How to Upgrade Ubuntu
Part 1 of 3:
Before You Start
-
 Backup your data. Although the upgrade process should not affect any of your personal data, there's always a small chance that something will go wrong. Having a fresh backup of all your important data will help turn a bad situation into a manageable one.
Backup your data. Although the upgrade process should not affect any of your personal data, there's always a small chance that something will go wrong. Having a fresh backup of all your important data will help turn a bad situation into a manageable one.- Click here for detailed instructions on backing up your data.
-
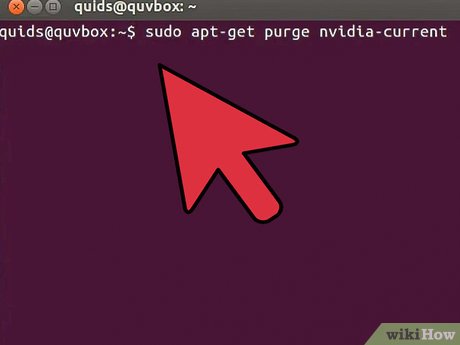
 Uninstall any proprietary graphics drivers. These drivers can cause problems when you are upgrading Ubuntu, so you'll want to revert to the open drivers during the upgrade process. You can reinstall the proprietary drivers after upgrading. Enter the following commands in your terminal, depending on the graphics card you have installed.
Uninstall any proprietary graphics drivers. These drivers can cause problems when you are upgrading Ubuntu, so you'll want to revert to the open drivers during the upgrade process. You can reinstall the proprietary drivers after upgrading. Enter the following commands in your terminal, depending on the graphics card you have installed.
AMD[1]sudo apt-get purge "fglrx.*" sudo rm /etc/X11/xorg.conf sudo apt-get install --reinstall xserver-xorg-core libgl1-mesa-glx:i386 libgl1-mesa-dri:i386 libgl1-mesa-glx:amd64 libgl1-mesa-dri:amd64 sudo dpkg-reconfigure xserver-xorg sudo reboot
Nvidia[2]sudo mv /etc/X11/xorg.conf /etc/X11/xorg.conf.BACKUP sudo apt-get install nouveau-firmware sudo dpkg-reconfigure xserver-xorg
-
 Remove some potentially troublesome PPAs. These are software packages created in the Ubuntu community, and a couple of them are known to cause issues when upgrading: "x-swat" and "xorg-edgers". Remove these two PPAs if you have them installed, and then you can reinstall them after upgrading. Open the terminal and enter the following commands in order.
Remove some potentially troublesome PPAs. These are software packages created in the Ubuntu community, and a couple of them are known to cause issues when upgrading: "x-swat" and "xorg-edgers". Remove these two PPAs if you have them installed, and then you can reinstall them after upgrading. Open the terminal and enter the following commands in order.sudo apt-get install ppa-purge sudo ppa-purge ppa:ubuntu-x-swat/x-updates sudo ppa-purge ppa:xorg-edgers/ppa
-
 Clean up the system. Your upgrade process will go smoother if you clean up any package remnants and old installations. Run the following three commands in order to clear out some of the cruft from your package manager.[3]
Clean up the system. Your upgrade process will go smoother if you clean up any package remnants and old installations. Run the following three commands in order to clear out some of the cruft from your package manager.[3]sudo apt-get --purge autoremove sudo apt-get clean all sudo apt-get purge $(dpkg -l | awk '/^rc/ { print $2 }')
Part 2 of 3:
Upgrading Ubuntu
-
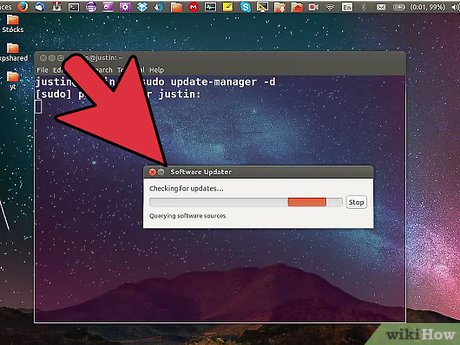
 Press the .⊞ Win and type updater. Select the "Software Updater" from the list of results.
Press the .⊞ Win and type updater. Select the "Software Updater" from the list of results.- If you don't have the Software Updater utility, or are upgrading an Ubuntu Server, see Step 6 of this section.
- If you don't have a network connection, you can use an Ubuntu ISO burned to a DVD to perform the upgrade process. Select "Upgrade" after inserting the DVD.
-
 Click "Check" to check for any available updates. You need to update your software before you can upgrade to a newer version of Ubuntu.
Click "Check" to check for any available updates. You need to update your software before you can upgrade to a newer version of Ubuntu.- Click "Install Updates" to install any available software updates.
-
 Click "Check" again to search for any newer versions of Ubuntu. Note that Ubuntu can only be upgraded to the next released version. For example, if you have an older version of Ubuntu like 10.04 LTS and want to upgrade to 14.04 LTS, you'll have to upgrade to 12.04 LTS first.
Click "Check" again to search for any newer versions of Ubuntu. Note that Ubuntu can only be upgraded to the next released version. For example, if you have an older version of Ubuntu like 10.04 LTS and want to upgrade to 14.04 LTS, you'll have to upgrade to 12.04 LTS first.- If you are upgrading from a significantly older Ubuntu release, you'll likely find it easier to simply install the newest version from scratch.
- You can check your current version of Ubuntu by opening the terminal and typing lsb_release -a.
-
 Click the "Upgrade" button if there is a newer version available. If you know there's supposed to be a newer version but it's not showing up, check out the Troubleshooting section below.[4]
Click the "Upgrade" button if there is a newer version available. If you know there's supposed to be a newer version but it's not showing up, check out the Troubleshooting section below.[4] -
 Review the release notes and click "Upgrade" again. Follow the prompts to install the newer version of Ubuntu. Note that each version of Ubuntu will upgrade slightly differently. You can find detailed notes on each version at help.ubuntu.com/community/UpgradeNotes.
Review the release notes and click "Upgrade" again. Follow the prompts to install the newer version of Ubuntu. Note that each version of Ubuntu will upgrade slightly differently. You can find detailed notes on each version at help.ubuntu.com/community/UpgradeNotes.- Your computer will reboot during the upgrade process.
-
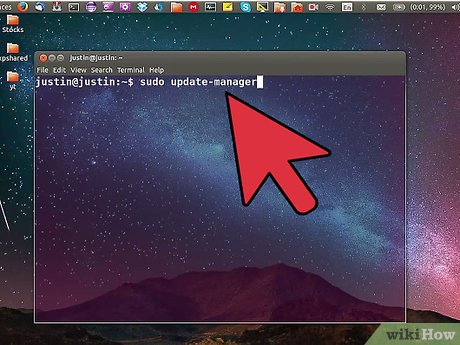
 Upgrade using the terminal. If you aren't using a graphical version of Ubuntu, or prefer to use the terminal, you can perform the entire upgrade process from the command line. If you are using the desktop version of Ubuntu, you can open the terminal by pressing Ctrl+Alt+T. Enter the following commands to update the software on your computer, install the upgrade manager, and then install the upgrade. Each command will take a while to process, and you may be prompted for input.
Upgrade using the terminal. If you aren't using a graphical version of Ubuntu, or prefer to use the terminal, you can perform the entire upgrade process from the command line. If you are using the desktop version of Ubuntu, you can open the terminal by pressing Ctrl+Alt+T. Enter the following commands to update the software on your computer, install the upgrade manager, and then install the upgrade. Each command will take a while to process, and you may be prompted for input.sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install update-manager-core sudo do-release-upgrade
Part 3 of 3:
Troubleshooting
-
 The Software Updater utility does not show a new version available. If you aren't seeing a new version but you know that there is one available, you may need to adjust your Software Updater settings.
The Software Updater utility does not show a new version available. If you aren't seeing a new version but you know that there is one available, you may need to adjust your Software Updater settings.- Open the Ubuntu Software Center.
- Click "Edit" → "Software Sources".
- Click the "Updates" tab.
- Find the "Release upgrade" section or "Notify me of a new Ubuntu version".
- Select "Long term support releases only" or "For long-term support versions".
-
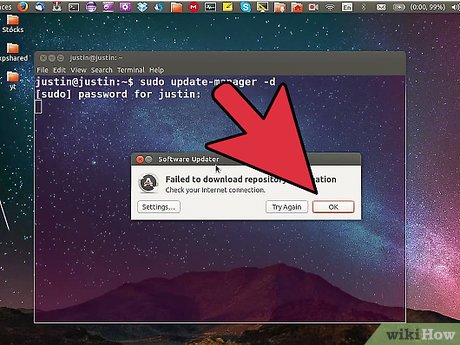
 The upgrade process is failing, or the Software Updater won't allow upgrading to the newest version. Problems with the upgrade process typically stem from running an outdated and unsupported version of Ubuntu. You'll need to either upgrade to each subsequent version until you reach the one you want, or you'll need to perform a fresh install of Ubuntu.
The upgrade process is failing, or the Software Updater won't allow upgrading to the newest version. Problems with the upgrade process typically stem from running an outdated and unsupported version of Ubuntu. You'll need to either upgrade to each subsequent version until you reach the one you want, or you'll need to perform a fresh install of Ubuntu.
Share by
Lesley Montoya
Update 04 March 2020