Work with data in Access 2016
In the previous lesson, you became familiar with the Access 2016 interface as well as the opening and closing of the basic database. This article will continue to go deeper into Access 2016 around the content of working with data in Access 2016.
Work with Access 2016 table
Open the Access 2016 table
To open the table, in the navigation pane, find the table to open, double click on it. The table will be opened in the right pane, as a tab.

Add new record
There are 3 ways to add new records for tables in Access 2016:
Go to Home > tab in Records group> New .

Open the log navigation pane at the bottom of the window> click the New record button.

Start entering the row below the last record in the table.

Sometimes when entering information into a record, you receive a message that the information you entered is invalid. That means that the input field has its own data type rules. Click OK , then follow the instructions in the pop-up to re-enter the data.
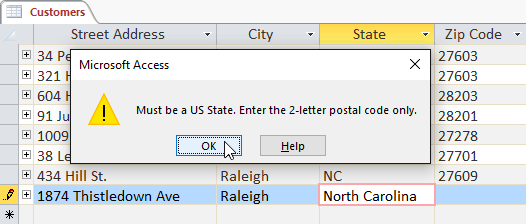
To save the record, on the Home tab> Records group> Save .
Edit the record
To replace a word in the record> Home > in the Find > Replace group, the Find and Replace dialog box appears.
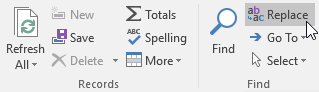
In Find What: enter the word to search, in Replace With: enter the word you want to replace. As an example below is a Fall replacement with Autumn.
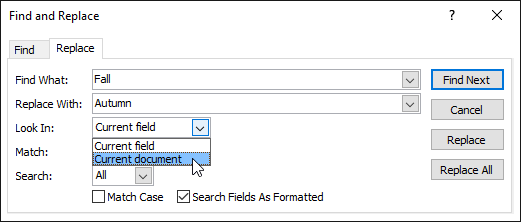
In Match: you can localize your search: Any Part of Field (find your word in every part of the cell), Whole Field (find only those that match the search term perfectly), Beginning of Field (find cell starts with search term).
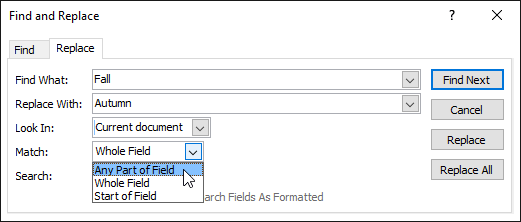
Click Find Next , if the text is found, it will be blacked out.
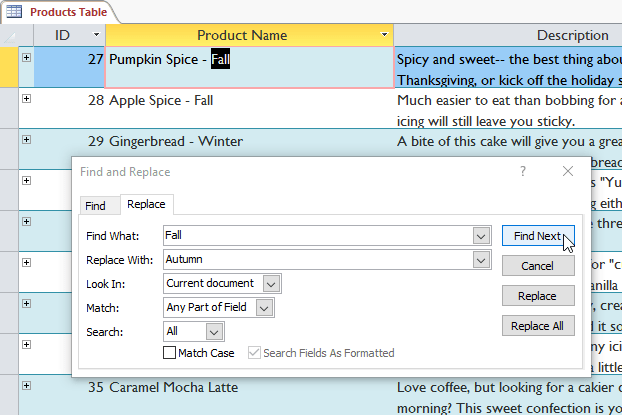
Review the text to make sure you want to replace it. Click Replace instead.
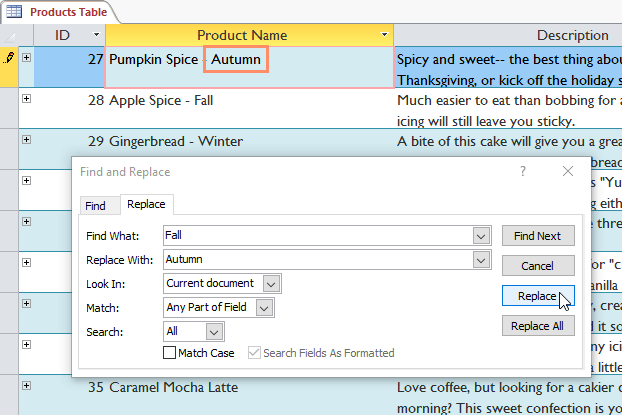
Access will move to the next word found in the table, if the replacement is completed, click Cancel to close.
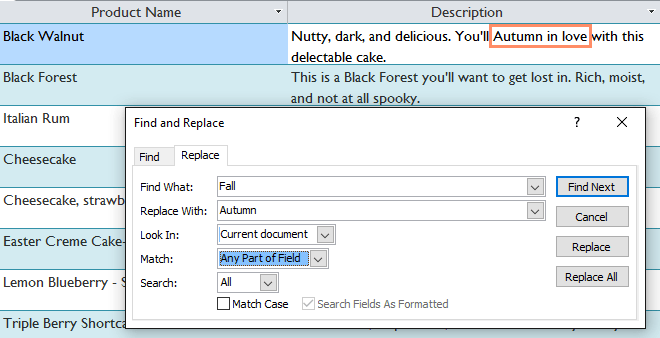
The Replace All option is quite powerful, but it can replace words you don't want. In the example below, since the fall does not mention the season, if replacing with Autumn is not correct. Be careful when using it.
Delete the record
Select the entire record by clicking on the gray border to the left of the record.
Click Home > Records group> Delete .
The dialog box appears> Yes , the record will be permanently deleted.
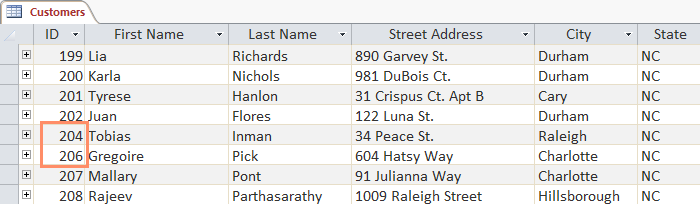
The ID number assigned to the record will remain the same, even if the record is deleted. Example: If you delete a record with ID 205 then the ID number will be . 203, 204, 206, 207 .
Customize table interface
Change the row and column size of the table
To change the column width, move the mouse to the right edge of the column, in the column header box, when the mouse turns into a cross with the arrow left and right, you drag the mouse to the desired position to increase or decrease. column width.
Change the field width in the Access 2016 data table
Similar to the row, you move the mouse to the line below the row to change in the gray area to the left of the row, the mouse turns into a cross with an up or down arrow, you drag the mouse to the desired position to change the degree. wide of rows.
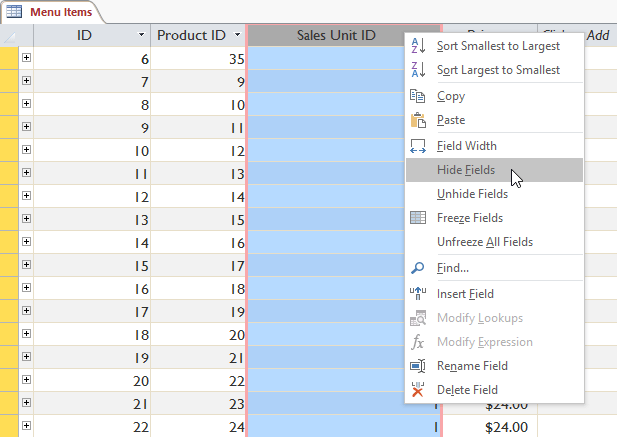
Hide column of table
To hide columns, right-click on the column heading> Hide Fields . If you want the column to show up again, just right-click the title of any column, select Unhide Fields , and in the dialog box, select the column you want to display again.
Change the color of the row
Go to Home > Text Formatting group> click on the Alternate Row Color arrow.
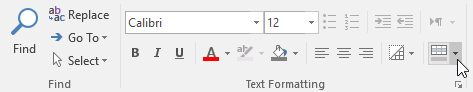
Select color from the drop-down menu, select No Color to remove the color.
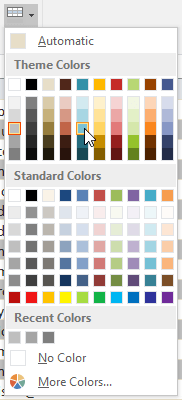
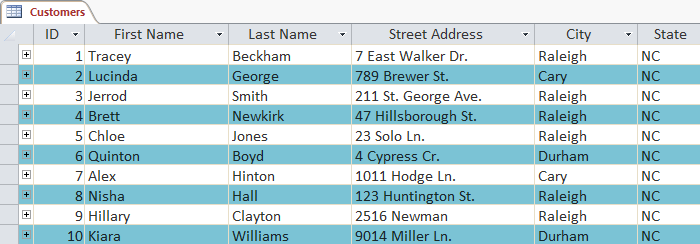
Table after changing color:
Custom lines
Go to Home > Text Formatting > click the Gridlines arrow.
Select the type of line you want:
The line style you just selected will apply:
Working with Form
Open the available form:
Open the database> navigation pane> double click on the form to open.
The form will appear on the right as a tab.
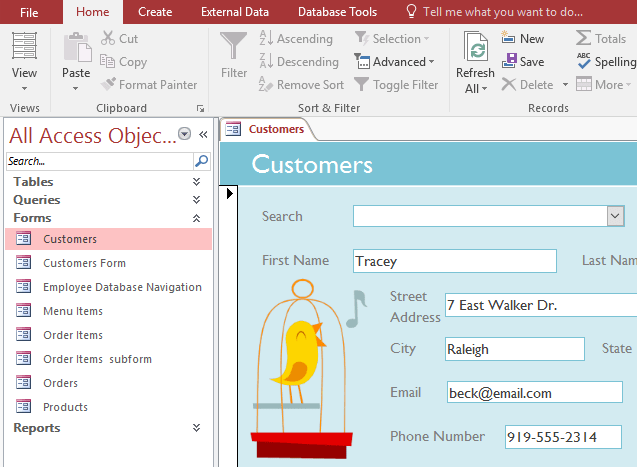
To add, save, delete the form is similar to the record.
Sort records
Select the field you want to use to sort the record, for example, the Last Name of Customers.
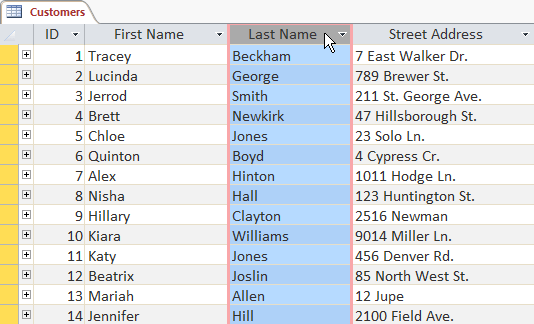
Click Home > Sort & Filter > select Ascending or Descending to sort ascending or descending.
The table will be sorted by the selected school:
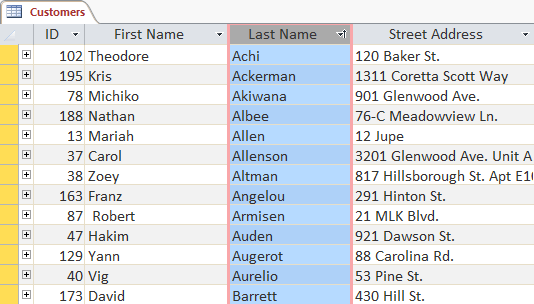
To save the arrangement click Save on the Quick Access Toolbar.
Filter records
Create a simple filter
Click the drop-down arrow next to the name of the field you want to filter, here filter by City.
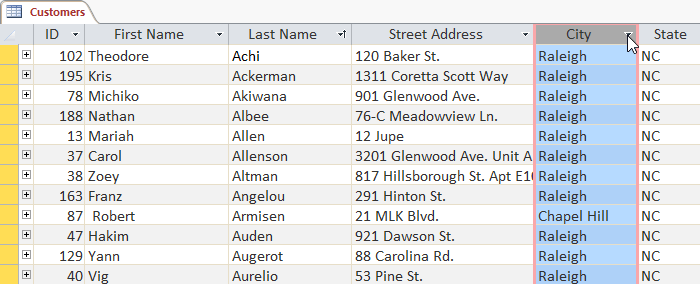
The menu appears to select the element you want to filter.
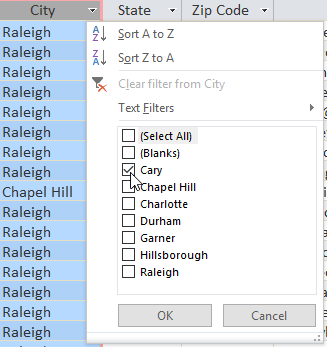
Select OK , the table will only show what you have selected to filter.
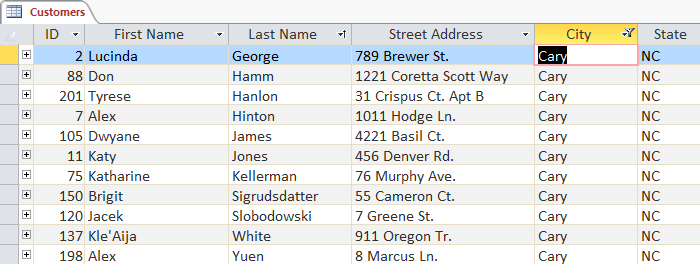
Create a filter from a selection
Select filtering allows you to select specific data from the table and look for similar or unlike data. For example: You are working with the database of the bakery, if you want to search for all products with 'chocolate' names, you can select that word in the product name and create a filter with it.
Select the cell or data you want to create a filter. In this example, we want to see a list of all products that contain chocolate in the name, so we choose Chocolate in the Product Name field.
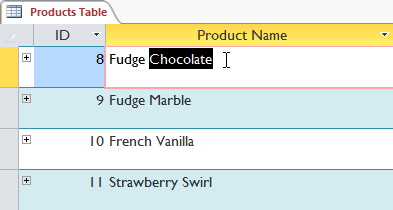
Go to Home > Sort & Filter > click on the Selection arrow.
Select the type of filter you want to apply. In this example we choose Contains "Chocolate" because we want to see a record containing Chocolate in school.
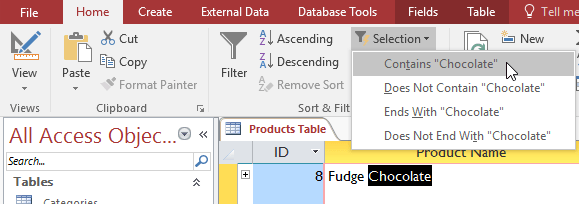
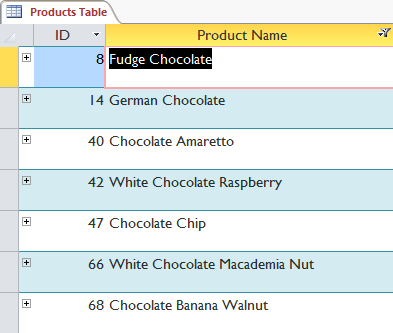
Filter will be applied. The table will only display the products in the name that contain Chocolate.
Create search word filter
Filtering text by search terms you can use some similar options when filtering with an option including: Contains (contains), Does Not Contain (not included), Ends With (ends with) and Does Not End With (does not end with).
Click the drop-down arrow next to the title of the field you want to filter. Here, we will filter to display only the orders containing the notes, so choose Notes.
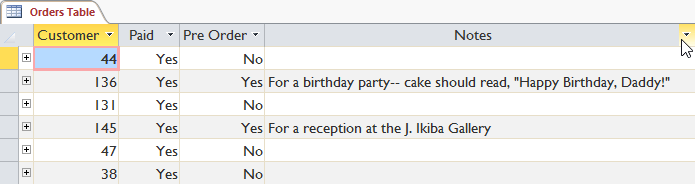
In the drop down menu, hover over Text Filters > choose how you want to filter in the list. Here, we want to see the record with notes containing the word 'party' so we will select Contains .
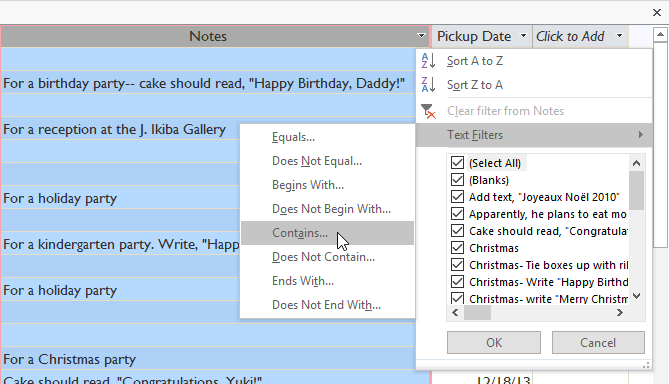
In the Custom Filter dialog box, you enter the word you want to filter, here is the party.
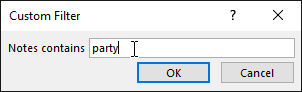
Click OK to apply the filter:
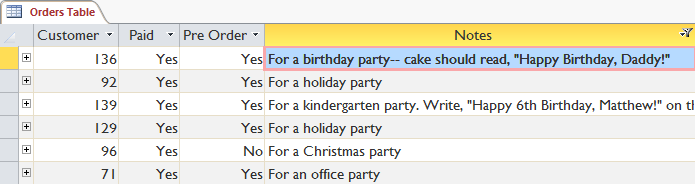
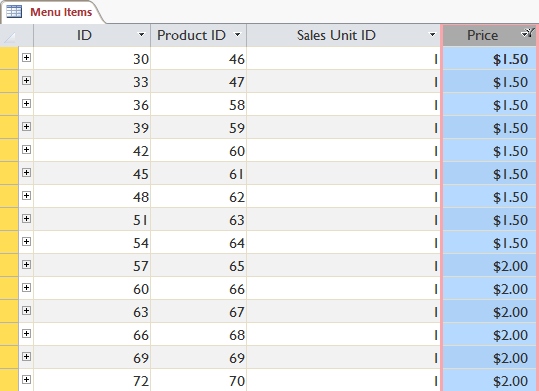
Filter numbers by search
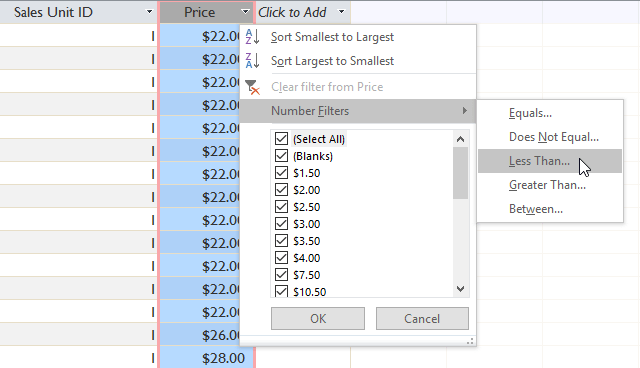
Select the column containing the number to filter, click the arrow to the right of the column name, hover over Number Filters. There are several options for Equals . (Not), Does Not Equal . (not equal), Less Than . (smaller), Greater Than . (larger), Between . (in the range). Suppose we need to filter products that cost less than $ 5 and choose Less Than .
In the Custom Filter dialog box you enter 5 (number to compare).
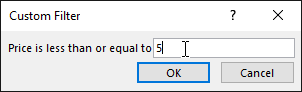
Click OK to apply the filter.
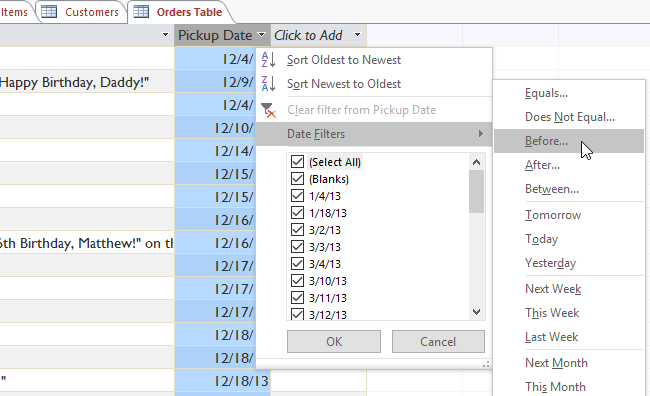
The above method may apply to date data as follows:
In the next article, you will learn how to create simple queries as well as complex queries, how to plan when building queries on Access 2016 and some advanced options. This lesson I found very interesting and has a lot of useful information, please don't ignore it.
Next article: Create data queries in Access 2016 from simple to complex
Previous article: Familiarize yourself with Acccess 2016 interface and basic operations