Everything you need to know about using Nala on Ubuntu
Advanced Package Tool (APT) is everyone's favorite package management tool when working on Debian-based distributions. However, despite the rich feature set, this is not a convenient way to manage packages for beginners.
One major drawback of APT is that it makes the content on your terminal screen look cluttered and there should be similarity in the text on your Linux terminal.
This is where Nala, with its streamlined containers and multicolored boundaries to make your terminal output look cleaner and better structured, comes into play. Here's what you should know about Nala.
What's special about Nala?
The question is, what is Nala and is it worthy of replacing APT? Nala is an open source, Python-based front-end replacement for APT. It performs various functions: Parallel download, package update and upgrade, history fetch, autofetch mirror repository and restore installation.
Without going into the benefits at this stage, explore Nala's settings, followed by the features and changes it brings in your terminal window.
Install Nala on Ubuntu
There are several ways to install Nala on Ubuntu/Debian:
- Install from official repositories
- Add Custom Repository
- Install the Nala DEB . package
On Ubuntu 22.04 and later, you can install Nala using any of the above methods. However, you need to work with Nala's custom repositories for older versions.
1. Install Nala from the official Ubuntu repositories
First, you have to update the package list on Ubuntu using apt update command as follows:
sudo apt updateThere is a difference between the apt update and upgrade commands, so it's best to use the update command in the first place.
Next, install Nala by running:
sudo apt install nala2. Add Nala Repository on Old Ubuntu Versions
If you are using an older version of Ubuntu, you can still successfully install and use Nala by installing via a third-party repository. First step, go to and add the Volian Scar repository to install Nala on Ubuntu:
echo "deb [arch=amd64,arm64,armhf] http://deb.volian.org/volian/ scar main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/volian-archive-scar-unstable.listYou can get the GPG verification key with the wget command:
wget -qO - https://deb.volian.org/volian/scar.key | sudo tee /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/volian-archive-scar-unstable.gpg > /dev/nullIf you are using this step to install Nala on Ubuntu 22.04 or later, execute the command below to install Nala:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install nala -yOn older versions, to install a legacy version of Nala, execute the following command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install nala-legacy -y3. Install via DEB . package
The last way is to install Nala through its DEB package. Here's how to download and install the package on your system:
1. Go to the download page and download the latest DEB package available.

2, After downloading the package, open the Downloads folder on the machine. Locate the DEB package and right click on it.
3. Click Open With GDebi Package Installer

4. In the following dialog box, select the Install Package option . Enter the root password in the prompt and let the installation complete.
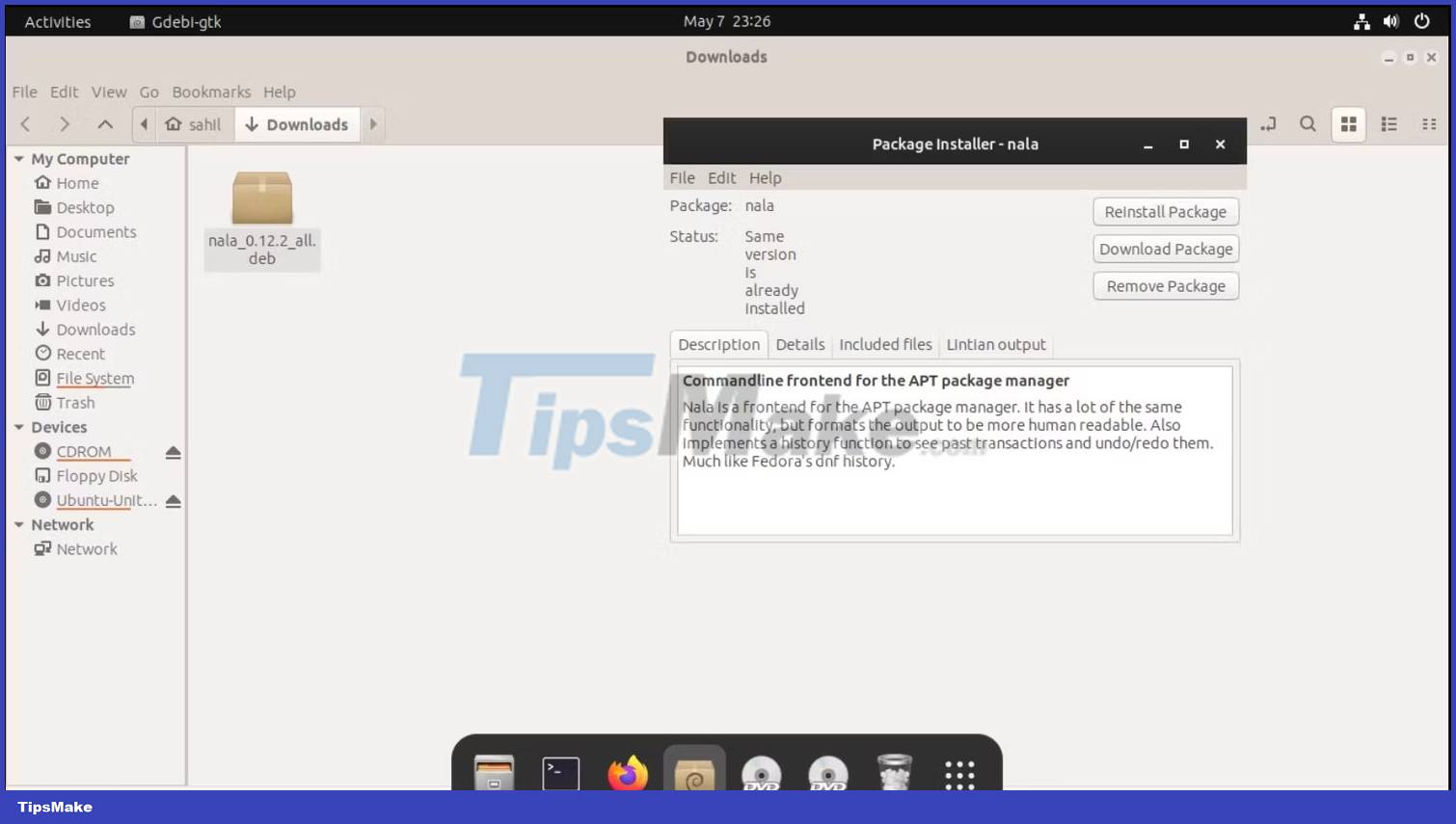
Alternatively, you can install the DEB package using dpkg as follows:
sudo dpkg -i packagenameTo verify the installation, update and upgrade the system's packages with the nala command:
sudo nala update && sudo nala upgrade -yIf the command executes successfully, you can be sure that Nala is ready to use on your machine.
Compare 2 package managers APT and Nala
Since Nala is up and running, compare the output of APT with the output of this Python-based package manager.
Update and upgrade existing packages using APT:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y 
If you look at the output after executing the apt command, you will notice a lot of text on your screen, some of which may not even make sense to you.
Also, there are lots of updates, package names, pending and completed installations, along with other details.
Then this time run update/upgrade commands with Nala, like below:
sudo nala update && sudo nala upgrade -y 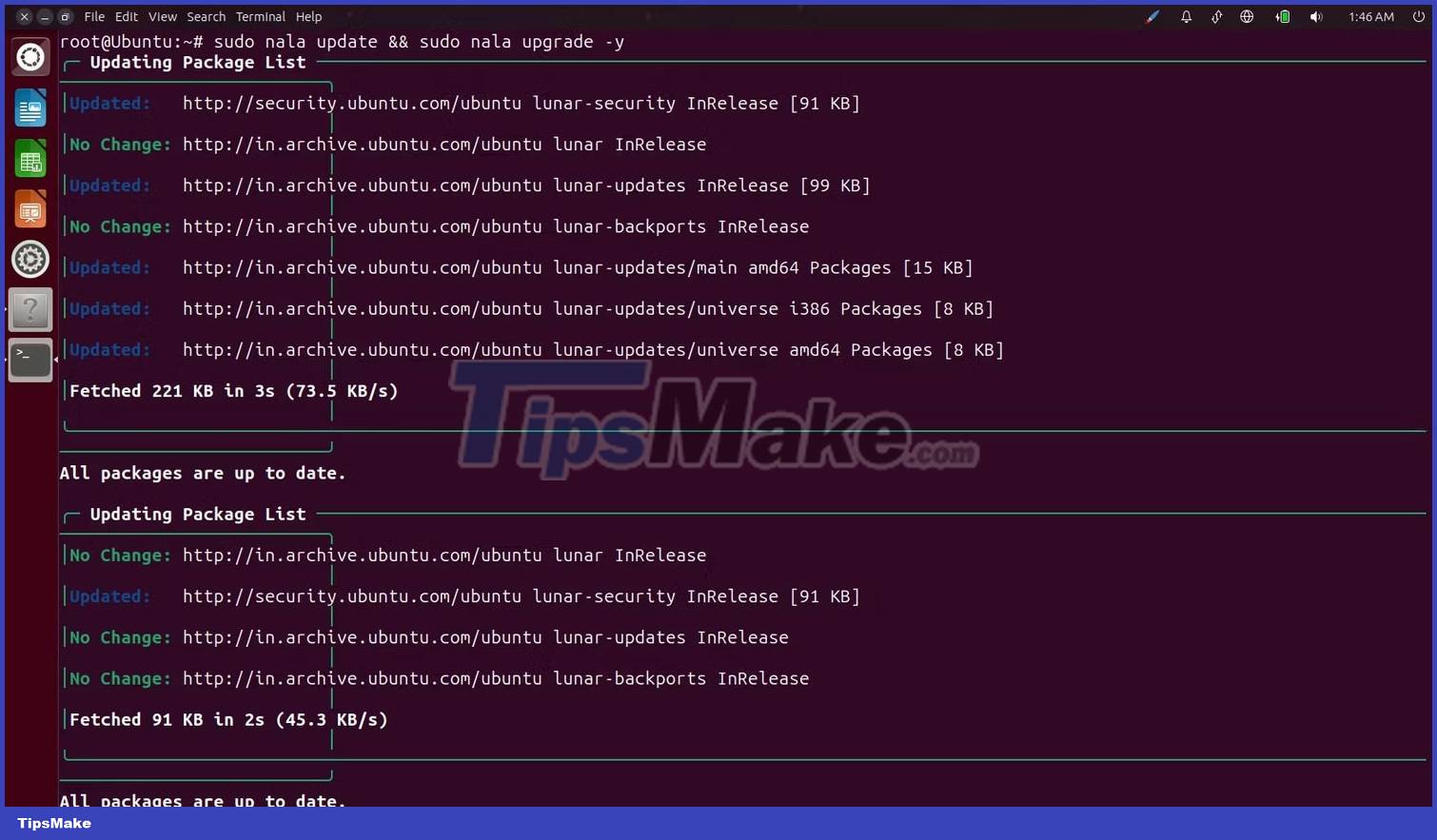
If you look at the text on your screen after executing the command, you'll notice how structured everything looks. Nala creates well-structured containers for each updated component and provides a status bar that shows how much time is left to install.
deb-get is another third-party package manager for Debian users, which you can use in place of dpkg for best results.
How to use Nala on Ubuntu/Debian
Using Nala on Ubuntu/Debian or their related Linux distributions is easy. You can use this UI package manager to update, upgrade and even install software.
Here's how you can use Nala in your usual activities:
1. Update/upgrade package
Like APT, you can use Nala to update and upgrade your system packages. Use the following commands to do so:
sudo nala update sudo nala upgrade To perform both tasks together, use the && operator:
sudo nala update && sudo nala upgrade2. List available packages
If you use dpkg --list or apt list to list the packages available on your Ubuntu/Debian distribution, you can replace the command with Nala:
nala listOnce done, you'll see a well-structured list of all the apps available for download. However, this command takes up a lot of screen space, making it difficult to scroll around.
In such a case, you can combine the list command with the less command as follows:
nala list | less 
To display a list of your installed applications, you can use the -i or --installed option:
nala list -iOr:
nala list --installed 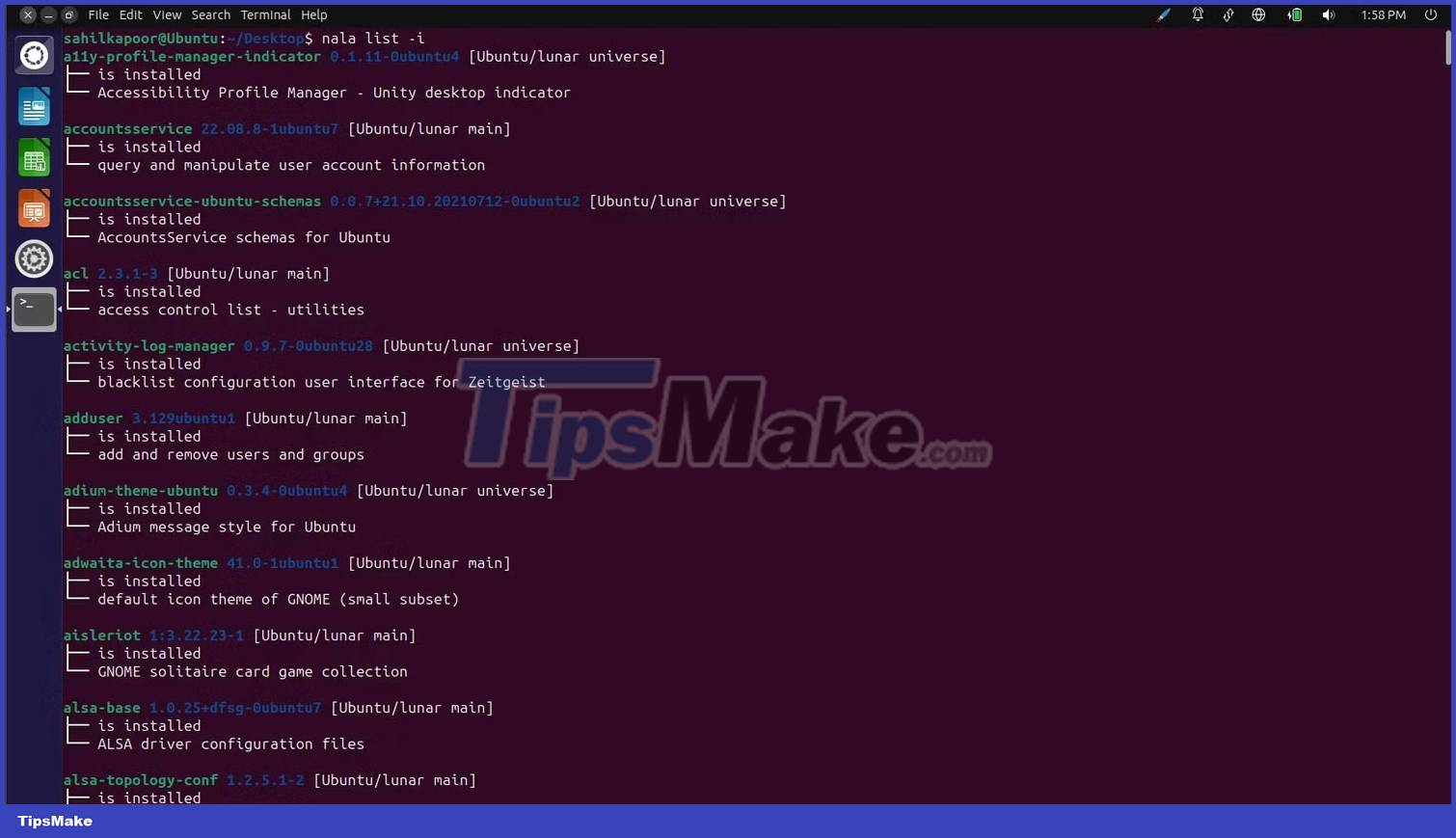
3. Show package details
Who likes to be snooped before installing an application on Linux?
Let's say you want to know some details in advance. In that case, you can use the show command to learn more about a package and other related information, such as its source, structure, and size, among other details.
nala show For example, if you want to know more about the snap package before installing it on Ubuntu, you can use the following command:
nala show snap 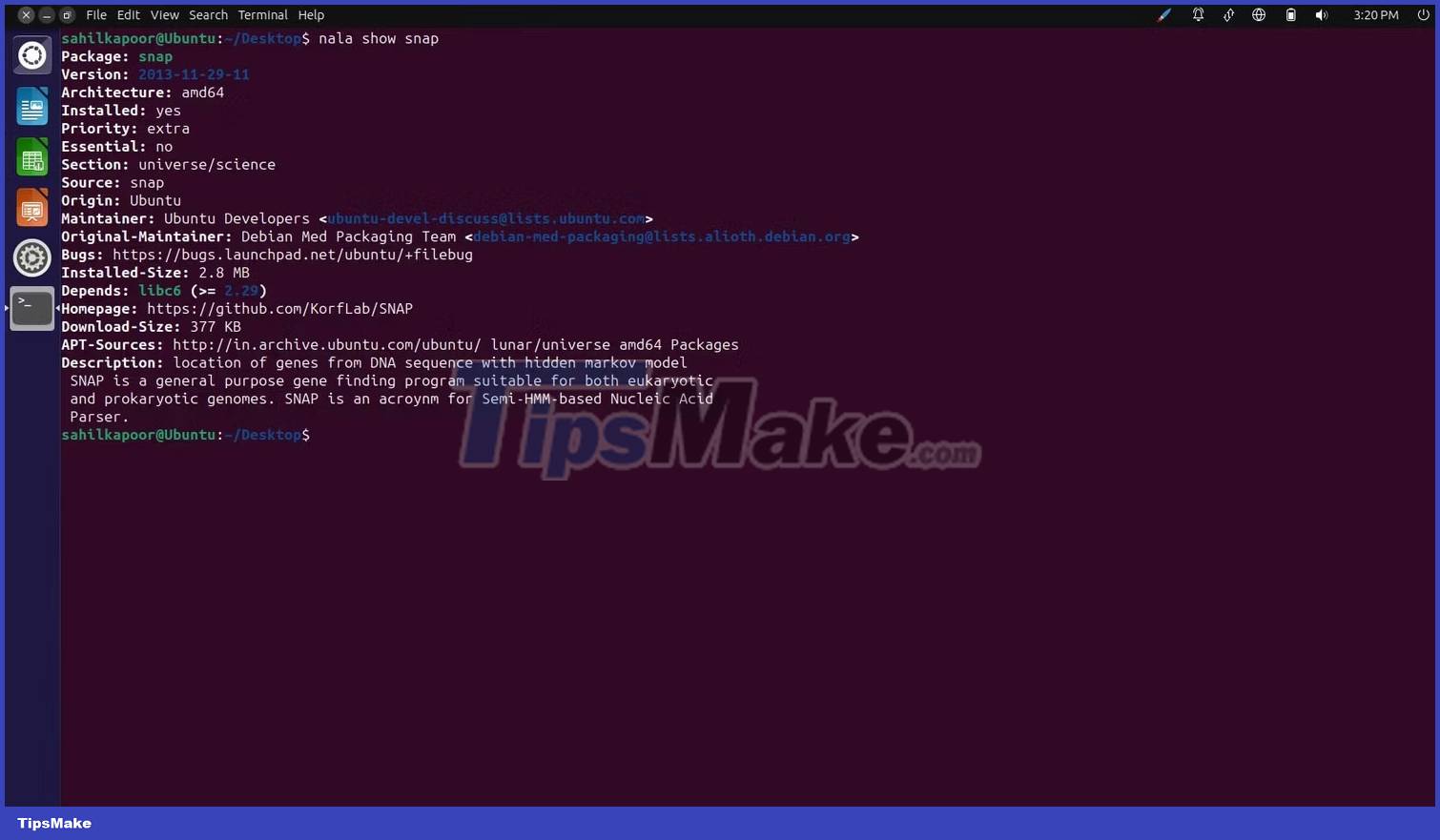
There are several other benefits to using Nala that you can discover by checking out Nala's manual page.
You should read it
- What's new in Ubuntu 18.04 LTS just released?
- How to prolong the life of Ubuntu 18.04 installation with Ubuntu Pro
- What is the difference between Ubuntu Desktop and Ubuntu Server?
- What is Ubuntu? Why should you use Ubuntu to replace Windows?
- Ubuntu 21.04 users need to update the system ASAP
- 5 things to do after upgrading to Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
 Difference between which, whereis and whatis in Linux
Difference between which, whereis and whatis in Linux How to improve gaming performance on Linux
How to improve gaming performance on Linux How to Run a Large Language Model (LLM) on Linux
How to Run a Large Language Model (LLM) on Linux You Don't Need Microsoft Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL): Here's Why!
You Don't Need Microsoft Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL): Here's Why! Ubuntu 23.04 'Lunar Lobster' launches with improved Azure Active Directory and Steam snap
Ubuntu 23.04 'Lunar Lobster' launches with improved Azure Active Directory and Steam snap How to Customize Ubuntu 23.04 to Look Like macOS
How to Customize Ubuntu 23.04 to Look Like macOS