How to assign static IP addresses in Windows 7, 8, 10, XP or Vista
Sometimes, assigning an IP address to a better computer will allow the router to automatically assign an IP address. Read this article to learn about assigning static IP addresses in Windows.
Static IP address with automatic IP address
Typically, IP addresses for personal computers and other devices can be automatically assigned by the router using a protocol called Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). This is a handy way to connect devices to the network because users do not have to configure IP addresses for new devices. The downside of automatically assigning an IP address is that the device's IP address may change over time.
This is not a big problem, but in some cases, users want the device to use a static, unchanged IP address. For example, in the case of:
- There are certain applications that can only connect to network devices that use their IP addresses, especially when many older network applications are restricted.
- When you want to forward ports through the router to devices in the network. Some routers can forward ports and dynamic IP addresses; But some routers can't.
Assigning a static IP address to the device is not difficult, but users should choose to do this from the router or device.

Assign a r outer static IP address
Although this article covers assigning static IP addresses to PC computers in Windows, there is another way to do this. Many routers allow users to specify a set of IP addresses to be distributed to specific devices (based on the device's physical MAC address). The method has certain advantages:
- The IP address is still managed by the router, which means you won't have to change on each device individually.
- Easily assign addresses in the same set of IP addresses that the router uses.
This article will show you how to assign a static IP address directly to Windows-based computers.
Set to assign static IP addresses in Windows 7, 8 or 10
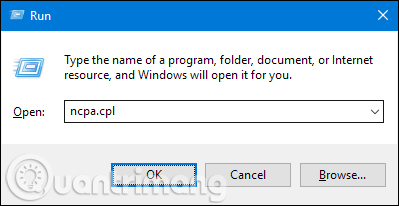
To change the IP address of the computer in Windows, open the " Network Connections " window. Press Windows + R , type " ncpa.cpl " in the Run box, then press Enter .
In the " Network Connections " window, right-clicking on the adapter wants to set a static IP address and then select the " Properties " command.

In the adapter properties window, select " Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP / IPv4)" and then click the " Properties " button.
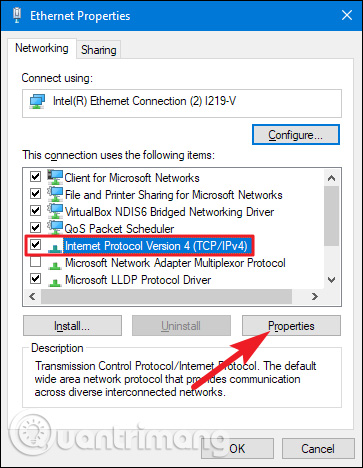
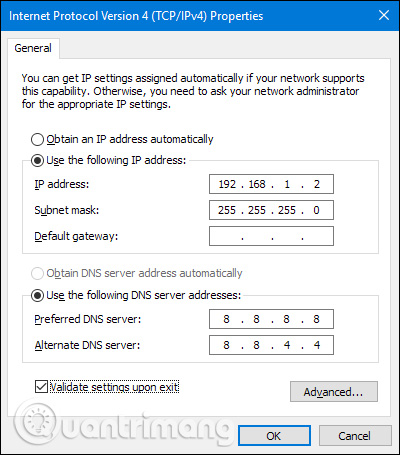
Select the " Use the following IP address " option, then type the IP address, subnet mask and default port corresponding to the network settings. Next, enter the DNS server address. Finally, select the " Validate settings upon exit " option to let Windows check the new IP address and the corresponding information to make sure it works well, then click the " OK " button when done.
And then close the properties window of the network adapter.
Windows automatically runs the network diagnostics to verify the connection. If there is a problem, Windows will provide the option to run a network troubleshooting wizard. However, if you really have a problem, this troubleshooting wizard doesn't really fix the problem, you should check the installation and try again.
Assign static IP addresses in Windows Vista
Changing IP from DHCP to a static address in Vista is similar to other Windows versions, but the location will be slightly different. Open the Start Menu, right-click Network, and select Properties.
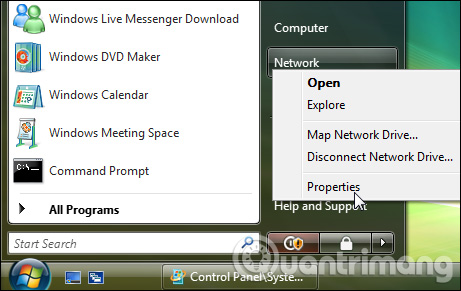
On the Network and Sharing Center window, click Manage network connections.
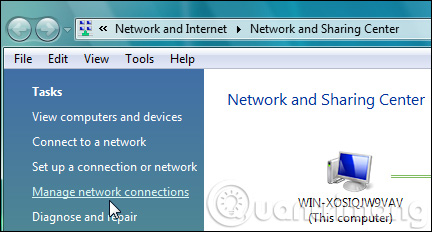
Right-click on the network adapter to assign an IP address and click Properties .
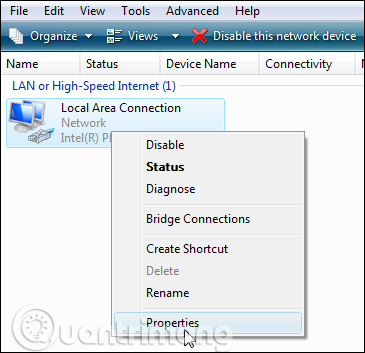
Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP / IPv4) then click the Properties button.
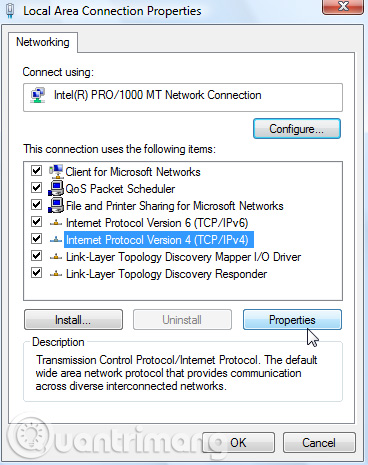
Now change IP, Subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server address, when finished click OK .

You need to close the Local Area Connection Properties window for the settings to take effect.
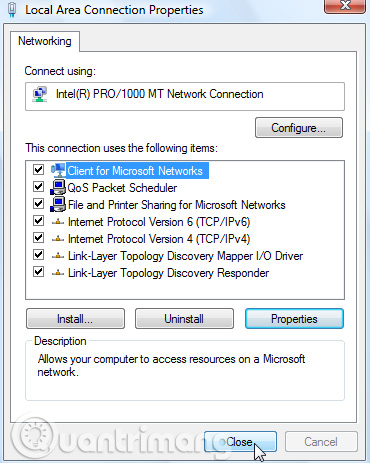
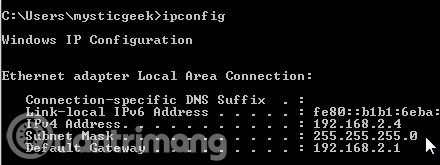
Open Command Prompt and use the ipconfig command to verify the changes were successful.
Assign static IP addresses in Windows XP
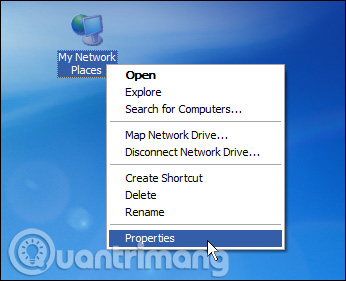
To assign a static IP address in Windows XP, right-click the " My Network Places " icon, then select " Properties ".
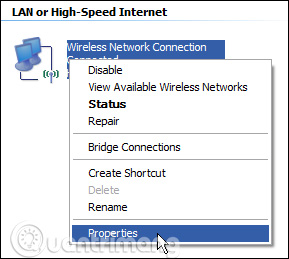
Right click on the adapter you want to set up IP and then select " Properties " from the context menu.
Select " Internet Protocol (TCP / IP) ", then click the " Properties " button.
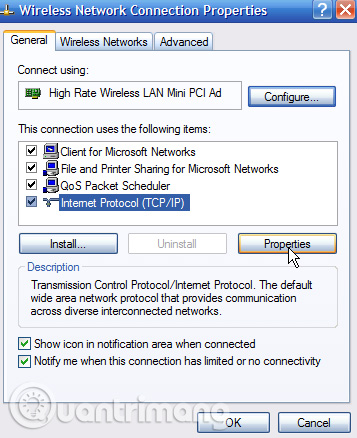
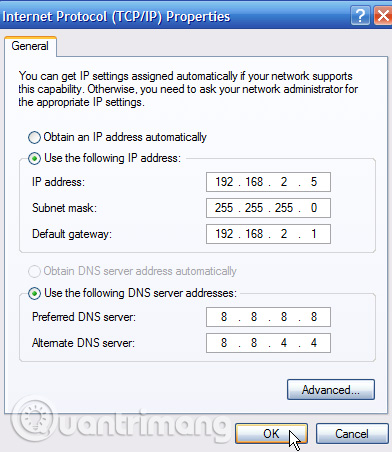
Select the " Use the following IP address " option. Enter the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway and DNS server address you want to use. When done, click the " OK " button.
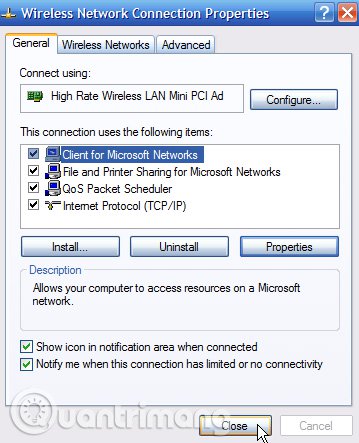
You need to close the adapter properties window before the change takes effect.
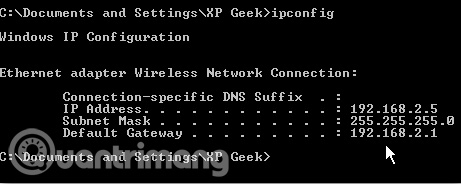
Users can verify new settings using the ipconfig command in Command Prompt.
In general, it is best to let the router automatically assign IP addresses to devices. Occasionally, you can set a static IP address for a specific device. Although it is possible to set static IP addresses on devices, users should still set a static IP address on the router if possible.
See more:
- Instructions to change IP address from Command Prompt
- Instructions for setting static IP addresses in Mac OS X
- Here's how to check if your IP address is static or dynamic