AVL tree in data structure and algorithm
What is an AVL tree?
What happens if the data entered into the binary search tree (BST) is in ordered form (ascending or descending). It will look like this:
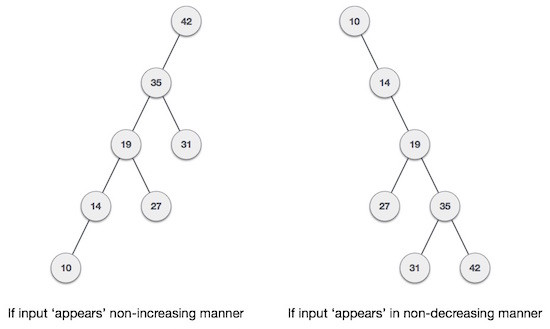
In general, the worst-case performance of a binary search tree (BST) is close to linear search algorithms, ie Ο (n). With real-time data, we cannot predict the data pattern and its frequencies. Therefore, it is necessary to balance here to balance the existing binary search tree.
The AVL tree (short for the names of A delson inventors, V elski and L andis) is a highly balanced binary search tree. The AVL plants check the height of the left seedlings and the right seedling and make sure that the difference between them is not greater than 1. This difference is called the Balance Factor .
Below is an example of an illustration of three trees in which the first tree is balanced, the second and third are unbalanced.

In the second tree, the tree on the left of C has an elevation of 2 and the right subtree has a height of 0, so the difference is 2. In the third tree, the right subtree of A has the height of 2 and the tree on the left has a height of 0, so the difference is also 2. While the AVL tree only accepts the difference (or Equilibrium factor) of 1.
BalanceFactor = height(left-sutree) − height(right-sutree)
If the difference between the height of the left subtree and the right subtree is greater than 1, the tree is balanced by using some AVL rotation techniques shown below.
Technology of rotating AVL trees
To make the tree balance itself, an AVL tree can perform the following 4 types of rotation techniques:
Left rotation technique
Right turn technique
Left-right rotation technique
Right-to-left spin technique
The first two spinning techniques are single rotation techniques and the other two rotation techniques are rotation techniques.
In the next section, we will explore in detail each rotation technique with simple and easy-to-understand illustrations.
Fruit rotation technique AVL
If a tree becomes unbalanced when a node is inserted in the right subtree of the right subtree, we can perform a single left rotation technique as follows:

In the above illustration, node A becomes unbalanced when a node (node C) is inserted into the subtree to the right of the right subtree of node A. We perform a left-turning technique to make A a tree. left child of B.
The technique turns to the AVL tree
The AVL tree becomes unbalanced if a node is inserted into the subtree to the left of the left subtree. In order to balance the tree, we must make the right rotation as follows:

As shown in the figure, an unbalanced node will become the right subtree of its left seedling by right-turning technique.
Technique turns left-right AVL tree
The rotation technique is quite complicated compared to the two techniques of the single rotation just introduced above. In order to understand this rotation technique faster, you need to note each action that is taken while recording. A left-right rotation technique is a combination of left-turning technique followed by right-turning technique.
Action Status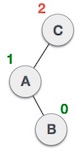 A button has been inserted in the right subtree of the left subtree. This makes the C node unbalanced. With this situation, the AVL tree can perform left-right rotation.
A button has been inserted in the right subtree of the left subtree. This makes the C node unbalanced. With this situation, the AVL tree can perform left-right rotation. 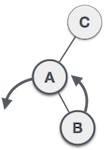 First, make a left rotation on the left subtree of C. This makes A the left subtree of B.
First, make a left rotation on the left subtree of C. This makes A the left subtree of B. 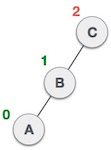 Now button C is still unbalanced, that is due to the appearance of the seedling to the left of the seedling to the left.
Now button C is still unbalanced, that is due to the appearance of the seedling to the left of the seedling to the left. 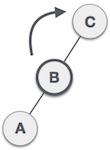 Now we will perform the right rotation technique to make B become the new root node of this tree. The C button now becomes the right subtree of its own left tree.
Now we will perform the right rotation technique to make B become the new root node of this tree. The C button now becomes the right subtree of its own left tree. 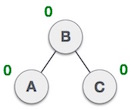 Now the tree is balanced.
Now the tree is balanced. Right-fruit rotation technology AVL
Another type of rotation technique is the right-to-left rotation technique. This technique is a combination of rotation techniques that must be followed by left-turning techniques.
Action Status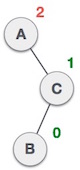 A button has been inserted in the subtree to the left of the right subtree. This makes the A button become unbalanced because the Balance Factor is 2.
A button has been inserted in the subtree to the left of the right subtree. This makes the A button become unbalanced because the Balance Factor is 2. 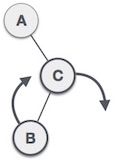 First, we perform the right-turning technique with node C, making C become a subtree to the right of the subtree on the left B. Now, node B becomes the right subtree of node A.
First, we perform the right-turning technique with node C, making C become a subtree to the right of the subtree on the left B. Now, node B becomes the right subtree of node A. 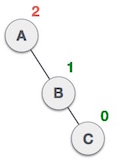 Now button A is still unbalanced because of the right subtree of its right subtree. Therefore it is necessary to implement a left rotation technique.
Now button A is still unbalanced because of the right subtree of its right subtree. Therefore it is necessary to implement a left rotation technique. 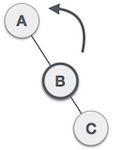 A left-turning technique is done to make B the new root node of the seedling. Button A becomes the left subtree of its right subtree B.
A left-turning technique is done to make B the new root node of the seedling. Button A becomes the left subtree of its right subtree B. 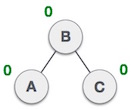 Now the tree is balanced.
Now the tree is balanced. According to Tutorialspoint
Previous article: Binary Search Tree (Binary Search Tree)
Next lesson: Spanning Tree in data structure and algorithm
You should read it
- ★ Learn about the Whaling network attack technique
- ★ PrintListener technique: Steal fingerprints just by listening to the sound of swiping the screen
- ★ Cold boot, an attack technique 10 years ago can crack the encryption of most PCs today
- ★ How to use Morphing morphing techniques in Photoshop
- ★ Is it possible to perform the 'bend curve' technique?