Heap data structure
What is the Heap data structure?
Data structure The heap is a special case of a balanced binary tree data structure, where the root node's key is compared to its children and arranged accordingly. If α has a child node β then:
key (α) ≥ key (β)
When the value of the parent node is greater than the value of the child node, this attribute creates a Max Heap. Based on this criterion, a Heap can be one of two types:
With data filled in → 35 33 42 10 14 19 27 44 26 31
Min-Heap : here the value of the root node is less than or equal to the values of the child nodes.

Max-Heap : here the value of the root node is greater than or equal to the value of the child nodes.
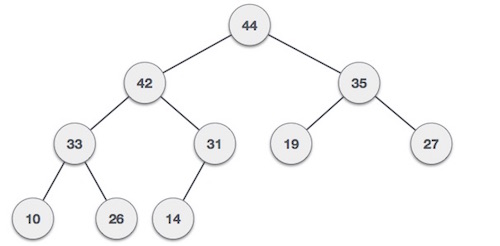
The above two example trees are all built on the same input data and the same order.
Max Heap construction algorithm
We will use the same example to illustrate how to create a Max Heap. The method to build Min Heap is similar.
We will deduce an algorithm for Max Heap by inserting an element at a time. At any time, Heap must maintain (obey) its properties. During the insert process, we also assume that we are inserting a node in HEAPIFIED Tree.
Bước 1 : Tạo một nút mới tại vị trí cuối cùng của Heap. Bước 2 : Gán giá trị mới cho nút này. Bước 3 : So sánh giá trị của nút con với giá trị cha. Bước 4 : Nếu giá trị của cha là nhỏ hơn con thì tráo đổi chúng. Bước 5 : Lặp lại bước 3 và 4 cho tới khi vẫn duy trì thuộc tính của Heap.
Note : In the Min Heap build algorithm, the value of the parent node will be smaller than the value of the child nodes.
For more details on Max Heap construction algorithm, let's look at the animated illustration below.
The algorithm deletes in Max Heap
Delete operation in Max (or Min) Heap always takes place at the root node and to delete the Largest (or Smallest) value. You follow the algorithm and animation below to understand more about this algorithm.
Bước 1 : Xóa nút gốc. Bước 2 : Di chuyển phần tử cuối cùng có bậc thấp nhất lên nút gốc. Bước 3 : So sánh giá trị của nút con này với giá trị của cha. Bước 4 : Nếu giá trị của cha là nhỏ hơn của con thì tráo đổi chúng. Bước 5 : Lặp lại bước 3 và 4 cho tới khi vẫn duy trì thuộc tính của Heap.
According to Tutorialspoint
Previous article: Spanning Tree in data structure and algorithm
Next lesson: Basics of recursion
You should read it
- Shell Sort in data structure and algorithm
- Is the data structure and algorithm necessary for a Web Developer?
- Search algorithm by width
- Binary Search algorithm (Binary Search)
- Concept of Buffer in Node.js
- What is algorithm?
- How does YouTube algorithm work?
- AVL tree in data structure and algorithm
- Deep search algorithm
- Panda 4.0 algorithm was updated by Google on May 20, 2014
- Selection sort algorithm (Selection Sort)
- Quick Sort (Quick Sort)
Maybe you are interested
Tabletop Simulator: Must-try co-op games Astronomers watch a dead star 'power up' for the first time Comet Borisov, just the second interstellar object to visit us, is spotted falling apart 10 important sayings should tell the opponent every day Study mysterious signals from a planet 94 light-years away from our Earth 'Ghost' radio station continuously transmits mysterious cryptography for 40 years without stopping
