Things you need to know about Private IP addresses
Private IP address (private IP) is the IP address reserved for internal use through a router or other Network Address Translation (NAT) device, completely isolated from external networks.
Private IP addresses are in contrast to public IP addresses, addresses are public and cannot be used in home or business networks.
Sometimes a Private IP address is also called a local IP address.
Find out about Private IP address
- Which IP address is private?
- Why is private IP address used?
- Addresses reserved IP
- How to find Private IP address
- Other information about Private IP address
Which IP address is private?
Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) stores the following IP address blocks to use as a Private IP address:
- 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
- 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
- 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
The first set of IP addresses above includes more than 16 million addresses, the second set contains more than 1 million addresses and the last set has more than 65,000 addresses.
Another range of Private IP addresses is 169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255, but these addresses are for Automatic IP Private Addressing (APIPA) only.
In 2012, IANA allocated 4 million addresses 100,64.0.0/10 to be used in a NAT environment as a service provider.
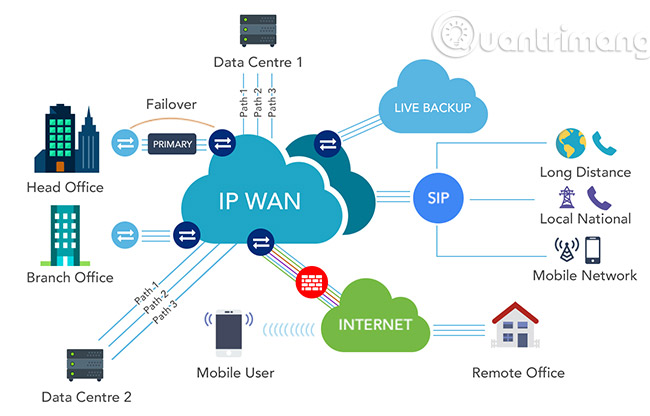
Why is private IP address used?
Instead of each device in a home or business network using a public IP address, with a limited supply, the Private IP address provides a completely separate collection of addresses, still allowing access on the network but does not account for public IP address space.
For example, consider a standard router on a home network. Most routers in the home and business globally, be it your or your neighbor's home, all have IP addresses of 192.168.1.1 and assign 192.168.1.2, 192.168.1.3 . to Other devices are connected to it (through an intermediate stage called DHCP).
It doesn't matter how many routers use 192.168.1.1 address, or how many devices inside the network share IP addresses with users of other networks, because they don't communicate directly with each other.
Instead, the devices on the network use routers to translate their requests via public IP addresses, which can communicate with other public IP addresses and eventually to other local networks.
Hardware in a specific network using a Private IP address can communicate with all other hardware within the network's limited range, but will require a router to communicate with devices outside the network, later. Then the public IP address will be used for communication exchange.
For example, before accessing this page, your device (could be computer, phone or anything), use Private IP address, page request to access (with Public IP address) right through the router. After the request is made and the page needs to be accessed, the content will be downloaded through the public IP address before reaching the router, then the data is sent to the private address (local address), so you can access that data from your device.
All devices (laptops, desktops, phones, tablets, etc.) are in private networks, can use virtually unlimited Private IP addresses, and addresses Public IP will be restricted.
Private IP addresses also allow devices that do not need Internet connectivity, such as file servers, printers, etc., to communicate with other devices on the network without using a public IP address.
Addresses reserved IP
A more restricted set of IP addresses is called Reserved IP addresses (reserved IP addresses). They are similar to Private IP addresses (cannot be used to communicate on the larger Internet, outside the local network), but Reserved IP addresses are even more restrictive.
The most famous reserved IP is 127.0.0.1. This address is called a loopback address and is used to check the network adapter (adapter) or integrated chip. No traffic sent to 127.0.0.1 is sent via local network or public internet.
Technically, the entire range from 127.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255 is reserved for loopback purposes, but you'll almost never see any addresses other than 127.0.0.1 used in practice. .
Addresses in the range of 0.0.0.0 to 0.255.255.255 are also reserved but not for anything. If you try to assign an IP address within this range to a device, it will not work, regardless of where it is installed on the network.
How to find Private IP address
Knowing your Private IP address is only useful in specific cases and for most people, it is a rare situation.
If you want to connect a computer to another computer on the network, like with a mapped network drive, you can do so through its local IP address. You can also use your local IP address with computer software to control it remotely. A Private IP address is also needed when controlling a specific network port from a router to a specific computer on the same network. This process is called port forwarding.
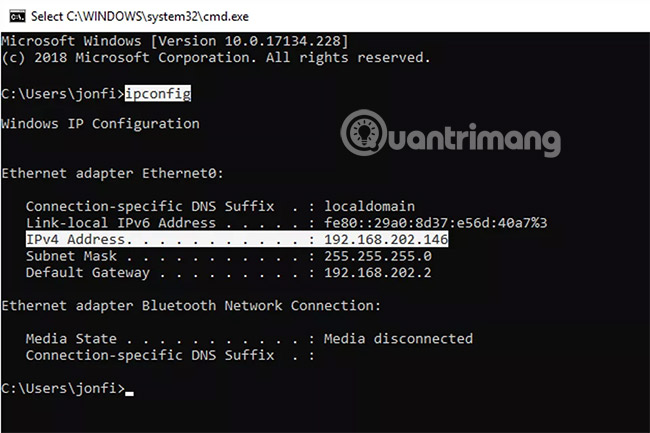
The easiest way to find your Private IP address in Windows is through the Command Prompt with the ipconfig command .
Tip: If you are not sure what your router or the default gateway's IP address is, refer to the article: How to find the default gateway IP address.
Other information about Private IP address
When a device such as a router is plugged in, it will receive a Public IP address from an ISP. These are devices that then connect to the router and are granted Private IP addresses.
As the article mentioned above, Private IP address cannot communicate directly with Public IP address. This means that if the device has a private IP address that is directly connected to the Internet (as a result it will not be able to route), the device will not have a network connection until the address is translated. The address is active, through a NAT or until the request it generates is sent via a device with a valid public IP address.
All traffic from the Internet can interact with a router. This is true for everything from regular HTTP traffic to things like FTP and RDP. However, because Private IP addresses are hidden behind a router, and the router must know which IP address to forward information to, if you want something like an FTP server set up on the home network. .
In order for this to work correctly with Private IP addresses, you must set up port forwarding. Forward one or more ports to a specific Private IP address that involves logging into the router to access its settings, and then select which port (s) to forward and where it should go.
See more:
- How to determine the device IP address on the local network
- How to check the computer IP address with TrueIP
- Instructions on how to determine the IP address on the computer