Troubleshoot network connectivity problems (Part 2)
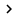 Troubleshoot network connectivity problems (Part 1)
Troubleshoot network connectivity problems (Part 1)
Brien M. Posey
TipsMake.com - In the first part, I showed you how to use the PING command to perform basic tests for connectivity, besides an introduction to how to clarify the results. In part two, I will continue the discussion by showing you some more simple tests that you can use to diagnose the state of the current connection.
Before start
As explained in the first part of this series, the purpose of this series is to create a troubleshooting guide for newcomers with basic skills. Therefore we will start with basic troubleshooting techniques and will gradually move to higher techniques.
Confirm connection
In the previous article, I covered some of the basics of using the PING command to test network connectivity. However, if you have a problem communicating with other hosts on the network, or hosts in the remote network, there are still some other types of PING so you can detect what's happening to your network. me
Before introducing these techniques, you need to understand how to configure hosts that are experiencing communication problems. The test procedure here is different for different versions of Windows, so I will show you how to check the network configuration on a computer running Windows Server 2003 operating system. The first thing you must do currently must determine whether the computer is currently running a static or dynamic IP address configuration. To do so, open Control Panel, then select the Network Connections option. Right-click the connection you want to diagnose, select the Properties command. By performing these operations, you will see a connection properties sheet appear as shown in Figure A.

Figure A: Property page of the network connection
Now scroll through the list of items that the connection uses until you find the TCP / IP protocol (selected in Figure A). Select this protocol, then click the Properties button to bring up the Internet Protocol (TCP / IP) Properties sheet, as shown in Figure B.
Figure B: Internet Protocol page (TCP / IP) Properties used to configure the TCP / IP protocol
When you encounter this screen, pay attention to the computer's IP address configuration. In particular, you need to pay attention to the following items:
-
Computer using dynamic or static configuration?
-
If the static configuration is being used, what is the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway?
-
Does the computer receive the DNS server address automatically?
- If the DNS server address is being specified with a specific address, what is the address being used?
Before we go on, we want to mention one problem: if a computer has multiple network adapters installed, then there are many network connections listed in Control Panel. So you need to know which connection corresponds to which network adapter.
If you suspect the correspondence between a particular connection and the network adapter, check the adapter's model. If you look at Figure A, you will see the type of network adapter listed at the top of the screen. If necessary, you can open the computer's case to see which network adapter your network cable is connected to, so you can be sure of your correct network connection.
Once you know how TCP / IP is configured for the network adapter, we have to determine if Windows is aware of that configuration. To do this, open a command prompt and enter the following command:
IPCONFIG / ALL
IPCONFIG can really tell you a lot of what's going on. For example, notice the screen shown in Figure C. When you enter the IPCONFIG / ALL command, the first thing you must do is find the correct network adapter. In this case, it is quite easy to find the correct adapter because there is only one adapter listed. Note that IPCONFIG can also provide you with a connection number (in this case, Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection 2). If you notice in Figure A, you will see the title of the property page shown in the picture also has the same name. Attached to the description of the physical network adapter will tell you exactly which network connection you are considering.
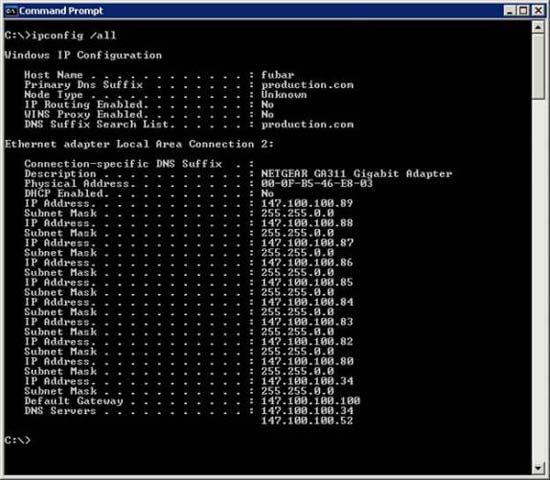
Figure C: The IPCONFIG / ALL command shows you the IP configuration of the computer
Obviously the first thing you can see in Figure C is that there are many different IP addresses of the connection. The reason for this is that we created a screenshot on a Web server. Web servers configure many websites, each with its own IP address. We want to use this server to demonstrate that the IP address configuration that you see when you first look at the TCP / IP properties page is not always the address that Windows is using. In this case, the IP configuration information shown in Figure B is still valid. It acts as the main IP address of the computer. However, there are still many other IP addresses that can still be used.
The next step in troubleshooting is much changed and depends on the current computer using a dynamic or static address configuration. If it uses a static configuration, check to make sure that the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server address are all listed in accordance with what is entered in the TCP properties page. / IP.
In the case of using a dynamic IP address you want to see the IP address and see if it is in the expected address range. If you have to troubleshoot the problem on a non-familiar network, in this case you might not know what the address range is. If you fall into this situation, there are some meaningful values that you can search here.
The most obvious clue a problem is a false IP address worth 0.0.0.0. The existence of this IP address usually indicates one of the following three issues:
The network adapter is not connected to the network (possibly because of a network cable or port contact).
IP address released.
The occurrence of IP address conflicts.
If you receive this address, try entering the following three commands:
IPCONFIG / RELEASE
IPCONFIG / RENEW
IPCONFIG / ALL
These commands will basically tell the computer to remove its current address, and retrieve a new IP address, and then show you the new configuration information. Sometimes this process also fixes the problem, but sometimes it doesn't fix it. However, it does bring clues to your network connection problem anyway.
Another problem that could cause your system to fail is the IP address within 169.254.xx but the subnet mask is 255.255.0.0. Some versions of Windows will automatically use this address if the IP address cannot be found from the DHCP server.
Conclude
In this section, I have shown you how to check the configuration of a computer's IP address to find clues that cause problems. In the next part of this article series, I will show you how to use configuration information to test the network connection.