Advanced TCP / IP settings in Windows 2003
In this article we will provide specific content on advanced settings in the Advanced TCP / IP dialog box and its respective tabs. Hopefully after this article you can understand in more detail the purpose of each option and how to configure it.
Windows 2003 has been released with some new components for TCP / IP such as: support for IP version 6, automatic detection of metric Interface, Gateway and Alternate configuration tab to allow specifying the next IP address to use when missing DHCP server (before APIPA joins).
The Advanced TCP / IP dialog box allows you to configure settings related to DNS, WINS and describe multiple IP addresses and gateways (can still be used even if you have only one network card on the machine).
To open the Advanced TCP / IP Settings dialog box, simply right-click the connection from the Network Connections folder. Open the Properties dialog box of the selected connection, see the list of properties that appear. Then hover over Internet Protocol (TCP / IP) and click Properties. The Internet Protocol (TCP / IP) Properties dialog box appears, click Advanced. At the top of Advanced TCP / IP Settings you will see 4 tabs:
IP Settings : allows adding IP addresses or changing the routing properties of network cards.
DNS : allows setting up TCP / IP connection using domain name system (DNS).
WINS : allows setting up TCP / IP connections using WINS for computers that cannot access Active Directory.
Options : allows setting up TCP / IP (TCP / IP Filtering) filters and describing the ports that will be used for TCP / IP communications.
Tab IP Settings
The IP Addresses box at the top allows you to assign additional IP addresses to a single network card. It is very useful if you own multiple websites on the same web server and want to provide them with each private IP address.
For example, simply click the Add button to add the IP address and Subnet Mask address. Click Edit to edit the selected object and click Remove if you want to delete them.

Figure 1 : IP Settings Tab
The Default gateways box in the middle is used for network connection using multiple default gateways. Click the Add button to add a Default gateway and assign it a Metric value. Metric is the cost of the description distance. "Cost" can be feedback speed, reliability and number of steps. The routing process uses the lowest metric value. So if you set two default gateways, one has a metric of 10, and one is 20, the entry with a metric of 10 will be selected first. The automatic metric value means that the route to the default gateway will be automatically calculated and the fastest process will be selected.
Note : If you open the Command Promp window and type "route print", nothing will be given. The IP Routing table is shown with a list of metric values as one of the attributes of each IP address and its combinations .
The Edit and Remove buttons in the Default gateways box have the same function as the IP address box (explained above).
The bottom of the Settings tab allows you to set your choice to either manually assign an Interface value, or to have it automatically assigned. By default, this option is marked as self-assigned. Uncheck it if you want to enter the metric value for Interface as you like.
DNS tab
The "DNS server addresses, in order of use box" component at the top of the DNS tab gives a list of DNS Server IP addresses, which are used to provide a name resolution solution. These servers are arranged in order and priority. If a server does not work, it will be transferred to the end of the row. To set the order for the IP address, select IP Address and press the up and down button on the right.
An important point to note is that TCP / IP will not transfer to the next server if it needs to stop to process the request. It only does this if the first server is not working (may be being stopped for maintenance, repair or in the middle of a restart).
"Append primary and connection specific DNS suffixes", "Append parent suffixes of the primary DNS suffix" is set by default. These options are used to give suggestions for unqualified names.
The first option will show unqualified names using the parent domain. For example, if you have a computer named "andrew" and the parent domain "ztabona.com", the suggestion is "andrew.ztabona.com". The query will fail if andrew.ztabona.com does not exist in the parent domain. The second option offers a solution for an unqualified name using the parent-child domain level. DNS queries will move to a domain level if it fails at the current level. If the next level continues to fail, the process is automatically transferred up to the new root level.
When the client environment has multiple domains, you can add a domain group to the "Append these DNS suffixes" list in a certain order. They will be searched as part of the DNS query, instead of using the parent domain.
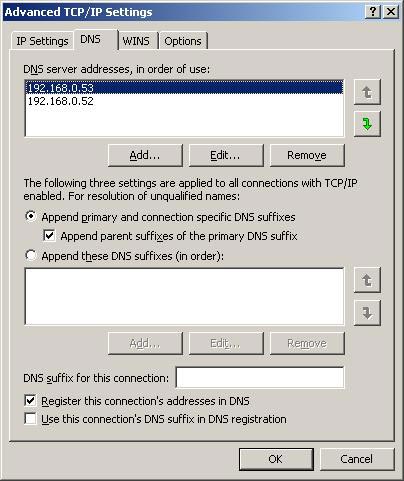
Figure 2
The textbox box to the right of the "DNS suffix for this connection" box is used to set up DNS suffix. to overwrite any previously created settings for the connection.
Register the address for the connection in DNS, which is to register the entire IP address of the connection in DNS under the computer's FQDN. Using the connection's DNS suffix in DNS registration will register the entire IP address for this connection in DNS under the parent domain.
WINS tab
The WINS tab is used to describe WINS-related settings such as the list of WINS servers used for NETBIOS names to handle IP addresses, the LMHOSTS file is used as an alternate means to look up and NETBIOS settings for binding. network connection.
Operating systems and applications before Windows 2000 often use NETBIOS to offer IP name solutions. If you have a Windows 2003 machine that acts as a file or server print and wants other clients to disconnect from it, you must use NETBIOS. Normally the network is now seldom available with Windows 2000 machines. But if your network is available, you should disable NETBIOS over IP. Doing so will save memory, CPU usage and resource release.
Use the "WINS addresses, in order of use box" option above to add the WINS server you want the system to use for IP to give valid names. Press the Add button, a small dialog box appears, waiting for you to enter the IP address of the WINS server. Use the Edit or Remove buttons to edit or delete a selected object. If you have more than one WINS server in the list, use the up and down keys to adjust the server priority of the first query. If a server is unavailable, the next server on the list will be used and so on.
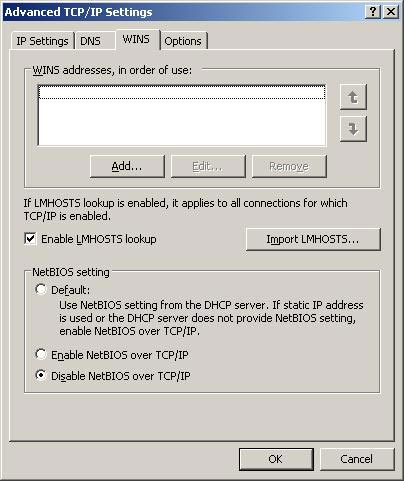
Figure 3
Check the "Enable LMHOSTS lookup" checkbox to ensure that if WINS cannot give a name, the local LMHOSTS file will be used. LMHOSTS file can be found in WINDOWSsystem32driversetc. Its full name is "lmhosts.sam" and can be changed in a text editor. The entry points are located at the end of the file. When used, the IP address on the list is paired with each hostname. If you already have an LMHOSTS file on another computer on the network, you can use the "Import LMHOSTS" button to select this file and import it into your local computer.
The NETBIOS settings at the end allow you to explicitly define how NETBIOS will be used on the system. Select Default if you want the DHCP server to assign the default NETBIOS setting. Select "Enable NETBIOS over TCP / IP" if you are using a static IP address or DHCP Server does not provide NETBIOS settings. Select "Disable NETBIOS over TCP / IP" if you do not want to use NETBIOS or WINS on the network.
Tab Options (TCP / IP Filtering)
The Options tab allows you to configure TCP / IP Filtering settings (TCP / IP filtering function). You can define allowed ports or protocols. Check the "Permit Only" box and use the Add button to add TCP / UDP ports or a protocol copy to the corresponding list. If you set up only allowing network traffic to take place in a defined port set, all other traffic will be deleted.
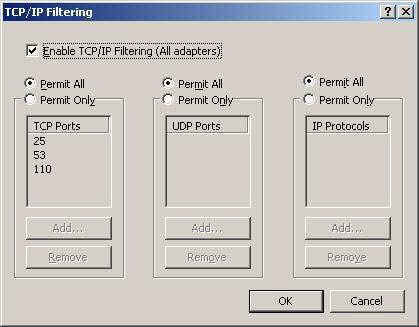
Figure 4
Conclude
This article provides you with an overview of Advanced TCP / IP settings in Windows 2003. Knowing about each option and how to use them is a great addition to configuring network communications. Hope this article helps you a lot.