Security features of OWA (Part 2)
In Part 1 of this series we looked at the network location of the Client Access Server and the Exchange 2007 method using the license for Outlook Web Access (OWA) security.
>> Security features of OWA (Part 1)
In this second part, we will look at different methods of authenticating OWA and some when choosing a suitable method.
Authentication in OWA - Forms-based Authentication
In Exchange 2007, we can choose between Forms-based Authentication method (FBA) and a group of other authentication methods according to standard authentication methods. Another security enhancement in Exchange 2007 is that FBA is used by default for OWA, here we will explore this method and then return to standard authentication methods. To see the authentication methods we need to open the Properties dialog box of the / owa virtual directory in Exchange Management Console and then select the Authentication tab. Then we will see a dialog box shown in Figure 1.

FBA was first introduced in Exchange 2003 and allows the display of a login page in addition to the basic authentication message that requires only the username and password to be entered. This login page increases security because the user's login name and password are stored as a cookie instead of being stored immediately in OWA. There are two main benefits from cookie validation. First, this cookie will be deleted when the OWA session ends, secondly, this cookie will also be deleted after a previously declared period of inactivity, such as when the user temporarily leaves the desk. In addition, this deadline can be configured for both public and private computers. In other words, a different time limit may apply to corporate workstations. The duration of the operation does not increase security because the OWA session cannot be performed when the cookie has expired. Figure 2 shows two options that users can select on the FBA screen to control the workstation being used whether it is a public or personal computer.

By default, when selecting a public computer option, the session will end after 15 minutes if no operations are performed, but we can change this value by adding Add or edit the following registry key on the Client Access Server in which the FBA has been activated:

Once done, we will have to restart IIS to apply the changes.
Authentication in OWA - Standard Authentication

Conclude
>> Security features of OWA (Part 1)
In this second part, we will look at different methods of authenticating OWA and some when choosing a suitable method.
Authentication in OWA - Forms-based Authentication
In Exchange 2007, we can choose between Forms-based Authentication method (FBA) and a group of other authentication methods according to standard authentication methods. Another security enhancement in Exchange 2007 is that FBA is used by default for OWA, here we will explore this method and then return to standard authentication methods. To see the authentication methods we need to open the Properties dialog box of the / owa virtual directory in Exchange Management Console and then select the Authentication tab. Then we will see a dialog box shown in Figure 1.
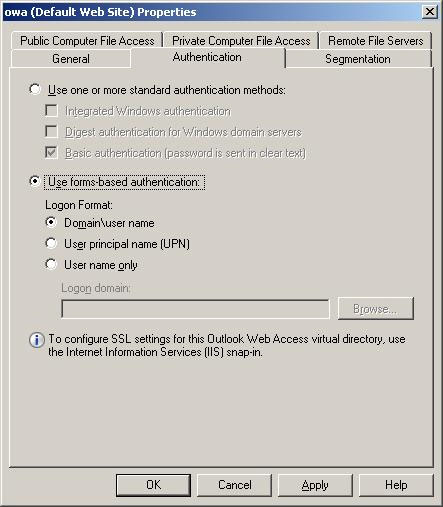
Figure 1: Authentication methods.
FBA was first introduced in Exchange 2003 and allows the display of a login page in addition to the basic authentication message that requires only the username and password to be entered. This login page increases security because the user's login name and password are stored as a cookie instead of being stored immediately in OWA. There are two main benefits from cookie validation. First, this cookie will be deleted when the OWA session ends, secondly, this cookie will also be deleted after a previously declared period of inactivity, such as when the user temporarily leaves the desk. In addition, this deadline can be configured for both public and private computers. In other words, a different time limit may apply to corporate workstations. The duration of the operation does not increase security because the OWA session cannot be performed when the cookie has expired. Figure 2 shows two options that users can select on the FBA screen to control the workstation being used whether it is a public or personal computer.
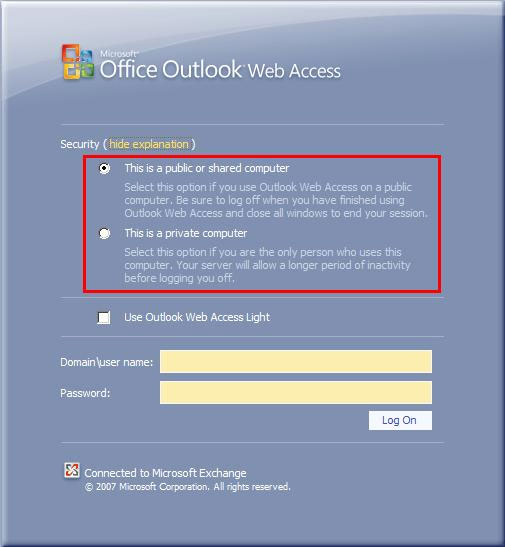
Figure 2: FBA security options.
By default, when selecting a public computer option, the session will end after 15 minutes if no operations are performed, but we can change this value by adding Add or edit the following registry key on the Client Access Server in which the FBA has been activated:
Key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesMSExchangeOWAWe can see this registry key in Figure 3. Note that after changing we will have to restart Internet Information Services (IIS) on the Client Access Server. To shorten this process we just need to open the Command Prompt and enter the iisreset / noforce command.
Name: PublicTimeout
Type: DWORD
Value: {number of minutes}
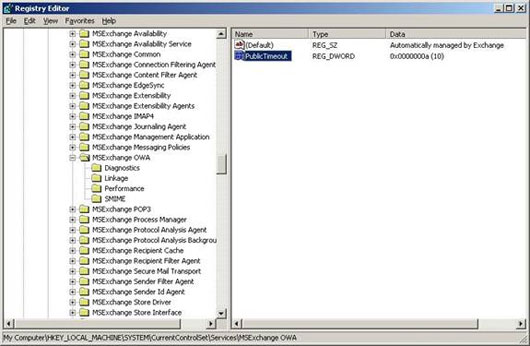
Figure 3: Timeout registry key of a public computer.
When selecting the private computer option, the default time of 8 hours without operation will be allowed before the session expires, obviously this time is much longer than the time limit in the option. choose of public computers. We can also change this deadline in a similar registry key:
Key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesMSExchangeOWA
Name: PrivateTimeout
Type: DWORD
Value: {number of minutes}
Keep in mind that these deadlines are not exact numbers and there will be a certain tolerance on the values used. Microsoft states that the real time limit will range from 1 to 1.5 times the set value due to the method by which the Client Access Server rotates through encryption keys. Therefore we need to note this when testing deadlines in OWA. Also, if you use ISA Server to connect to an external OWA, we need to install the same time values in ISA Server to suit the user.
In Figure 2, we see the FBA screen open. On this screen, the user must provide login information in domainusername format (default setting). We can change the login message to only ask for the username, or the User Principal Name (UPN). However before we do this we need to consider security issues.
If you want to change the login message that only requires a username, then we can do it via Exchange Management Console or Exchange Management Shell. In Exchange Management Console , open the Properties properties dialog box of the / owa virtual directory and select the Authentication tab (Figure 1). Here we can choose the type of FBA authentication that meets the requirements. In Exchange Management Shell , we can use the Set-OwaVirtualDirectory command with the LogonFormat parameter. The options of the LogonFormat parameter include:
In Figure 2, we see the FBA screen open. On this screen, the user must provide login information in domainusername format (default setting). We can change the login message to only ask for the username, or the User Principal Name (UPN). However before we do this we need to consider security issues.
If you want to change the login message that only requires a username, then we can do it via Exchange Management Console or Exchange Management Shell. In Exchange Management Console , open the Properties properties dialog box of the / owa virtual directory and select the Authentication tab (Figure 1). Here we can choose the type of FBA authentication that meets the requirements. In Exchange Management Shell , we can use the Set-OwaVirtualDirectory command with the LogonFormat parameter. The options of the LogonFormat parameter include:
- FullName : Same as the domainusername option in the figure, so the user must enter both the domain name and username when logging into OWA.
- PrincipalName : This parameter matches the UPN option in Figure 1 and it requires the user to enter the UPN to authenticate permissions.
- UserName : This option only matches the username only option in Figure 1. Note, if you use Exchange Management Shell to install this option we will have to install the default domain option via the DefaultDomain parameter of the Set command. -OwaVirtualDirectory .
Authentication in OWA - Standard Authentication
If you are already managing an Exchange 2000 or 2003 environment, you may already be familiar with the Standard Authentication method of the process of Basic Authentication, Digest Authentication (authentication). part) and Integrated Windows Authentication (integrated Windows authentication).
With Basic Authentication configured on the / owa virtual directory in a Client Access Server, the user will see the authentication dialog as shown in Figure 4. Default Basic Authentication will not be secure if SSL is not added.
With Basic Authentication configured on the / owa virtual directory in a Client Access Server, the user will see the authentication dialog as shown in Figure 4. Default Basic Authentication will not be secure if SSL is not added.
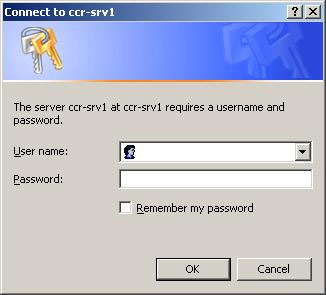
Figure 4: Basic Authentication dialog box.
Integrated Windows Authentication is useful in case the current login information of the user is used by the server to authenticate the user. With this method, users do not have to re-enter the login information. For example, a user can log on to a normal working computer using account information in Active Directory, and then access the Internet. This user can then choose to access a Client Access Server that has been configured to use Integrated Windows Authentication. In this case, this user will access OWA immediately without having to log in again. However, if ISA Server is used to access external OWA, and has been configured with FBA, with different authentication procedures depending on whether the user accesses internal or external access can be annoying. for users. Therefore, there are some companies deploying FBA on separate Client Access Servers that only support support for internal OWA sessions.
Digest Authentication is also used by users with an Active Directory domain account. With Digest Authentication, security is enhanced because passwords entered by users are sent as hash values when they are sent over the network to the authentication server. However, note that when using Digest Authentication, the user's credentials will be stored on OWA clipboard. Therefore we need to consider using FBA in case of security problems arise.
Digest Authentication is also used by users with an Active Directory domain account. With Digest Authentication, security is enhanced because passwords entered by users are sent as hash values when they are sent over the network to the authentication server. However, note that when using Digest Authentication, the user's credentials will be stored on OWA clipboard. Therefore we need to consider using FBA in case of security problems arise.
Conclude
In this section, we have explored the existing authentication methods and explored the configuration options of Forms-Based Authentication (FBA).
Share by
Marvin Fry
Update 26 May 2019