Shell Sort in data structure and algorithm
What is Shell Sort?
Shell Sort is a highly efficient sorting algorithm based on insertion sorting algorithm (Insertion Sort) . This algorithm avoids the case of swapping positions of two distant elements in the selection algorithm (if the smaller element is in the right position quite far from the larger element on the left).
First, this algorithm uses a sorting algorithm on elements that are far apart, then arranging elements with a narrower distance. This distance is also known as interval - the number of positions from one element to another. This range is calculated based on the following Knuth formula:
h = h * 3 + 1 trong đó: h l à Kho ả ng ( interval ) v ớ i gi á tr ị ban đâ u l à 1
This algorithm is quite effective for medium sized data sets when the worst case complexity and the average case are O (n), where n is the number of elements.
How Shell Sort works
To make it easier to learn, below I provide illustrations for how Shell Sort works. We use an array of values as shown below. Suppose the initial value of interval is 4. For example, for element 35, with a range of 4, the remaining element will be 14. Therefore we will have pairs of values {35, 14}, { 33, 19}, {42, 27}, and {10, 14}.
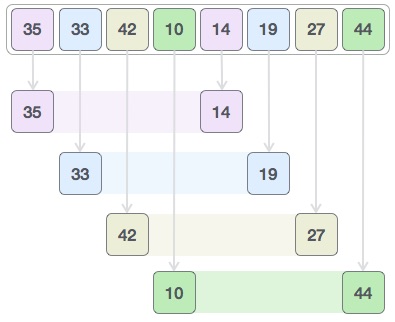
Compare these values together in sub-lists and swap them (if needed) in the original array. After this step, the new array will be empty as follows:

Then, take the value of 2 interval and with this distance will give two sub-lists: {14, 27, 35, 42}, {19, 10, 33, 44}.
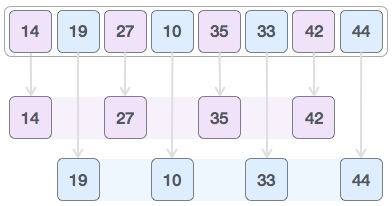
Continue to compare and swap values (if needed) in the original array. After this step, the array will look like this:
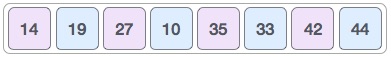
Finally, we arrange this remaining array with interval equal to 1. Shell Sort uses an insertion sort algorithm to sort the array. Below is an illustration of each step.
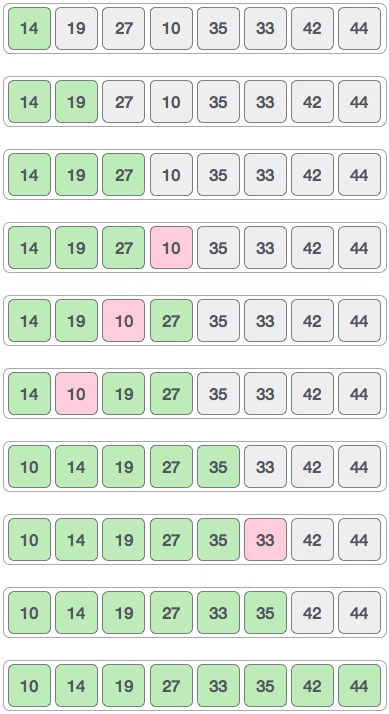
As shown above, you see that we only need 4 swaps to sort out this remaining array.
Algorithm for Shell Sort
Now we will monitor the algorithm for Shell Sort:
Bước 1 : Khởi tạo giá trị h Bước 2 : Chia list thành các sublist nhỏ hơn tương ứng với h Bước 3 : Sắp xếp các sublist này bởi sử dụng sắp xếp chèn (Insertion Sort) Bước 4 : Lặp lại cho tới khi list đã được sắp xếp
Sample algorithm for Shell Sort
From the above steps we can design a sample algorithm for Shell Sort as follows:
B ắ t đầ u h à m shellSort () A : m ả ng c á c ph ầ n t ử /* Tính toán giá trị Khoảng (interval) */ while interval < A . length / 3 th ự c hi ệ n : interval = interval * 3 + 1 k ế t th ú c while while interval > 0 th ự c hi ệ n : for outer = interval ; outer < A . length ; outer ++ th ự c hi ệ n : /* chọn giá trị để chèn */ valueToInsert = A [ outer ] inner = outer ; /*dịch chuyển phần tử sang phải*/ while inner > interval - 1 && A [ inner - interval ] >= valueToInsert do : A [ inner ] = A [ inner - interval ] inner = inner - interval k ế t th ú c while /* chèn giá trị vào vị trí trên */ A [ inner ] = valueToInsert k ế t th ú c for /* Tính toán giá trị Khoảng (interval) */ interval = ( interval - 1 ) / 3 ; k ế t th ú c while K ế t th ú c h à m
According to Tutorialspoint
Previous lesson: Mixing algorithm (Merge Sort)
Next lesson: Quick Sort (Quick Sort)