Deep search algorithm
What is the depth search algorithm?
Deep search algorithms (Depth First Search - DFS for short), also called depth-first search algorithms, are algorithms that browse or search on a tree or graph and use the stack ( stack) to remember adjacent vertices to start the search when the adjacent vertex is not encountered in any loop. The algorithm continues until you reach the top of the search or a node without children. Then the algorithm returns to the top that has just been searched in the previous step.
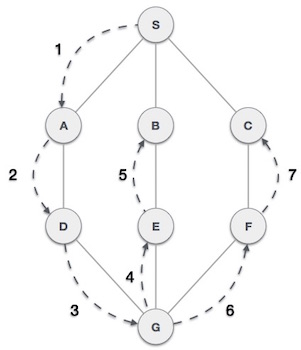
In the above illustration, the first depth search algorithm browses from vertices A to B to C to D then to E , then to F and finally to G. This algorithm follows the following rule:
Rule 1 : Browse to the adjacent vertices without approval. Mark the vertex that has been approved. Display that vertex and push into a stack.
Rule 2 : If no adjacent vertices are found, then take a vertex from the stack (pop up operation). (The algorithm will retrieve all vertices from the stack without any adjacent vertices)
Rule 3 : Repeat rules 1 and rule 2 until the stack is empty.
The following table illustrates the rules with the example image above:
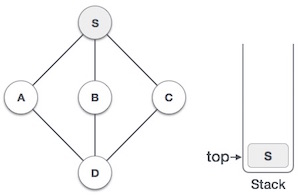
Initialize stack (stack)

Mark the top S as approved and place this vertex in the stack. Search for any adjacent vertices that have not been approved from the top S. We have 3 vertices and we can take any of them. For example, we take vertex A in alphabetical order.
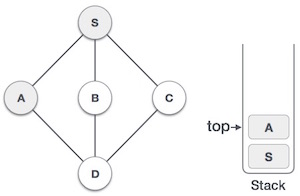
Mark the top A as approved and place it in the stack. Search for any adjacent vertices with vertex A. Both S and D are adjacent two vertices A but we only care about the unopened vertex.
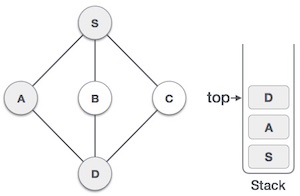
Browse vertex D , mark this vertex as browsed and place it in the stack. Here, we have B and C as two vertices adjacent to D and both are unapproved. We will choose alphabetically again.
Select B , mark as browsed and place in the stack. Here B does not have any adjacent vertices that have not been approved. So we take B out of the stack.
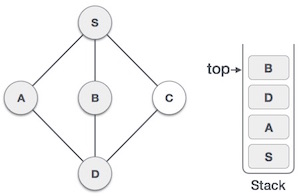
Check the top element of the stack to return to the previously browsed node and check if this vertex is adjacent but not yet approved. Here, we find vertex D at the top of the stack.
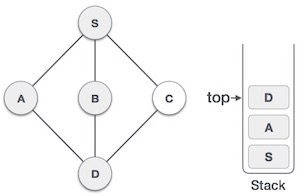
Only one vertex adjacent to D has not been approved, it is vertex C. We browsed C , marked as browsed and placed in the stack.
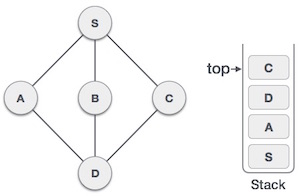
Since C does not have any adjacent vertices that have not been approved, we continue to take the vertices from the stack to find out if there are any adjacent vertices that have not been approved. In this example is not available, and we continue until the stack is empty.
According to Tutorialspoint
Previous article: Graph data structure (Graph)
Next lesson: Search algorithm by width