Troubleshoot network connectivity problems (Part 1)
Brien M. Posey
 Network administration - Today's network hardware and software are becoming more reliable but, sometimes there are still things that happen unexpectedly. Therefore, in this series, we will discuss some troubleshooting techniques for you to use when network computers encounter communication difficulties. For the purpose of introducing people who still have little experience in working with TCP / IP, we will start with the basics, then work with more advanced techniques.
Network administration - Today's network hardware and software are becoming more reliable but, sometimes there are still things that happen unexpectedly. Therefore, in this series, we will discuss some troubleshooting techniques for you to use when network computers encounter communication difficulties. For the purpose of introducing people who still have little experience in working with TCP / IP, we will start with the basics, then work with more advanced techniques.
Verify network connection
When a host has a problem with communicating with another host, the first thing you need to do is gather information about the problem. More specifically, you need to read the documentation of the host configuration, indicating whether the host has communication problems with other computers on the network and see if the problem can affect other hosts. .
For example, assume that a workstation has a communication problem with a server. It doesn't really give you much information. However, if you learn a little more deeply and find that the client cannot communicate with all other servers on the network, the problem may be in the network cable, whether it is connected, or the port. of the switch is broken or may be a problem in network configuration for example.
Similarly, if the workstation can communicate with some servers in the network, but not all, it also gives you a hint about the location to find the problem. In that type of situation, you can check to see which servers cannot be contacted. Are they all on a subnet? If so, routing problems can cause this error.
If many workstations are having trouble communicating with a specific server, the problem may not be on the workstations unless these workstations were recently reconfigured. In this case, the problem is prone to the problem occurring at the server.
We will start from the basic tests. The tests we will show you will not show many of the causes of the problem, but they will help narrow down a lot of things so you know where the troubleshooting process comes from.
PING
PING is the simplest TCP / IP diagnostic utility that has been created, but the information it can give you is invaluable. Most simply, PING lets you know if your server can communicate with other computers.
The first thing we recommend is to open the Command Prompt, then enter the PING command, then enter the IP address of the machine on which you are having communication problems. When performing ping, the machine you specified will give 4 responses, as shown in Figure A.

Figure A: Each machine will generate 4 responses
These responses will basically tell you how much time the computer is assigned to respond to 32 bytes of data. For example, in Figure A, one of the 4 responses received is less than 4 ms.
When you execute a PING command, one of the 4 situations will occur, each of which has its own meaning.
The first situation can happen is that the specified machine will generate 4 responses. This indicates that the client can communicate with the host specified at TCP / IP level.
The second scenario may appear that all 4 requests time out, as shown in Figure B. If you look at Figure A, you will see that each response ends with TTL = 128. TTL stands for Time To Live. It means that each of the 4 queries and responses must be completed within 128 ms. TTL is also reduced each time when the jump on the way back. The jump occurs when a data packet moves from one network to another. We will talk more about jumps later in this article.

Figure B: If all requests have been timed out, it indicates that communication between these two addresses has failed
Any speed, if all 4 requests have been timed out, it means that the TTL expires before the response is received. This means one of the following three ideas:
-
Communication problems will interfere with the transport packets between the two machines. This may be due to bad cable or routing tables, or some other reason.
-
Communication appears, but too slowly in response. This can be caused by a congestion in the network, because the hardware or the wiring problem of the network is faulty.
- Communication still works but the firewall blocks ICMP traffic. PING will not work unless the destination host's firewall (and any firewall between the two machines) allows ICMP echo.
The third scenario that may occur when you enter the PING command is still receiving some feedback but some time out. This may be due to bad network cables, hardware failures or congestion in the network.
The fourth situation may appear when ping is an error message similar to the one shown in Figure C.

Figure C: Error indicating that TCP / IP is not properly configured
The 'PING: Transmit Failed' error indicates that TCP / IP is not configured correctly on the computer you are entering into the PING command. This error appears in Windows Vista. Older Windows versions also generate an error when TCP / IP is misconfigured, but an error message is displayed as 'Destination Host Unreachable'.
What will be the success of PING?
Believe it or not, a successful ping is not a strange phenomenon, even if two machines have communication problems with each other. If this happens, it means that the underlying network infrastructure is still good and computers can still communicate with each other at TCP / IP level. Often this is still a good sign because the problem is not too serious.
If the communication between the two machines fails but the two machines can PING together successfully (when executing the PING command from the two machines), there is another problem you can try here. Instead of pinging a host by an IP address, replace the IP address with its complete domain name, as shown in Figure D.
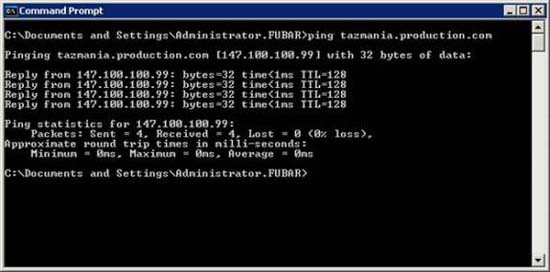
Figure D: Try ping the host of the network with the complete domain name
If you can ping with an IP address, but can't ping with a complete domain name, the problem might be DNS. The workstation can be configured to use a wrong DNS server, or the DNS server can include a host record for the machine you are trying to ping.
If you look at Figure D, you can see that the machine's IP address is listed to the right of the complete domain name. This proves that the computer can switch to a complete domain name. Make sure the IP address that the name is transferred to is correct. If you see an IP address that is different from the expected address, you can host the DNS record of the error.
Conclude
This article has introduced you to some basic steps to test basic connectivity between two computers. In the next section, we will introduce some techniques for you to use in the troubleshooting process.