Some useful tips with Windows Task Manager
Windows Task Manager is quite familiar to many computer users, with the familiar boot key combination from Windows XP as "Ctrl + Alt + Delete". Most users often use the Windows Task Manager to turn off stubborn or corrupted applications, sometimes used to check the status of CPU activity.
However, there are quite a few useful tips with Windows Task Manager that you may not know.
These features are tested on Windows 7. In Windows 7, to open the Windows Task Manager you can right-click on the Taskbar at the bottom of the screen and select Windows Task Manager, or use the key combination "Ctrl + Shift + Esc "to quickly open the Windows Task Manager window.
1. Send a message to another user
On the Users tab of the Windows Task Manager window, you can see the accounts that are logged on your computer, possibly remote connections. You can send a message to those accounts, simply by clicking on the account name and selecting Send Message. When that account is logged in, a dialog box will appear with your message.

2. Arrange and manage windows
In the Applications tab, you can see that the program windows are currently open. You can right click on those windows, select Switch To to switch over, or select Minimize / Maximize to hide or enlarge the window to full screen. Alternatively, you can select multiple windows at the same time by holding down Ctrl, then right-clicking and selecting Tile Horizontally or Vertically to arrange them horizontally or vertically.

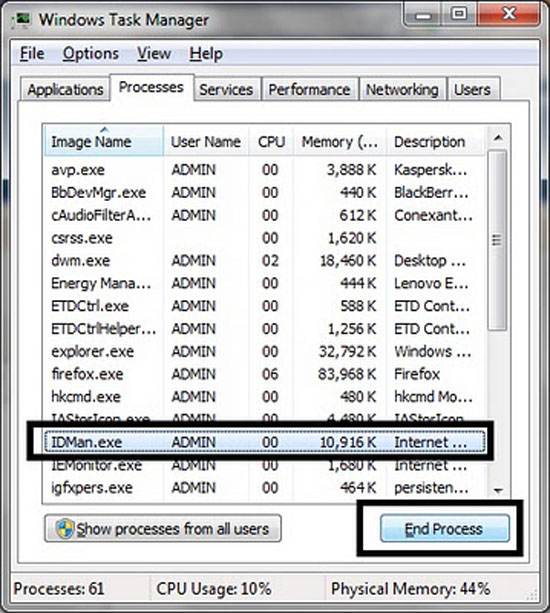
3. View CPU usage time of applications
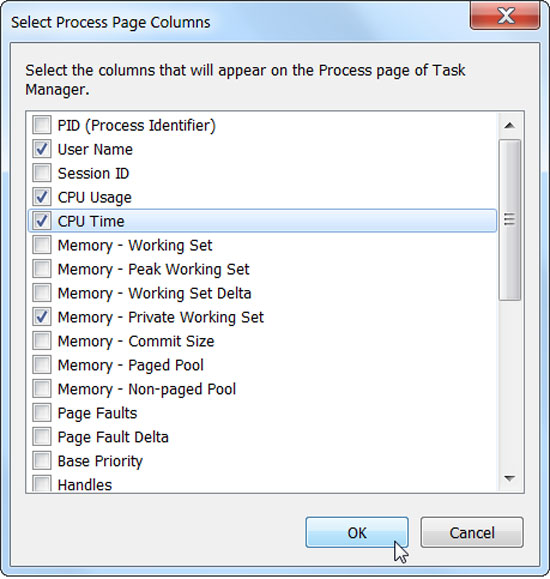
The Processes tab allows you to keep track of running applications and the amount of memory they use. You can also monitor the CPU usage time of applications, by enabling the CPU Time feature. To enable this feature, go to View on the menu bar, select Select Columns, and then click CPU Time.
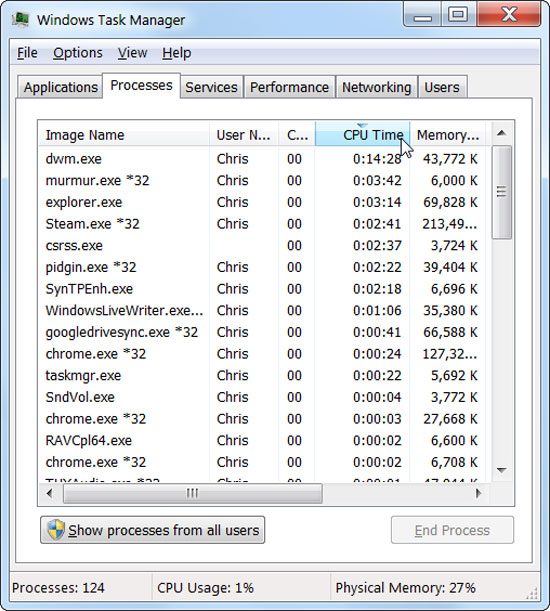
You can arrange applications, by clicking on the CPU Time column, to see which applications have the longest use time. However, the Processes tab only displays running applications, if an application is turned off, you cannot see information about them.
4. Manage application priorities
Windows has a set of priorities for some applications, whereby the system will provide memory and handle pre-prioritized applications with more resources, and non-priority applications will be limited. You can also change the priority of each running application in the Processes tab.
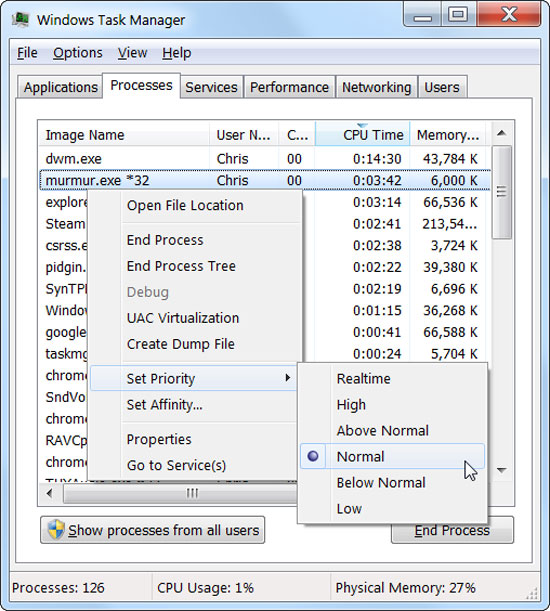
By right-clicking on the application, and selecting Set Priority, then select the priority you want. There are 6 priority options for you to choose from, high priority setting will help the application run better, besides setting low priority for many unnecessary applications. It will limit hanging and machine lag.
5. Reset Compatibility for the application
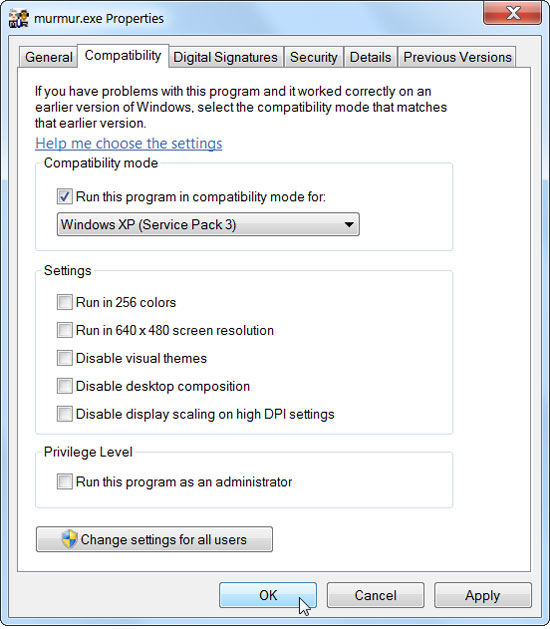
Usually you may encounter some problems when the application is incompatible, and you will have to change the Compatibility setting in Properties, when right-clicking the application's icon. However, you can quickly change the Compatibility of the application in Windows Task Manager. By right-clicking on the application and selecting Properties. You can also from the Applications tab, right-click on the running application and select Go To Process, to quickly switch to that application in the Processes tab.
6. Tab Services
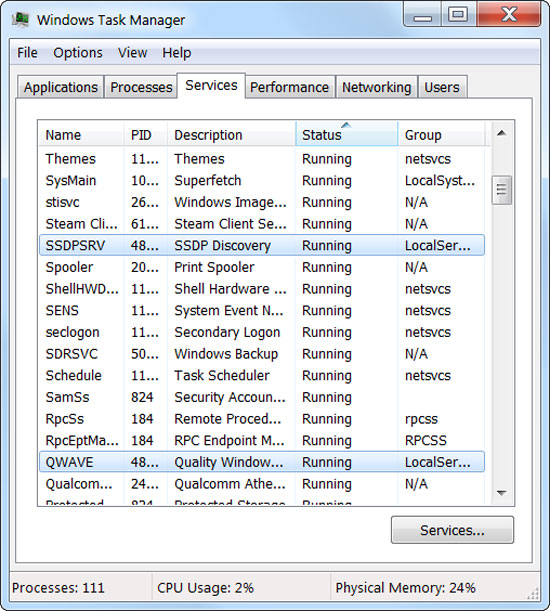
Have you ever wondered what "svchost.exe" really is? There are quite a lot of different Svchost.exe, and they are really functional files to run the Services functions that help Windows work. Each Svchost.exe takes care of running different Services functions. If you want to see which svchost.exe is actually running, you can right-click it and select Go To Services. It will take you to the Services tab, and you can see the Services running under Svchost.exe and the function it takes in the Description column. You can choose to turn off Services that feel unnecessary.
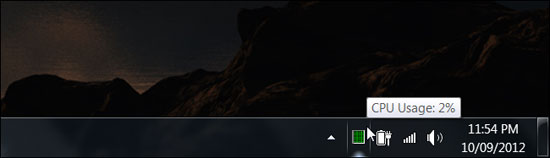
7. Icon CPU Usage
Task Manager includes a CPU Usage icon in the system tray, making it easy to see how the CPU works. However by default this icon will be hidden, so you click on the arrow in the system tray, drag and drop the CPU Usage icon into the Notification frame. And you can easily monitor CPU status continuously on the system tray.