attention:
- Poission function is calculated by the formula:
+ cumulative = TRUE:

+ cumulative = FALSE:

- If x is a decimal, the function takes an integer value of x.
- x and the value must be numeric otherwise the function returns the #VALUE error.
- If x
- If mean the function returns the value #NUM !.
For example:
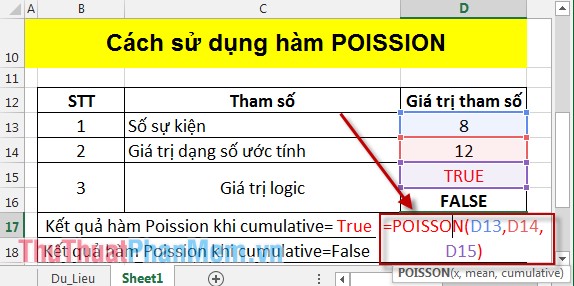
- Calculate Poission when cumulative = True :
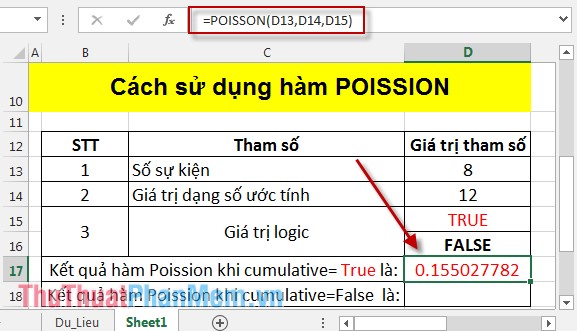
In the cell to calculate enter the formula: = POISSON (D13, D14, D15) .
Pressing Enter results as:
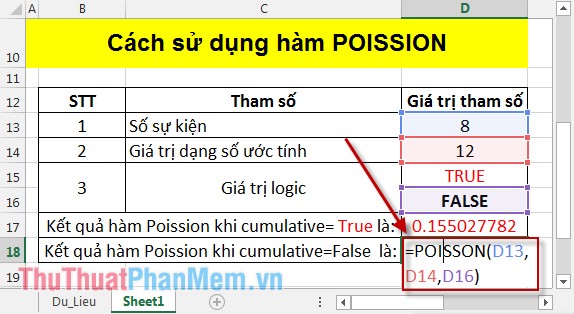
- Calculate Poission when cumulative = False :
In the cell to calculate enter the formula: = POISSON (D13, D14, D16) .
Pressing Enter results as:
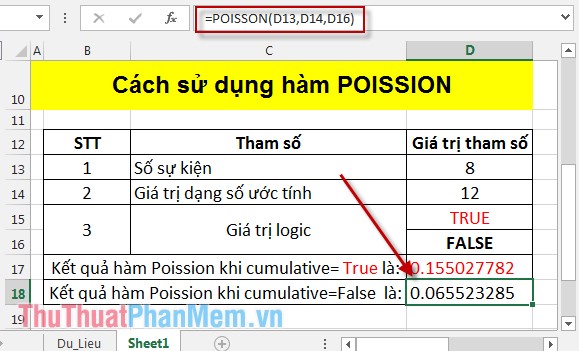
Thus the Poission function value at the cumulative value is different. Hopefully the Poission function will help you in predicting events that occur in a specified time period.
Good luck!
You should read it
- ★ GAMMA.INV function - The function returns the inverse of the gamma distribution in Excel
- ★ GAMMA.DIST function - The function returns the gamma distribution in Excel
- ★ CHIDIST function - Function returns the right end probability of the distribution when squared in Excel
- ★ PHI function - The function returns the value of the density function for a normal distribution in Excel
- ★ BETA.DIST function - The function returns the Beta distribution in Excel