AMORDEGRC function - The function returns the depreciation for each accounting period in Excel
Excel is a powerful tool in financial accounting. In each accounting period depreciation values are always mentioned. The following article details the AMORDEGRC function, the function returns the depreciation for each accounting period.
Description: The function calculates the depreciation of assets in each accounting period, the preferred function is to look at the French accounting system.
Syntax: AMORDEGRC (cost, date_purchased, first_period, salvage, period, rate, basis) .
Inside:
- cost: The value of the property when purchased, is a required parameter.
- date_purchased: The date the asset was purchased, a required parameter.
- first_period: The last day of the first accounting period, is a required parameter.
- salvage: The recovered value of the real ship at the end of the service life, which is a mandatory parameter.
- period: The number of periods for which depreciation is to be calculated and required.
- rate: Depreciation rate.
- basis: The basis for determining the number of days, is an optional parameter if ignoring the default value is 0. Basis has the following values:
+ Basis = 0: The number of days per month is 30, the number of days per year is 360 according to US standards.
+ Basis = 1: The number of days per month is equal to the actual number of days per month, the number of days in a year is the actual number of days per year.
+ Basis = 2: The actual number of days in a month / 360 days a year.
+ Basis = 3: The actual number of days in a month / 365 days a year.
+ Basis = 4: The number of days per month is 30 / A year has 360 days according to European standards.
Attention:
- Enter the date using the DATE function (year, moth, day) .
- The function calculates depreciation to the end of the term or depreciation until the accumulated depreciation value is greater than the capital spent minus the residual value of the asset when it expires.
- The depreciation value reaches 50% in the period before the last period and increases by 100% in the last period.
- If the asset's life cycle is from 0 to 1, 1 to 2, 2 to 3, 3 to 4 => the #NUM!
For example:
The depreciation in the first period of an asset is calculated as follows:
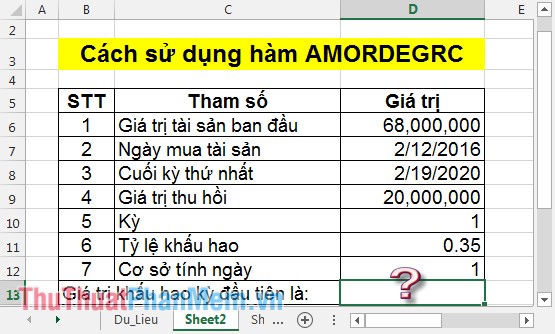
In the cell that you want to enter the formula: = AMORDEGRC (D6, D7, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12) .
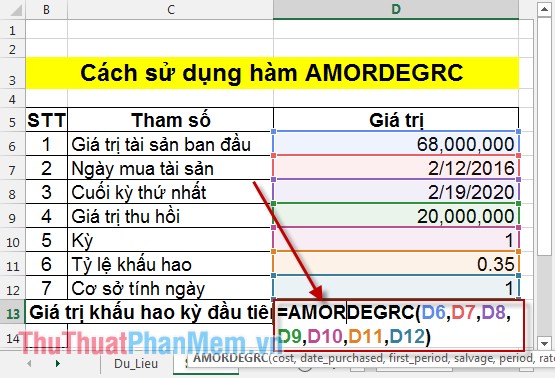
Pressing Enter will calculate the depreciation value in the first period of the 68 million property value:
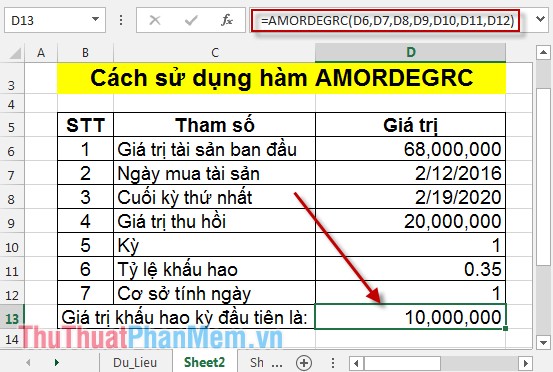
Thus, the depreciation value of the asset is 68 million VND in the first period, the depreciation value is 10 million.
Above is a guide to using AMORDEGRC function, hoping to help you in your work.
Good luck!
You should read it
- ★ SYD function - Calculate depreciation for an asset by remaining value in Excel
- ★ Basic Excel functions that anyone must know
- ★ DB function - The function calculates the depreciation of assets with specific maturity in Excel
- ★ VDB function - Calculate asset depreciation by the declining balance method in Excel
- ★ How to use the IF function in Excel