Overview of security deployment for iPhone and iPad
QuanTriMang - iOS, the operating system for iPhone and iPad, is built on a security platform. This will help iPhone and iPad access secure services of businesses as well as the ability to protect important data. iOS provides strong encryption when transferring data, there are methods of authentication when accessing services as well as hardware encryption for all remaining data is safe. The operating system also provides secure protection by using policy passcodes that can be used at any time. Besides, if the device accidentally falls into the wrong hands, users or IT staff can completely create commands to remotely delete all personal information on the machine.
>>> Deploying, iPhone applications in business model - part 1

When considering using iOS operating system in an enterprise environment, you should know the following:
- Device security : Provide methods to prevent unauthorized use of equipment
- Data security : Continuous data protection, even if the device is lost or stolen
- Network security : Network protocol and data encryption when transmitting
- Application security : Security platform for iOS
These features work together to provide a mobile security platform.
Device security
Setting up strong policies to access iPhone and iPad is very important to protect information on the device. The password for the device will be the first 'defense' against unauthorized access and can be configured and set up very quickly. The device running the iOS operating system uses a unique password (created by the user) so that it can create a strong encryption key that helps protect email and other important data on the device. In addition, iOS also provides security methods to configure the device for enterprise environments to use. These methods provide a lot of flexible options to set up a standard security layer, which helps protect legitimate users.
Policy Passcode
Password protection devices can prevent users from invalid, making them unable to access data or gain access to the device. IOS allows users to choose from a set of passcode to meet security needs, including waiting time, strength of the password as well as the time to change the password.
The following passcode types are supported by iOS:
- Request passcode on device
- Allow simple values
- Requires values including letters and numbers
- The shortest length for the passcode
- Minimum number of special characters
- The shortest life span for a passcode
- Time before automatic lock
- Passcode record
- Time extension when locking the device
- Maximum number of failed login attempts
Compliance Policy
The policies listed above can be set up on iPhone and iPad devices in different ways. They are provided as part of the Configuration Profile for users to install. A profile can be set up so that deleting profiles can only be done when an admin password is available, or users can set a profile so that it stays attached to their device and can only be removed when the entire device is deleted. suffered. In addition, you can also remotely configure passcode settings using the Mobile Device Managemen t (MDM) solution to 'impose' policies directly to the device. This helps set up and update policies without user interaction. Additionally, if the device is configured to access Microsoft Exchange and Microsoft Exchange ActiveSync accounts, it will be set up quickly. Remember that policy collection is more or less dependent on the version of Exchange (2003, 2007 or 2010). Refer to Exchange ActiveSync and iOS devices for specific configuration for your device.
Security configuration for the device
The configuration profile is an XML file, containing VPN configuration information, restrictions, device security policies, Wifi settings, email, calendar accounts, and confirmation information that allows iPhone and iPad to work in the environment. business school. The ability to set up a policy passcode along with the settings in the Configuration Profile ensures that the device used in the enterprise environment is configured correctly and meets the security standards set by the company. In addition, because the Configuration Profile can be encrypted and locked, settings cannot be removed, replaced or shared with others.
The Configuration Profile can be managed by signing and encryption. Signing a Configuration Profile helps ensure that the installed settings will not be replaced. The Configuration Profile encryption will protect the content within the profile and only allow installation on the device that created it. Configuration Profile is encrypted using CMS encryption algorithm (Cryptographic Message Syntax, RFC 3852), support for 3DES and AES 128. For the first time use a encrypted Configuration Profile, users can install it via USB or via Over-the-Air Enrollment.

Limited on the device
Restrictions on devices will determine which features users can access on the device. Basically, they relate to 'related' applications to networks, such as Safari, YouTube or iTunes Music Store. However, restrictions also have the ability to manage the functions of the phone, such as installing applications or using cameras. They not only help you configure the device to suit your requirements, but also allow users to optimize the device in a variety of ways. Users can manually configure restrictions on each device, forcing to use the Configuration Profile or remotely setting up with the MDM solution. In addition, it is similar to policy passcode, restricting web browsers or cameras to be implemented quickly via Microsoft Exchange Server 2007 and 2010.
In addition to policy settings and restrictions on devices, IT staff can also configure and manage iTunes applications. These configurations include the ability to disable access to content, determine which network services users can access to iTunes and determine whether the software has new updates.
Data security
Data protection on iPhone and iPad devices is important in any environment. In addition to encrypting data when transmitting, iPhone and iPad are capable of encrypting the hardware for all data it contains and the ability to encrypt email and application data and protect data.
If the device is stolen or lost, it is important to delete and stop it. Users should also set a policy to delete the device after a number of unsuccessful logins - a key element against unauthorized access.
Encode
iPhone and iPad provide hardware-based encryption. Hardware encryption uses 256-bit AES encryption algorithm to protect all data on the device. This feature is always enabled and users cannot turn it off.
In addition, the data on iTunes backed up on the user's computer will also be encrypted. Users can enable this feature on their own or set up using limited settings in Configuration Profiles.

iOS supports S / MIME in mail, enabling iPhone and iPad to open and send encrypted email messages. Users can also apply restrictions to prevent forwarding email or recipients who move email between multiple accounts.
Data protection
Built on the hardware encryption capabilities of the iPad and iPhone, email messages and attachments saved on the device will be more secure thanks to the data protection feature included in iOS. Data protection also affects device passcode when working with hardware encryption on iPhone and iPad to help create strong encryption key. This key will prevent data from being accessed when locking the device, ensuring that important information is always safe in all cases.
To enable data protection, simply create a passcode on the device. The effectiveness of data encryption depends on a strong passcode. So, IT staff needs to ask and force users to create a strong passcode instead of setting up a common passcode. Users can confirm whether the data protection feature has been activated by viewing the passcode settings screen. The Mobile Device Management solution also has the ability to query the device for this information.
Delete remote
iOS supports remote wipe. If you lose your phone or tablet, the admin or device owner can perform a remote wipe to remove all data and disable the device. If the iPhone / iPad is configured with an Exchange account, admin staff can create remote wipe commands using the Exchange Management Console (Exchange Server 2007) or Exchange ActiveSync Mobile Administration Web Tool (Exchange Server 2003/2007) . Exchange Server 2007 users can also create remote delete commands directly from Outlook Web Access . Remote delete commands can also be performed using the MDM solution even if no Exchange service is used.
Local deletion
The devices can also be configured to automatically create local deleting commands after a few failed attempts to enter the passcode. This will help protect the device if a hacker uses a brute force attack to gain access to the device. When the passcode is set, the user is able to activate local deletion directly in the settings. By default, iOS will automatically delete the device after 10 failed attempts. For other policy passcode, the maximum number of failures can be set via Configuration Profile, set by MDM server or via Microsoft Exchange ActiveSync policy.
icloud
iCloud stores music, photos, calendar, data and other information, automatically transferring them to all users' devices. iCloud can also back up information, including device settings, application data, SMS / MMS messages via Wi-Fi networks. iCloud protects content on the phone by encrypting it when sent over the Internet, storing it in encrypted format and using a secure token to confirm. In addition, iCloud features, including Photo Stream , Document Sync and Backup , can be disabled via the Configuration Profile .

Network Security
Mobile users need access to the corporate network anywhere in the world. Therefore, it is very important to validate the user and the protected data is transmitted. iOS provides advanced technologies to meet such needs for both Wi-Fi networks.
In addition to the current infrastructure, every FaceTime and iMessage sessions are encrypted. iOS creates a unique ID for each user, ensuring that communications and communications are always encrypted, transmitted and correctly connected.
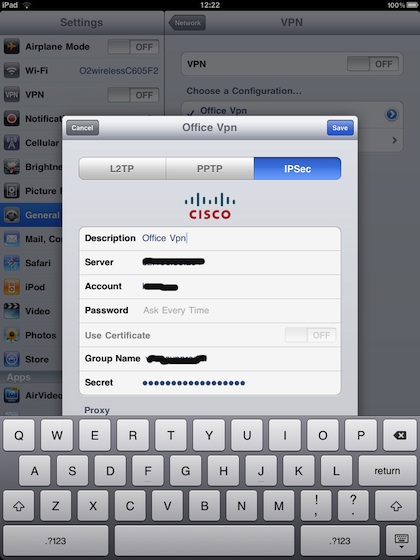
VPN
Many businesses use virtual private networks (VPNs). These network protection services have been deployed and require minimal installation and configuration to work with iPhones and iPads.
Besides, iOS integrates with many popular VPN technologies today through support for Cisco IPSec, L2TP and PPTP. It also supports SSL VPN through applications such as Juniper, Cisco, and F5 Networks. Supporting these protocols will help ensure IP-based encryption is always at the highest level when transmitting important information.
In addition to supporting secure access to the existing VPN environment, iOS also provides methods to authenticate users. In addition, the iOS authorization certificate takes advantage of VPN On Demand, making VPN validation easier while securing secure access to network services. For enterprise environments that require two-factor token validation, iOS integrates with RSA SecurID and CRYPTOCard.
SSL / TLS
iOS supports SSL v3 as well as Transport Layer Security (TLS v1.0, 1.1 and 1.2), the new security standard for the Internet. Safari, Calendar, Mail and other Internet applications will automatically start these mechanisms to enable encrypted communication channels between iOS and business services.
WPA / WPA2
iOS supports WPA2 Enterprise to provide access to the corporate network (verified access). WPA2 Enterprise uses 128-bit AES encryption, providing users with the highest level of security and ensuring that data is protected when sent and received over Wi-Fi networks. In addition, with 802.1X support, iPhone and iPad can integrate with many different RADIUS validation environments.
Application security
iOS is designed with a central core of security. It includes a 'sandboxed' method to protect running applications and requires application signatures to ensure that they are not tampered with. iOS also has a security framework that securely stores network applications and services in an encrypted key. For developers, it provides common encryption features that can be used to encrypt application data warehouses.
Protection in real time
Applications in the device will be quarantined so that they cannot access data stored by other applications. In addition, the file system, source and kernel will be protected from the user's application space. If an application needs to access other application's data, it can only be done using the API and the services provided by iOS. Creating code is also not supported.
Required to sign code
All iOS apps will have to sign. Applications provided with the device will be signed by Apple. The 3rd party applications are signed by the vendor using a confirmation issued by Apple. This helps ensure that the application is not replaced or falsified. Not only that, check the run time created to make sure that the application is always reliable.
The use of custom applications or internal applications is managed with a provisioning profile . Users need to install the provisioning profile to run the application. Provisioning profile can be set up or canceled very quickly using the MDM solution. The admin staff also has the ability to restrict the use of an application for a specific device type.
Security confirmation framework
iOS provides a series of secure encryption keys (keychain) to store digital information, user names and passwords. Keychain data is partitioned so that 3rd party application information cannot be accessed by other applications. This provides confirmation of protection on iPhone and iPad for various applications and services within the enterprise environment.
Popular coding method
Software developers have access to APIs encryption so they can use to protect their data. Data can be encrypted using popular proven methods such as AES, RC4 or 3DES. In addition, the iPhone and iPad also provide hardware acceleration capabilities, optimizing performance for the application.
Application data protection
Applications can also take advantage of the built-in encryption feature of the iPhone and iPad hardware to protect critical application data. Developers can choose a number of files to protect the data, instructing the system to encrypt the file contents. After that, the contents of the file will not be accessible by both the application and the unauthorized intruder when the device is locked.
Application has been managed
Server MDM can manage 3rd party applications of App Store as well as enterprise applications. Specifying a managed application will help the server determine whether the application and its data can be removed from the device by an MDM server. In addition, this server also helps prevent data of managed applications from being backed up to iTunes and iCloud. This allows IT staff to manage applications that contain important business information more easily than the user application directly down.
To be able to install a managed application, the MDM server sends an installation command to the device. This application will require users to accept them before they are installed.
Revolutionary device comes with security
iPhone and iPad provide methods to encrypt data when transmitted, when stored on the device and when backing up to iCloud or iTunes. Whether users access corporate email, visit a personal website or confirm to log in to the corporate network, iOS ensures that only valid people can access important company information. . Besides, with enterprise network support and methods to prevent data loss, users can use devices running iOS operating system with certain confidence that their device is safe and data always protected.