PhotoShop - Lesson 2: Color theory
Color correction for images is one of Photoshop's most important functions, so understanding color theory will help you use Photoshop effectively .
I. Additive color model
Plus color is the foundation of all colors, because it comes from the principle of eye color perception. The retina in the back of the human eye has sensitive cones with red (red), green (green) and blue (blue) colors. These cells transmit individual signals to the brain, where images are synthesized into all colors. There are also rod cells that are sensitive to the shades of light and color.
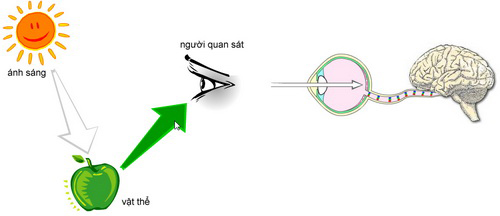
We feel the colors thanks to the reflected light
from objects and go to our eyes
In 1704, the famous British scientist Isaac Newton resolved white light into seven rainbow colors - violet - blue - green - yellow - orange - red, in which purple, indigo, yellow, orange could created from red, green and blue. So red, green and blue are considered the three basic colors (primary colors) to create any other color.
On the other hand, science also proves that light is a form of energy radiated in the form of waves spreading at 300,000 km / sec. The color of light is different due to different wavelengths. The spectrum that the human eye can see is just a very narrow slit on the electromagnetic wave scale, stretching from 380nm dark purple (nanometer, unit of length equal to 1 millionth of a millimeter) to 780nm deep red.
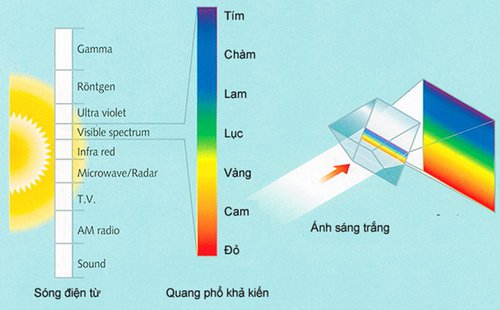
Visible spectrum
People call the plus color model as RGB model. This principle is applied in the technology of manufacturing television screens, computer monitors, video techniques, lighting .
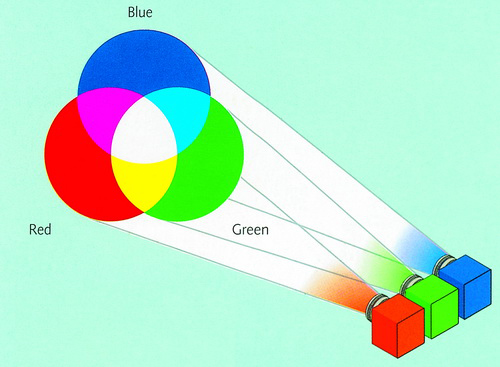
All colors that are in visible suffering can be created
By changing the intensity of 3 lights: red, green, blue
In Photoshop:
R G B Red (Red) 255 0 0 Green (Green) 0 255 0 Lam (Blue) 0 0 255 Lam - green (Cyan) 0 255 255 Red lotus (Magenta) 255 0 255 Yellow ( 255 ) Yellow 255 0 Black 0 0 0 White 255 255 255 Gray 50% 128128128
II. Subtractive color model ( subtractive color model )
The plus color model starts from black (a blank TV screen and adds color R, G, and B to get white). In contrast, the minus color model starts with white (a blank sheet of paper is projected with white light and subtracts the R, G, B colors of white light to get black).
The removal of light R, G, B is done by printing overlapping blue ink colors - green (cyan), red lotus (magenta) and yellow (yellow). Cyan ink works to absorb red light, Magenta ink absorbs green light, Yellow ink absorbs blue light.
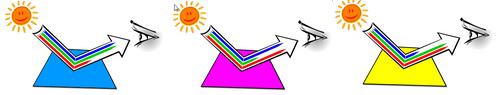
Cyan ink absorbs red light - Magenta ink absorbs green light -
Yellow ink absorbed blue light
Any color in the restored color range (CMYK gamut) can be achieved by changing the color ink ratio C, M, Y. The color model except for the modern and internal color photography techniques all industrial color printing processes. In fact, because the ink is not pure, when the three colors C, M, Y overlap, they still cannot produce true black. And the printing industry must use a print with black ink to complement C, M, and Y to create more detail and depth for the image.
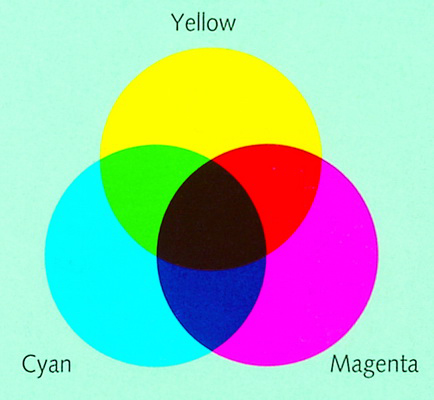
In printing industry, 4 CMYK colors are called 4 colors process colors
In printing, to create red flags ( Red ) people print the red lotus ( Magenta ) and yellow ( Yellow ). Similarly we have:
C (%) M (%) Y (%) K (%) Red flag (Red) 0 100 100 0 Green (Green) 100 0 100 0 Blue purple (Blue) 100 100 0 0 White 0 0 0 0 Orange 0 50 100 0 Green jade 40 0 20 0 Sky blue 60 20 0 0 Pink 5 40 5 0 Beige color 55150
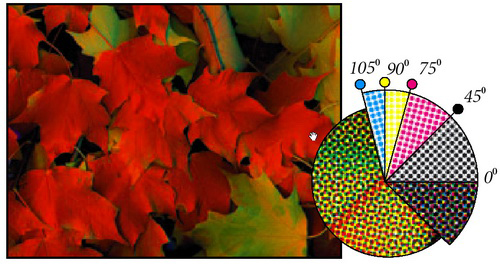
By screening techniques, color images are restored by superimposing overlapping particles ( screen dot ) with 4 colors C, M, Y, K in 4 different angles.
III. HSB model ( Hue, Saturation, Brightness )
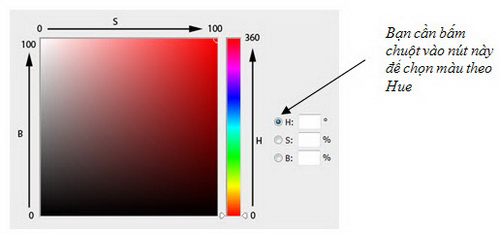
a. Hue (color) : Normally, color is the name of the color. For example: red, orange, green . Different colors are represented in colored circles and are valued at 0 o to 360 o .
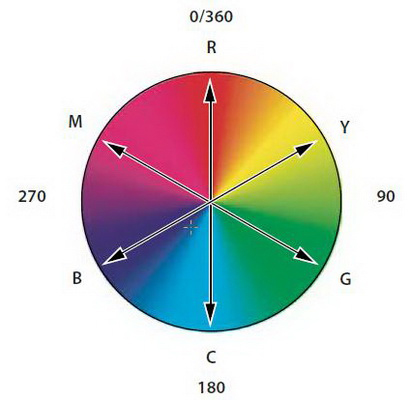
Color circle
People can also perform Hue in the 3-dimensional model below:
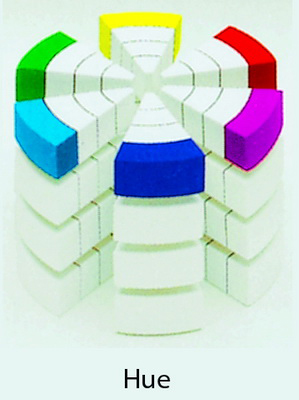
In Photoshop, to select a color, click on the Foreground color or Background color icon.
Then, the Color Picker dialog box will appear:
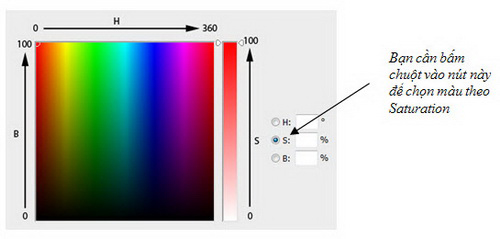
b. Saturation : The color saturation represents the purity of the color. When there is high saturation, the color will be clean and bright. When there is low saturation, the color will be cloudy and dull. Saturation varies from 0% (gray) to 100%.

On the color circle, the color saturation increases gradually from the center to the circumference
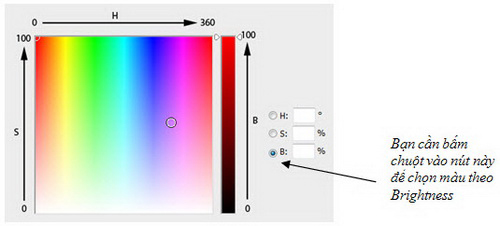
c. Brightness : The brightness of a color describes how bright or dark it is. Brightness varies from 0% to 100%.

In the 3D model, the brightness gradually increases from the bottom to the top
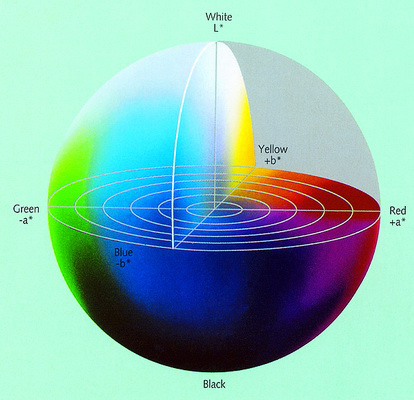
IV. CIE Lab model
The CIE L * a * b * model is built on the ability of the human eye to perceive color. Lab values describe all the colors that an ordinary person's eyes can see. Lab is considered an independent color model for the device and is often used as a reference base when converting a color from one color space to another.
According to the Lab model, all colors with the same brightness will be on the same plane with a circle shape in the two axes a * and b *. The color with a value of a * positive is red, the color has a negative value. Similar to positive b *, yellow and b * negative are blue. The brightness of the color changes along the vertical axis.
V. Why colors are not the same
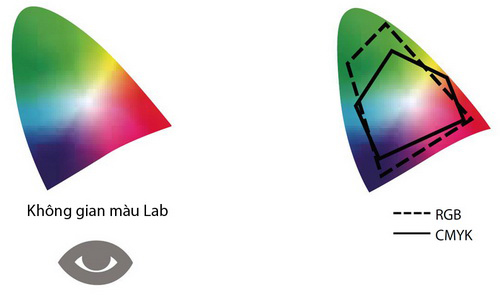
There is no device in the printing system that can recover the entire spectrum of colors visible to the human eye. Each device operates in a finite color space. CIE Lab models have a fixed color space because they are built on the ability of the human eye to perceive color. Lab model is independent of the device. The remaining models such as RGB, CMYK, HSB may have many different color spaces and depend on the device.
Due to the different color spaces, the color of the documents shown on different devices will not be the same. Differences in color may arise due to images created from various sources (from scanners, digital cameras .); Graphics software defines different colors; different printing materials (newsprint with a smaller color space than couché paper); and due to equipment manufactured from different manufacturers; Different device life .
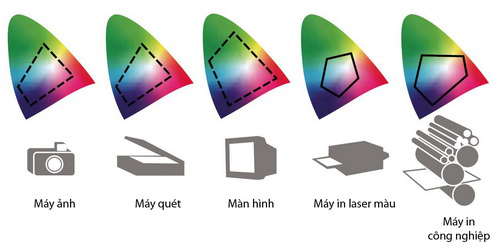
Different devices have different color spaces
( Also )
NGUYEN KHOA CAT teacher
Khai Thien Company Limited (KTC Co., Ltd) - Training center
 Flash - Simulates the Windows boot process
Flash - Simulates the Windows boot process Adobe Systems released Photoshop Elements 8
Adobe Systems released Photoshop Elements 8 Flash - Simulation of Windows boot process (P2)
Flash - Simulation of Windows boot process (P2) Flash - Simulating the windows startup process (P3)
Flash - Simulating the windows startup process (P3) Flash - 5 OLYMPIC rings
Flash - 5 OLYMPIC rings Flash - Water drop effect
Flash - Water drop effect