How to find the Process ID of the application on Windows 10
On Windows 10, every process of an application or service receives an identifier called a Process ID (PID). The PID has many different uses, but mainly, it exists to uniquely identify each process throughout the system and distinguish programs running multiple instances (such as when editing two text files with Notepad).
Although most common users don't need to worry about system processes, knowing their IDs can be useful in many cases. For example, when you need to debug an application. An application freezes and you have to manually end the process. Or you need to check the system resources that a particular process is using.
There are at least 4 methods to check Process ID (PID) for any active process in Windows 10, using Task Manager, Resource Monitor, Command Prompt and PowerShell.
In this Windows 10 guide, Tipsmake will show you the steps to determine the Process ID for an application or service.
How to identify Process ID with Task Manager
To check the Process ID for an application on Windows 10, follow these steps:
Step 1. Open Start.
Step 2. Search for Task Manager and click on the top result to open the application.
Quick Tip : You can also open the application by right-clicking on the taskbar and selecting the Task Manager option, right-clicking the Start buttonand selecting the Task Manager option,or using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Shift + Esc .
Step 3. Click the Details tab .
Step 4. Confirm the Process ID of the application in the PID column.

Step 5. Click the Services tab .
Step 6. Confirm the Process ID of the service in the PID column.

After completing the steps, you will know the Process ID number for the services and applications that are running or suspended on Windows 10.
How to determine Process ID using Resource Monitor
To find the Process ID for an application using the Resource Monitor panel, follow these steps:
Step 1. Open Start.
Step 2. Search for Resource Monitor and click on the top result to open the application.
Step 3. Click the Overview tab .
Step 4. Confirm the Process ID of the application and service in the PID column.
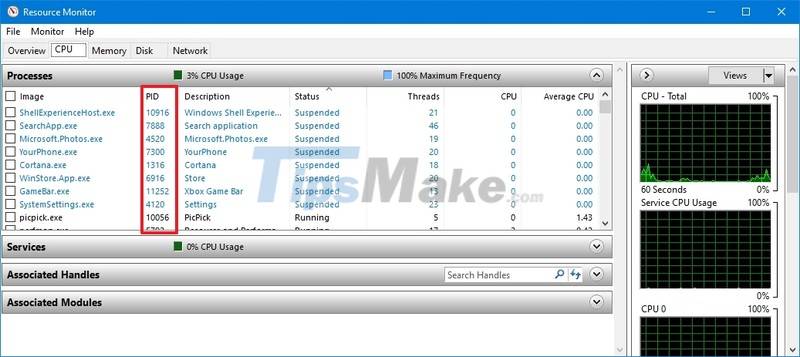
After completing the steps, you will have an overview of IDs for running and suspended processes.
How to determine Process ID using Command Prompt
To find out the ID of a process using commands, follow these steps:
Step 1. Open Start.
Step 2. Search for Command Prompt and click on the top result to open terminal.
Step 3. Type the following command to see the Process ID list and press Enter :
tasklist 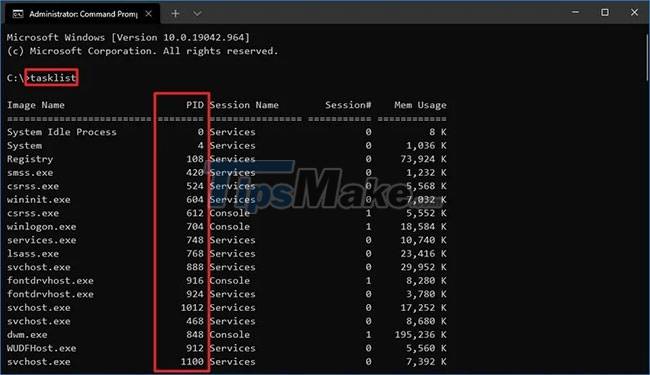
Step 4. Type the following command to see the list of Process IDs for Microsoft Store apps and press Enter :
tasklist /apps 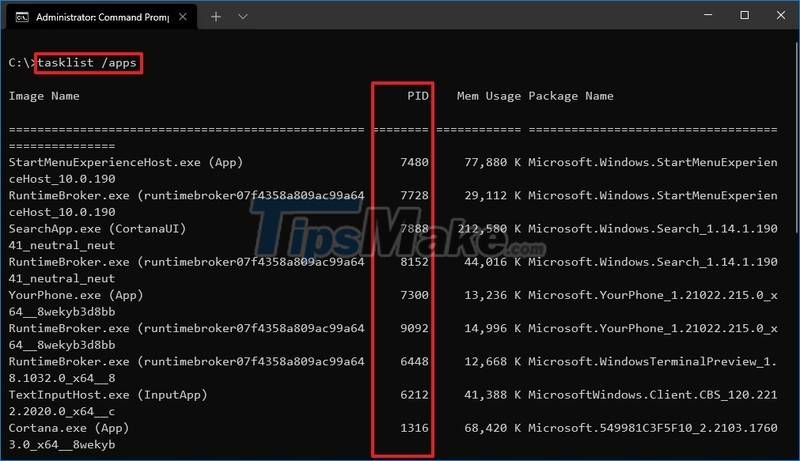
Step 5. Type the following command to get the ID from the process name and press Enter :
tasklist /svc /FI "ImageName eq PROCESS-NAME*" 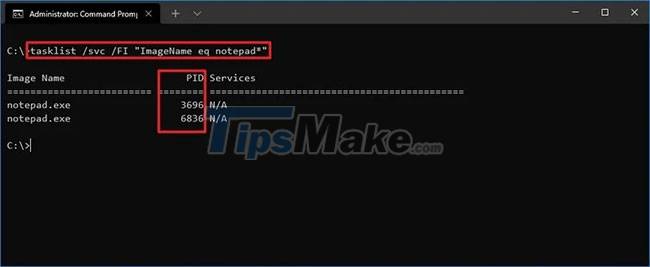
In the command, make sure to substitute PROCESS-NAME for the .exe name of the process. The * is a wildcard to match part of the name without having to enter the exact name of the process.
This example shows the progress for Notepad:
tasklist /svc /FI "ImageName eq notepad*"After you complete the steps, the output will show the IDs for the processes running on the device.
How to determine Process ID using PowerShell
To determine the Process ID of an application or service with PowerShell, follow these steps:
Step 1. Open Start.
Step 2. Search for PowerShell and click on the top result to open Terminal.
Step 3. Type the following command to see the Process ID list and press Enter :
Get-Process 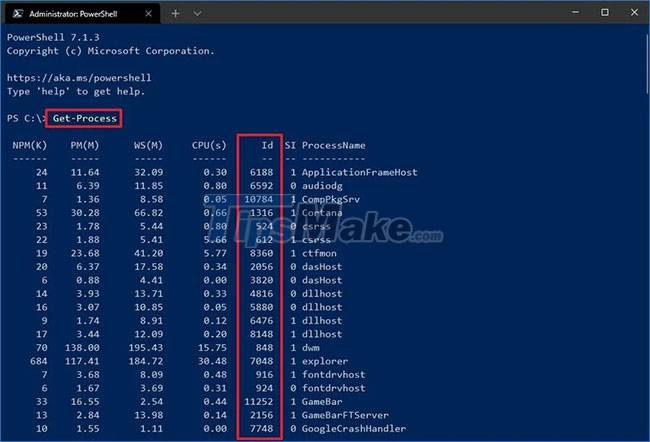
Step 4. Type the following command to view information (including ID) about a process and press Enter :
Get-Process PROCESS-NAME* | Format-List * 
Step 5. In the command, make sure to substitute PROCESS-NAME for the .exe name of the process. The * is a wildcard to match part of the name without having to enter the exact name of the process.
This example shows Process ID Notepad and all available information about the process:
Get-Process notepad* | Format-List * 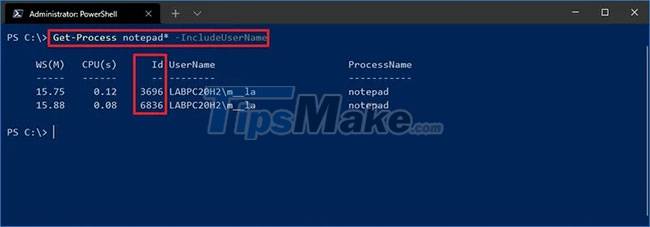
Step 6. Type the following command to determine the ID, owner of the process and press Enter :
Get-Process PROCESS-NAME* -IncludeUserNameStep 7. In the command, make sure to substitute PROCESS-NAME for the .exe name of the process. The * is a wildcard to match part of the name without having to enter the exact name of the process.
This example shows the Notepad processes:
Get-Process notepad* -IncludeUserNameAfter you complete the steps, the result will return the Process ID along with other information about the application or service.
Good luck.
You should read it
- ★ How to Make a Process Document
- ★ What is Windows Logon Application and why is it running on the system?
- ★ Information about DbxSvc.exe file, Find out what is DbxSvc.exe file?
- ★ What is the Host Process for Windows Tasks and why does it run much on the computer?
- ★ How to set priorities for applications in Windows 10