7 files and folders Windows can delete to free up space
Let's take a look at a few Windows files and folders that are actually safe to remove and why we can do it. Some files are in protected areas so be careful before deciding to delete them.
The best way to clean up Windows folders: Disk Cleanup or Storage Sense
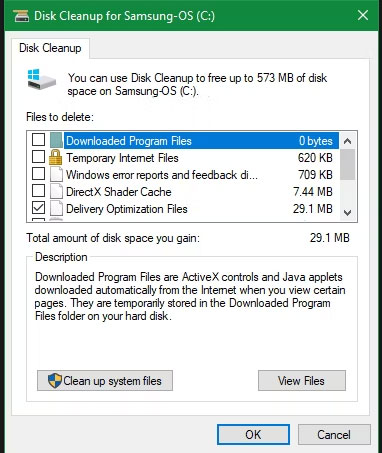
Before looking at files and folders that Windows can safely delete, you should know that deleting them manually is usually not the best practice.
Besides doing this yourself when you could automate the process it would be an extreme waste of time. Using the Disk Cleanup tool to perform these cleaning tasks will be safer. This helps you avoid common Windows maintenance errors, such as accidentally deleting important files or deleting the wrong folder.
The Disk Cleanup tool helps you reclaim disk space on your Windows computer and is very simple to use. You can open it by searching for Disk Cleanup in the Start menu and selecting a drive (C: in most cases). Let the tool scan and you will see several categories of files that you can delete. For more options, select Clean up system files and provide admin rights before you look through the list.
If you find this interface too cumbersome, you can browse to Settings > System > Storage to try out the newer memory cleaning tool in Windows 10 and 11. Click on Temporary files in the list of options, then you'll see a list similar to what Disk Cleanup provides.

What to delete from Disk Cleanup?
This is not a complete guide to the Disk Cleanup tool, so we won't look at every item in this menu. Here are some of the most prominent options:
- Windows Update Cleanup : This will delete old copies of Windows Update files. In most cases, you can safely delete these, but if you have update-related problems, you should keep them to fix the problem.
- Windows upgrade log files : Similar to above, these are data files that Windows Update stores to help you investigate upgrade or installation-related issues. You can delete these if you haven't encountered errors related to upgrading Windows to a new version.
- Language resource files : If you have previously downloaded another language or keyboard layout that you do not use, this will allow you to easily delete it.
- Recycle Bin : Although you can do it through the separate window, you can also do it easily here. Just make sure there's nothing important inside that you accidentally left out.
- Temporary files : As the name suggests, temporary files are not used for any purpose for a long time, so you can delete them without worry.
Now let's see what you can safely remove from Windows 10 and Windows 11. Typically, these files are located on the C: drive, but you may find them elsewhere if you have multiple storage drives and have Windows installed with customization options.
1. Hibernation File
Located at location C:hiberfil.sys
Hibernation mode is similar to Sleep mode, but the difference is that the system will save all open work to the hard drive before shutting down. You can remove the battery from the computer and leave it in this mode for a few weeks, after starting the backup and what you did before will still be intact. Of course, this also takes up space.
The hibernation file will take up a few GB or more depending on the size of your hard drive. If you do not use these features and want to disable them, you can also easily do so through Command Prompt. Remember that you should not delete the hiberfil.sys file because Windows will recreate it automatically. Open Command Prompt (Admin) by right-clicking Start on the desktop. Type the following command to disable hibernation mode:
powercfg.exe /hibernate off
This video is all the steps to disable hibernation function. When completing the operations, Windows will automatically delete hiberfil.sys, you can choose to delete it or not. Note that stopping using this mode also means that the computer will stop booting quickly on Windows 10, but it will not have a major impact on booting.
2. Temp folder
Located at C:WindowsTemp
Temporary files in Windows are junk files whose use is only temporary and becomes redundant when the task at hand is completed. Such temporary files are created to hold data temporarily while the file is being created or processed or used. Windows temporary files are created by the operating system during normal running when there may not be enough memory allocated to the task.
As you know, temporary files on Windows are no longer valid after the first use. These files and folders contain information that is only used once by Windows. You can delete all the items inside by opening the folder and pressing Ctrl + A to select all and then pressing Delete. When doing this, Windows may say errors for a few items, but ignore them and continue cleaning up the rest. The C:WindowsTemp folder contains some additional files that you no longer need to keep. Open that Temp folder and delete anything you find in there.
The Temp folder is not the only place where temporary files and other unnecessary file groups are stored on Windows computers.
The Settings app in Windows 10 has an entire section dedicated to deleting temporary files. Get there via Settings > System > Storage > Temporary files . Includes things like delivery optimization files, Windows upgrade log files, temporary files left over by applications, etc. Select the content to delete, then select Remove files .

Similar, harder-to-find temporary file locations are also accessible in older versions of Windows, like Windows 7, through Disk Cleanup. This utility is included in all versions of Windows and can automatically delete the contents of some other temporary folders for you. You can open it in the Run dialog box (WIN + R) via the cleanmgr command.
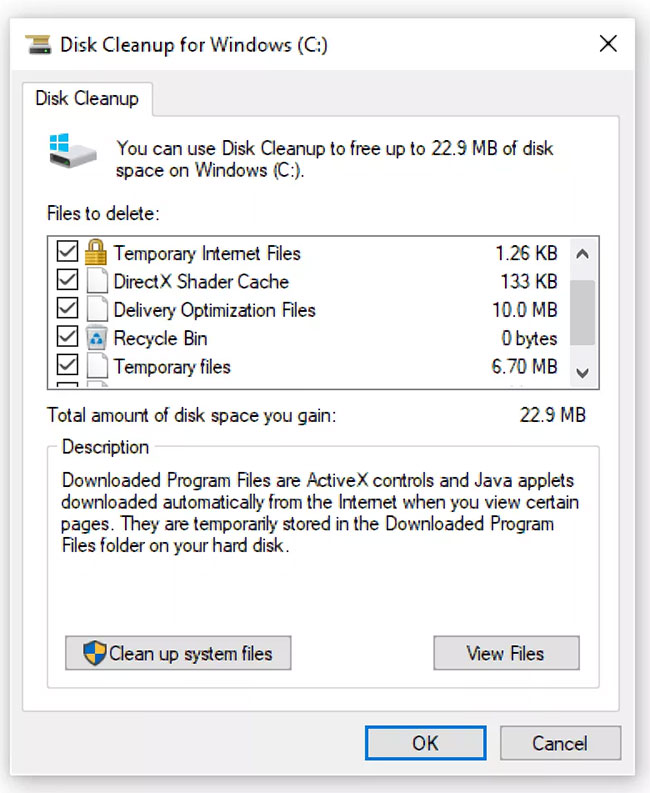
3. Recycle Bin
Located at shell:RecycleBinFolder
The Recycle Bin is not actually a folder and obviously many people already know about it but for some readers who don't know, we can explain it to you as follows: whenever you delete a file on system, Windows will move it to the Recycle Bin. This is a special place where deleted files are kept until the user permanently deletes them or restores them. If you don't pay attention to the trash, there may be many GB of old data still in there.
You can access the Recycle Bin on your desktop. If not found, type shell:RecycleBinFolder in the Run menu (press Windows + R button ) or in the File Explorer navigation bar . There, you'll see all your recently deleted items. Click on individual items and select Delete to permanently delete them or Restore to return them to their original location. On the Ribbon, you will see Empty Recycle Bin or Restore all items buttons .
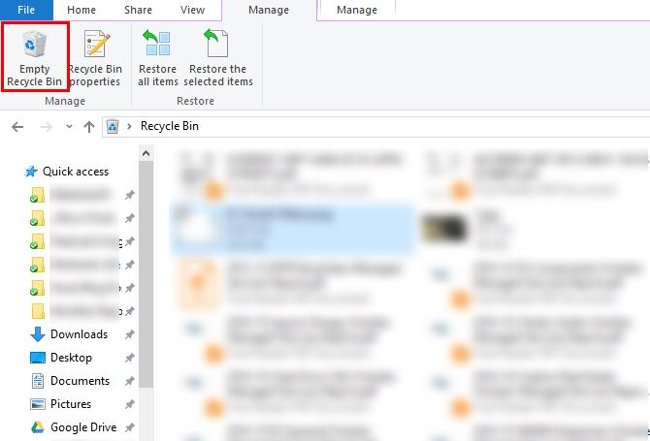
To fine-tune how the Recycle Bin works, click Recycle Bin Properties on the Ribbon. In this section, you can limit the size of the trash or select Don't move files to Recycle Bin (do not move files to Recycle Bin). This customization will permanently delete items and completely bypass the trash. But we do not recommend using this option because when accidentally deleted, the Recycle Bin is the place to find them again.
4. Windows.old folder
Location is C:Windows.old
When you upgrade your Windows version, your system saves a copy of the old Windows files called Windows.old. This folder essentially holds everything that was created on your old computer in case the conversion goes wrong. In a bad situation, you can use this folder to restore a previous version of Windows or you can also open the folder and retrieve a few lost files when necessary.
Windows automatically removes folders after 10 days, but you can manually delete them when you need more space. It will not delete on File Explorer, so type Disk Cleanup into the Start menu and launch the tool. Click Cleanup system files at the bottom of the window and enable scanning of system files. Once completed, find Previous Windows installation and delete it using this tool.
Obviously, removing these files is more difficult than restoring them. With the upcoming Windows 10 Creators Update, we recommend that you keep this folder until you are sure everything is working properly.
5. Downloaded Program Files
Located at C:WindowsDownloaded Program Files
This file actually holds the files used for Explorer ActiveX controls and Java applets , so if you use a feature on the same website you won't have to download it twice. Therefore, this folder is completely useless because ActiveX is an extremely mature technology but has many vulnerabilities, Java applets are quite rare. ActiveX is exclusive to Internet Explorer and you'll probably only encounter it on legacy company websites. Most home users don't use IE anymore. Therefore, the Downloaded Program Files file will probably be empty, but if it is, we can still delete all of its contents.
6. LiveKernelReports
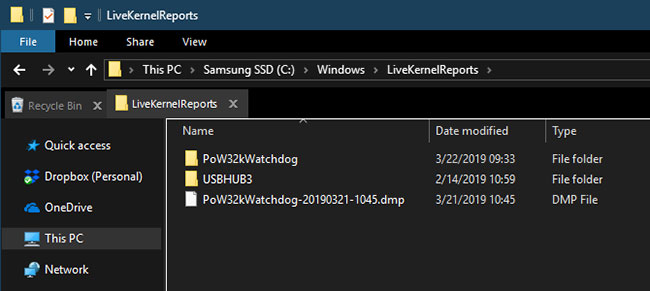
Located at C:WindowsLiveKernelReports
The LiveKernelReports folder is another folder that may appear when you are scanning large files on your computer. This folder is where dump files (continuous records of information that Windows keeps) are stored. If your computer has problems, you can analyze the contents of these files to start fixing your problem.
Any large files ending with the DMP file extension in this folder can be safely deleted. However, like the above locations, the article recommends that you use Disk Cleanup instead of deleting files yourself.
When Windows crashes or you encounter other major computer problems, don't delete these dump files immediately. You can use a program like WhoCrashed to get more information.
7. Rempl folder
Located at C:Program Filesrempl
Although the Rempl folder is not large, you may be surprised to see it appear on your system. It contains some small files and you might even notice a few Task Manager processes connected to it.
This folder is connected to Windows 10 update distribution. It includes "reliability improvements" to help smooth Windows 10 updates and fix compatibility issues.
So can you delete the Rempl folder? There appear to be no side effects from doing so. However, since it only takes up a few megabytes and can make upgrading Windows less frustrating, it's best to keep it.
What's the best way to delete these folders?
We just mentioned a few items you can delete them but deleting them manually is not the best way. Additionally, you should use a safer automatic cleaning tool. This avoids accidentally deleting essential files.
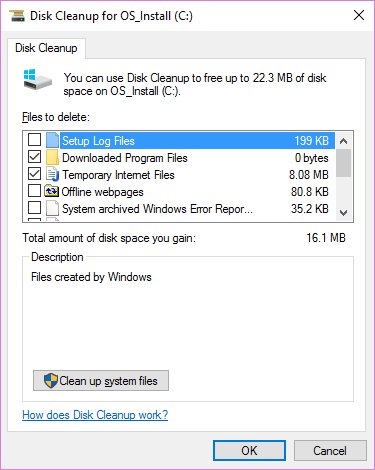
Windows Disk Cleanup has a lot of functions and is easy to use. For more control, you can also consider third-party cleaning tools like CCleaner that allow cleaning of more locations and provide some additional features.
summary
Windows contains many unnecessary files or folders. Remember, your computer does a pretty good job of keeping itself clean so you shouldn't have to delete the contents of these folders unless you're low on space. Run the Disk Cleanup tool once or twice a month to keep your computer clean.
You should read it
- 7 small tips with folders in Windows
- Secure folders with Secure Folders software
- Open multiple folders at once on Windows 10 with just one shortcut
- Instructions for setting password to protect files and folders in Windows
- Connect your Windows XP computer from Windows Vista
- How to bookmark folders on Windows 10
 How to set a blank name Among Us, not leave a name in Among Us
How to set a blank name Among Us, not leave a name in Among Us Is it worth the investment to play 4K games?
Is it worth the investment to play 4K games? Why Fotor is our favorite affordable AI photo editing app
Why Fotor is our favorite affordable AI photo editing app 5 great photography effects on mobile devices
5 great photography effects on mobile devices 9 useful tips for using Apple Watch you should know
9 useful tips for using Apple Watch you should know How to transfer files between virtual machines and PCs on VMware and VirtualBox
How to transfer files between virtual machines and PCs on VMware and VirtualBox