Interesting things about computers may not be known
This is probably the most erroneous prediction in history. In the 1940s, Thomas Watson - chairman of multinational computer technology group based in Armonk, New York, USA, predicted that: The world will not need more than "five computers" . Sixty years later, the number of computer users in the world increased to one billion!
Obviously, computers have changed many things during that time. In the 1940s, computers were a strange scientific phenomenon and a great support for the military authorized by the government, each worth up to millions of dollars. Even today, most computers are used in everyday devices from microwaves to mobile phones and digital radios. What makes a computer so versatile that it can operate in many other devices? How can they become so extraordinary? And how can it work exactly like that? Please read the information below!
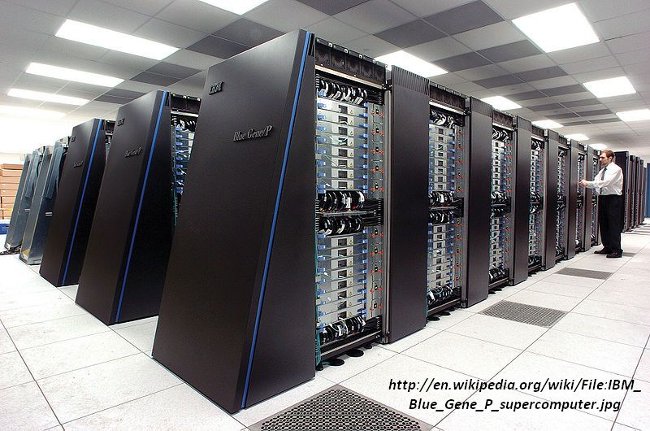 Photo: IBM Blue Gene / P supercomputer system at Argonne National Laboratory - one of the world's major computer research sites - but in fact it is just a larger version of your computer use. Photos taken at Argonne National Laboratory posted on Flickr in 2009, Creative Commons license.
Photo: IBM Blue Gene / P supercomputer system at Argonne National Laboratory - one of the world's major computer research sites - but in fact it is just a larger version of your computer use. Photos taken at Argonne National Laboratory posted on Flickr in 2009, Creative Commons license.
1. What is a computer?
 Photo: Microchip on the fingertips
Photo: Microchip on the fingertips
Computers are electronic devices used to process information - in other words, the information processor. The computer carries hard information ( or data ) at one end, stores information until it is ready to operate, type and process information, and then quickly output the result to the other end. All of these processes have a unique name: where the information is called input , storage information is memory ( or storage ), information processing is information processing and The output is called the output .
Imagine a computer is a human, you will have a friend who is very good at math. That friend was very kind and everyone asked her math problems. Every morning, the computer went to check its mailbox and received a series of questions about mathematics that needed to be solved. The computer puts them on the table to watch. In the afternoon, the computer took out each letter to read, examine the issues, proceed with processing and outline the answers. Then, the computer puts them back into the envelope and sends it to the person who sent the issues and stowed them into the tray, ready to solve another problem. The computer continues to move to read the next letter. You will see your friend act like a computer. The computer's mailbox is the input, the document placed on the desk is memory, the brain is the processor that solves the problems and trays on the output table.
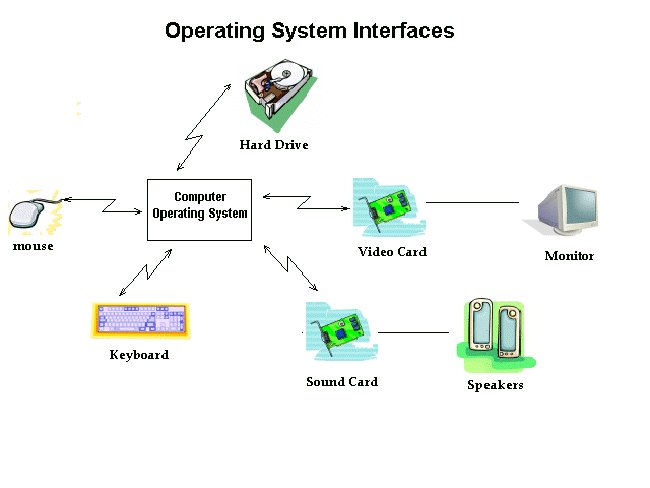 Artwork: Computer works by combining inputs, storage, processor and output. All major parts of the computer include one of the four combinations above.
Artwork: Computer works by combining inputs, storage, processor and output. All major parts of the computer include one of the four combinations above.
You understand that computers have inputs, memory, processors and outputs, all of which have their own effects:
Input : For example, the keyboard and mouse are input units - the place to receive information to the computer needs to be processed. If you use a microphone and speech recognition software, it's another form of input.
Storage memory : The computer can store all your documents and files on a hard drive: huge storage memory. Smaller devices are similar to computers like digital cameras and mobile phones that use other types of storage such as memory cards.
Processor : A computer processor ( known as a pre-programmed data processing circuit ) is a microchip embedded deep inside. It works extremely strongly and heats up during processing. That is why a computer has to have a cooling fan on the inside of the computer - so the computer does not become too hot!
Output: A computer with an LCD screen displays high-resolution images ( details ) and speakers to produce sound. You can also add color inkjet printers on the table to print fixed archives.
2. What is a computer program?
You can read more about the history of the computer's birth, the first computer is just a giant computing machine, but they quickly handle " numbers ": solve all math problems. long, hard to understand and boring. Today, computers can solve many more problems - but basically still use calculations. The computer can do everything from editing images that were taken with digital cameras displayed on the web to manipulating numbers in a different way or in different ways.
 Photos: Computers and pocket computers are the same because they all handle numbers. However, pocket computers often only give the results of calculations and that is all pocket computers can do. Computers can store complex programs called programs and use them to make things more interesting.
Photos: Computers and pocket computers are the same because they all handle numbers. However, pocket computers often only give the results of calculations and that is all pocket computers can do. Computers can store complex programs called programs and use them to make things more interesting.
Suppose you want to search for a digital photo or a mirror image ( in other words flip it from left to right ), you just need to go to the painting or image editing software. Maybe those pictures are made up of millions of pixels ( colored squares ) arranged in grid pattern. Computers store each pixel with a number, so getting a digital photo is like a quick sorting exercise by writing numbers. To flip a digital photo, the computer simply needs to reverse the sequence of numbers running from right to left instead of running from left to right. Or you want to increase the brightness of the photo, just slide the " light " icon lightly. After that, the computer will rely on the pixels of the image to gradually increase the brightness, adding 10% to make the image brighter. So it relates to numbers and calculations.
The difference between computers and pocket computers is how they work. You just need to show how to guide (call the program ), turn it off and perform a kind of both long and complicated operations. Back in the 1970s and 1980s, if you wanted to have a home computer to do everything, you had to write small programs to do it yourself. For example, before typing on a computer, you have to write a program that can read the words you type on the keyboard, store them in memory and display them on your screen. Writing programs often takes longer than anything you want to do at first ( write letters ). Soon after, people began selling software such as word processing to save things that you wrote yourself.
Today, most computer users rely on pre-written programs such as Microsoft Word and Excel or downloaded applications for tablets and phones without having to do as many things as before. Currently, almost no one writes such programs anymore, which is a pity, because it is really interesting and useful. Everyone considers computers as a tool to help them work, not just complex electronic devices that need to have preinstalled programs. Some people will find it more useful because we can do much better than computer programs. Once again, if we all rely on the computer programs and applications available, someone will have to write them down and the skills need to be retained. Fortunately, there are also many people who are interested in computer programs recently. " Encryption " (the official name of a program, sometimes called " encryption ") is used to teach at schools like easy-to-use programming languages like Scratch . The development changes according to preferences related to personal gadgets like Pi Raspberry and Arduino . And Code Clubs is the place where volunteers teach children how to program, are present all over the world.
3. What is the difference between hardware and software?
Good computers can start a word processing program within a minute and open a photo editing program after 5 seconds. In other words, although we don't really think so, computers can reprogram as many times as you want. This is why these programs are called software. " Soft " is understood in the sense that it is not fixed: it can be easily changed. In contrast, computer hardware - small pieces and pieces ( peripherals like mice and printers can be plugged into them ) - are quite fixed when you buy them from the store. Hardware is what makes your computer run better, the ability to run different software is what makes it more flexible. Computers can do many different useful things and that's why millions of us can't live without it!
4. What is the operating system?
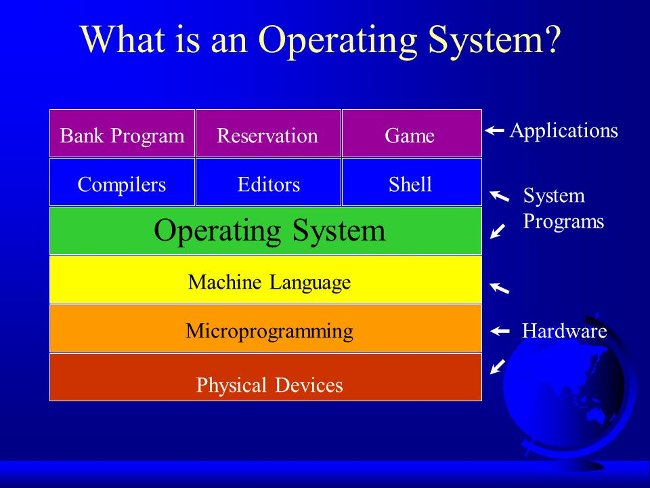
Imagine you were living in the late 1970s, before the computer programs were invented. Want your computer to be able to handle text, type your first novel - this is quite easy but you will have to take a long time to do this. A few weeks later, you want to write a few more things and decide to reprogram it, so it will be like playing a game. Then you decide to write the program to store the photo gallery. Each different work program has some similar things. For example, all programs need to be able to read the keys you press down on the keyboard, store them in memory, then find them again, and display the characters ( or images ) on the screen. If you write many different programs, you will realize that the programs are the same in some basic activities. That's a bit of programming, so why not just collect all those programs to run basic functions and reuse them a few times?
History of Microsoft Windows operating system throughout the ages
5. Typical configuration of computers
That is the basic structure behind an operating system: the main software in the computer (needed ) controls basic tasks at the input, output, storage and processor. You can think of the operating system as the " base " of the computer software that other programs ( called applications ) are built on. Therefore, word processing software and chess games are two different applications, but both must be based on the operating system to perform input, output and more steps. The operating system based on the basic program parts on the computer is called the Basic Input / Output System ( Basic Input Output System, BIOS ), which relates to the software operating system and the hardware operating system. Unlike the operating system, the basic Input / Output system is usually the same, the BIOS does not change from one machine to another according to the hardware configuration and it is often written by hardware manufacturers. BIOS is not hardware but software: it is a semi-permanent program stored on one of the computer's main chips - known as the firmware (usually designed to can be updated regularly.
Operating systems have another great benefit. In the 1970s and early 1980s , almost all computers were different. They all run on their own properties with unique hardware ( different processor chips, memory addresses, screen sizes and the rest) . Programs written specifically for one machine ( like Apple ) often cannot run on other machines ( like IBM ) without using the adapter. It is a big problem for programmers because it means they have to rewrite all the programs whenever they want to use another computer. How did the operating systems support? If you already have a standard operating system and edit it to be able to run on any computer, all you need to do is write down applications that can work on operating systems. And any application can run on the computer. Of course, this groundbreaking operating system is Microsoft Windows written by Bill Gates. ( It is important to note that in there still exist the previous operating systems ).
See also: Learning to use basic computer lesson 1 - Introduction to computers