How to Upgrade Oracle Java on Ubuntu Linux
Method 1 of 4:
32-bit Oracle Java instructions:
-
 Become root user and copy the new compressed Oracle Java binaries from our download directory to /usr/local/java
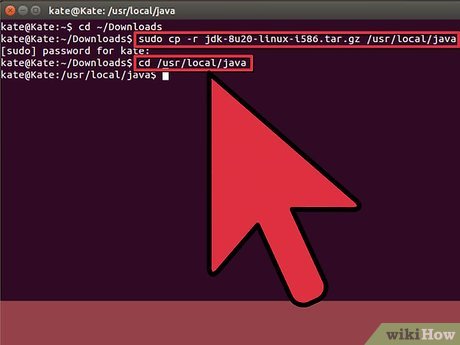
Become root user and copy the new compressed Oracle Java binaries from our download directory to /usr/local/java- Type/Copy/Paste: cd /home/"your_user_name"/Downloads
- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo cp -r jdk-7u40-linux-i586.tar.gz /usr/local/java
- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo cp -r jre-7u40-linux-i586.tar.gz /usr/local/java
- Type/Copy/Paste: cd /usr/local/java
-
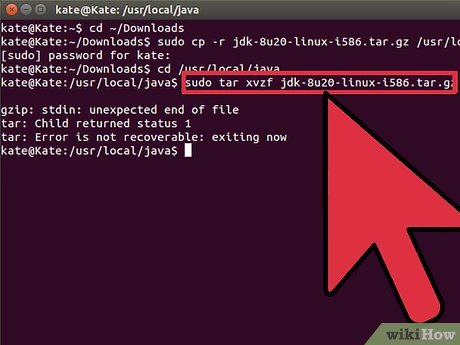
 Next we are going to unpack our new version of Oracle Java binaries, in the directory /usr/local/java
Next we are going to unpack our new version of Oracle Java binaries, in the directory /usr/local/java- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo tar xvzf jdk-7u40-linux-i586.tar.gz
- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo tar xvzf jre-7u40-linux-i586.tar.gz
Method 2 of 4:
64-bit Oracle Java instructions:
-
 Become root user and copy the new compressed Oracle Java binaries from our download directory to /usr/local/java
Become root user and copy the new compressed Oracle Java binaries from our download directory to /usr/local/java- Type/Copy/Paste: cd /home/"your_user_name"/Downloads
- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo -s cp -r jdk-7u40-linux-x64.tar.gz /usr/local/java
- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo -s cp -r jre-7u40-linux-x64.tar.gz /usr/local/java
- Type/Copy/Paste: cd /usr/local/java
-
 Next we are going to unpack our new version of Oracle Java binaries, in the directory /usr/local/java
Next we are going to unpack our new version of Oracle Java binaries, in the directory /usr/local/java- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo tar xvzf jdk-7u40-linux-x64.tar.gz
- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo tar xvzf jre-7u40-linux-x64.tar.gz
-
 At this point you should have two new uncompressed binary directories in /usr/local/java for the Java JDK/JRE listed as:
At this point you should have two new uncompressed binary directories in /usr/local/java for the Java JDK/JRE listed as:
jdk1.7.0_40
jre1.7.0_40
Along with:
jdk1.7.0_25
jre1.7.0_25
Method 3 of 4:
Modify your Linux system PATH:
-
 Edit the system PATH file /etc/profile and add the following system variables to your system path. Use gedit, nano or any other text editor, as root, and open up /etc/profile
Edit the system PATH file /etc/profile and add the following system variables to your system path. Use gedit, nano or any other text editor, as root, and open up /etc/profile- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo gedit /etc/profile
or - Type/Copy/Paste: sudo nano /etc/profile
- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo gedit /etc/profile
-
 Scroll down using your arrow keys to the end of the file and add the following lines below to the end of your /etc/profile file in Ubuntu Linux,at this point you are going to be changing the version numbers from the old Oracle Java to the new version of Java, you will change the versions numbers in the following system PATH file /etc/profile:
Scroll down using your arrow keys to the end of the file and add the following lines below to the end of your /etc/profile file in Ubuntu Linux,at this point you are going to be changing the version numbers from the old Oracle Java to the new version of Java, you will change the versions numbers in the following system PATH file /etc/profile:
Modify the /etc/profile file:
JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/java/jdk1.7.0_25
PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin:$JAVA_HOME/bin
JRE_HOME=/usr/local/java/jre1.7.0_25
PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin:$JRE_HOME/bin
export JAVA_HOME
export JRE_HOME
export PATH
Change to this:
JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/java/jdk1.7.0_40
PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin:$JAVA_HOME/bin
JRE_HOME=/usr/local/java/jre1.7.0_40
PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin:$JRE_HOME/bin
export JAVA_HOME
export JRE_HOME
export PATH
Save the file and exit
Method 4 of 4:
Inform your system of the updated Oracle Java version:
-
 Inform your Ubuntu Linux system where your Oracle Java JRE/JDK is located, now you will want to update the system to use Oracle Java 1.7.0_40
Inform your Ubuntu Linux system where your Oracle Java JRE/JDK is located, now you will want to update the system to use Oracle Java 1.7.0_40- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo update-alternatives --install "/usr/bin/java" "java" "/usr/local/java/jre1.7.0_40/bin/java" 1
- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo update-alternatives --install "/usr/bin/javac" "javac" "/usr/local/java/jdk1.7.0_40/bin/javac" 1
- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo update-alternatives --install "/usr/bin/javaws" "javaws" "/usr/local/java/jre1.7.0_40/bin/javaws" 1
-
 Inform your Ubuntu Linux system, that Oracle Java JRE 1.7.0_40 must be the new default Java
Inform your Ubuntu Linux system, that Oracle Java JRE 1.7.0_40 must be the new default Java- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo update-alternatives --set java /usr/local/java/jre1.7.0_40/bin/java
- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo update-alternatives --set javac /usr/local/java/jdk1.7.0_40/bin/javac
- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo update-alternatives --set javaws /usr/local/java/jre1.7.0_40/bin/javaws
-
 Reload your system wide PATH /etc/profile by typing the following command:
Reload your system wide PATH /etc/profile by typing the following command:- Type/Copy/Paste: . /etc/profile
- Note your system wide PATH /etc/profile file will reload after reboot of your Ubuntu Linux system
-
 Test to see if the new version of Oracle Java was installed correctly on your system by running the following commands and noting the version number of the new Java update.
Test to see if the new version of Oracle Java was installed correctly on your system by running the following commands and noting the version number of the new Java update.- Type/Copy/Paste: java -version
- this command displays the version of Java running on your system
- Type/Copy/Paste: java -version
-
 You should receive a message which displays:
You should receive a message which displays:- java version "1.7.0_40"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.7.0_40-b08)Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build build 25.1-b02, mixed mode) - Type/Copy/Paste: javac -version
- this command lets you know that you are now able to compile java programs from the terminal
- You should receive a message which displays:
- javac 1.7.0_40
- java version "1.7.0_40"
-
 Afterwards, you have the option of removing the old Oracle Java JDK/JRE, by simply removing the directory's which hold the old Java JDK/JRE binaries.
Afterwards, you have the option of removing the old Oracle Java JDK/JRE, by simply removing the directory's which hold the old Java JDK/JRE binaries.- Type/Copy/Paste: cd /usr/local/java
- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo rm -rf jdk1.7.0_40
- Type/Copy/Paste: sudo rm -rf jre1.7.0_40
-
 Reboot your Ubuntu Linux system and your system will be fully configured for running and developing Java programs.
Reboot your Ubuntu Linux system and your system will be fully configured for running and developing Java programs.
Share by
Kareem Winters
Update 04 March 2020