What is VRM and how does it affect the performance of the processor
The voltage regulator module (Voltage Regulator Module - VRM) is one of the important hardware components in the general structure of a motherboard system, but VRM has not received much attention for a long time. and even people don't even know its existence.In theory, VRM ensures your CPU or GPU receives the cleanest power source possible at a consistent voltage level.
Poor VRM can lead to degraded performance as well as limiting processor performance when it loads tasks, and may even lead to unexpected system shutdowns, especially when Overclocking.In fact, before the known causes of software, weaknesses in VRM design are also thought to be related to Apple's recent adjustments to the i9 MacBook Pros.

Now let's explore what VRM really is and how it affects processor performance.
What is VRM
VRM is a circuit that converts DC voltage from this value to a lower value and at the same time keeps this voltage within the permissible limits at different load levels. another name is 'DC to DC converter'.It is impossible to say that this conversion function is a new technology because it has a life time equal to the life of the electronics and electronics industry.It is easy to see that there are many VRM circuits on the motherboard of the computer, it provides power to the CPU, RAM from + 5VDC or + 12VDC source voltage to the lower voltage that the CPU and RAM have. can work.
How does VRM work?
The VRM in the computer power supply is a DC voltage stabilizer that operates according to the PWM modulation method similar to the main power PWM circuit.It also has equivalent component components such as oscillator IC, Mosfet, PWM coil and filter capacitor.
The first job of VRM is to convert 12 volt power from the computer's power supply into a voltage so that the microprocessor can be used.For microprocessors, this voltage usually ranges from 1.1V to 1.3V.Sophisticated electronic devices within each microprocessor can easily fail to achieve the necessary effect due to power reasons.Accuracy is also important when powering the processor and the required voltage must be distributed as accurately as possible.That's why the structure of VRM is much more complex than a simple wire segment.However, the "heart" of VRMs is basically a buck converter - a device that accurately reduces the voltage to the appropriate level.
VRM uses the following three components to perform its work:
- MOSFET (short for Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor, meaning "Metal Oxide effect transistor - Semiconductor).
- Inductors (also called inductors).
- Capacitor.
There is also an integrated circuit (IC) to control them all, sometimes called PWM controllers.Here is a simple diagram of a single-phase VRM system:
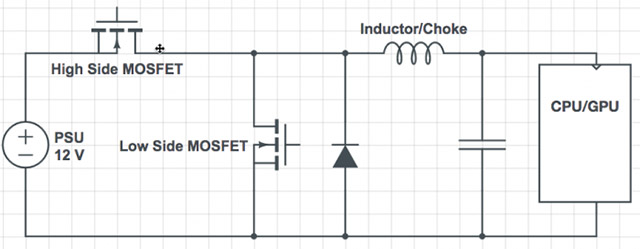
Multi-phase VRM
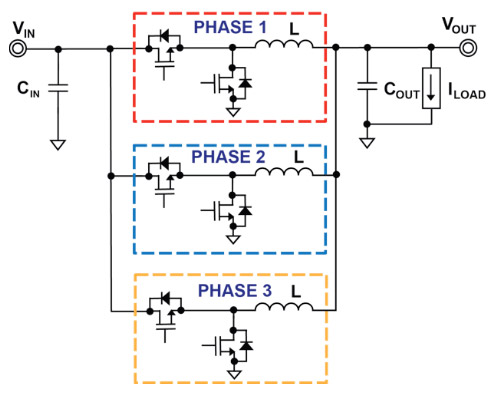
The power of microprocessors on modern computer systems requires more than a single-phase VRM, so manufacturers equip their processors with multi-phase VRM systems.Multiple phases help to transmit the power on a wider physical area, reduce the production of temperature, reduce the pressure on components in the system as well as bring about related power improvements. Performance and operating costs of each part in the motherboard.
Each phase in a state-of-the-art multiphase VRM system will provide the necessary power, taking turns to power the CPU.These sessions will be done individually, each phase provides energy for a short period of time.You can imagine this process as a square wave in the illustration below:
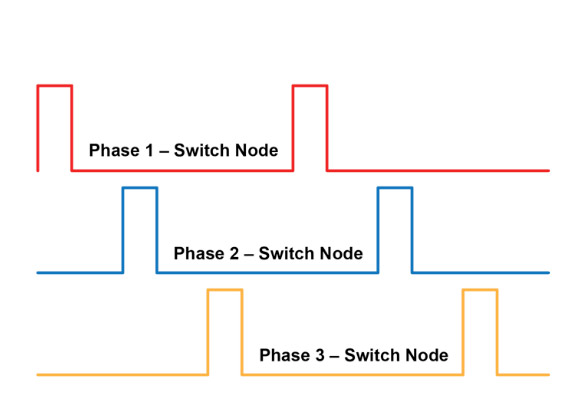
The energy in each phase is 'pumped' to the staggered processor, so even if only one phase is active at a time, the total power supply is always maintained stable, simultaneously. create a stable, reliable energy source, which can be considered as a 'clean' energy source needed for a CPU to operate in the most optimal condition.You can see the model describing the operation of VRM phases in the diagram below.
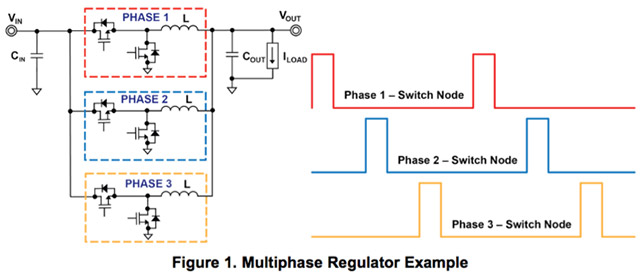
The number of phases of VRM affects the marketing of the manufacturers
VRM is usually sold as '8 + 3' or '6 + 2.'The number before the plus sign indicates the number of phases that are dedicated to cleaning the source for the CPU.The number after the plus sign indicates the remaining phases in VRM to power other motherboard components such as RAM.
When the first number is greater than 8, such as '12 + 1, '' 18 + 1 'or even higher, the manufacturer often uses a device called a doubler.A doubler allows the manufacturer to take advantage of the current phase without installing additional phases into the system.Although these mirrored phases are not quite as efficient as the completely separate phases, it allows significant savings in production costs, resulting in a much more competitive price.
Some manufacturers, especially Gigabytes, have also begun to advertise parallel phases as if they were two separate phases.In fact, this is actually a mirrored phase.Its electrical signals are synchronized instead of staggered as mentioned above, and of course it cannot be as effective as a truly independent phase.But manufacturers often are not afraid to 'bend' and equate these relatively abstract concepts if it is necessary to ensure their interests.If it is said that these are moral issues, it may seem a bit heavy, which can be considered as a way to 'circumvent the law'.It is still important that consumers themselves need to be alert and equip themselves with the basic knowledge of a product before deciding to buy it.
How does VRM improve performance?

The goal with VRM is to provide a clean and stable energy for the motherboard.However, even a basic VRM can provide enough performance to maintain a mid-range CPU at the base rate, but when overclocking or pushing the component limits, the quality of VRM becomes important. more important.
Imagine, the main power transformer of the power supply is a water tank, with the normal power supply having 3 compartments corresponding to 3 nozzle heads, 3 main power lines, so each compartment (capacity each line) will be lower than the total capacity of the container (total power supply capacity).For a VRM power supply, the container has only 1 compartment and 1 12V water supply, so it can be said that the total storage capacity will be equal to the total capacity for the 12V line, 12V power supply for The remaining 2 lines are via VRM circuit or it can be said that the other two lines are the load of 12V line.In theory:
PSU capacity = Capacity 12V = Power 5V = 3.3V capacity provided that 2 of the 3 lines have zero load.
Consequently, if you have 2 power supplies with the same power level, the VRM power supply will always give you a higher level of power for each line.Based on the needs of the new system, which currently uses a lot of energy from the 12V line, this will help you not need to buy a larger power supply.
To make it easier to understand, we can compare the two different power sources of AcBel, R8 607W, which do not have VRM and R88 features VRM for both 5V and 3.3V lines.We see that although the same power level is 600W, but the total output (max output) of each power line, R88 has a higher capacity.The 12V R88 line is 540W @ 45A and R8 only has 480W @ 40A.When you need a 12V power supply with a capacity of 40A, with no VRM power supply you have to choose to buy a power supply with a capacity of over 680W but with a VRM power supply, only a 600W power supply is enough.
Conclusion: Find yourself a good VRM
Even if you know the basics, it is never easy to choose suitable VRM power supplies.The information from the manufacturer as mentioned above, is very misleading.Therefore, it is best to consult with those who have expertise or participate in groups and forums about hardware and electronic components, people will always be ready to help each other.
Hope the above information can help you!
See more:
- How to enable performance optimization in Windows 10
- Learn about how the CPU works
- The difference between a mid tower and a full tower computer case
- Instructions for setting up and installing Microphone on computer