How to Optimize Wi-Fi on Windows Using Preferred Band Settings
Wi-Fi networks typically operate on two frequency bands: 2.4GHz and 5GHz. Here's how to choose between them.
How are 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands different?
The main differences between 2.4GHz and 5GHz Wi-Fi bands lie in range, speed, and interference.
Both bands work well for the average user, but each has its own strengths and limitations. Depending on the situation, switching to a particular band can improve your Wi-Fi performance.
The 2.4GHz band provides wider coverage, better wall and obstacle penetration, making it ideal for maintaining stable connections over longer distances.
The 5GHz band, on the other hand, has a shorter range and is less effective at penetrating walls and obstacles, but is less susceptible to interference. This is because many household appliances, such as microwaves, baby monitors, and cordless phones, operate on the 2.4GHz frequency. This makes it more susceptible to interference, while the 5GHz band is less susceptible to interference due to fewer devices using it.
This means you can generally rely on the 5GHz band to provide a more stable connection, as long as there aren't many walls or obstacles between your router and your device.
The 5GHz band also supports faster data transmission speeds due to less interference. However, the 2.4GHz band is slower due to congestion from other devices.
When should you use 2.4GHz vs 5GHz?
Based on how the bands work, you should choose the 2.4GHz band if you need Wi-Fi to cover a larger area. This is ideal if your device is far away from the router, there are many walls or obstacles between the router and your computer, or you only use the Internet for basic tasks like browsing the web or checking email.
Avoid using the 2.4GHz band if you have other devices nearby that operate on the same frequency, as they may cause interference.
The 5GHz band is better if your device is close to the router with few barriers in between. It allows you to maintain a more stable connection and avoid interference from 2.4GHz devices. This band is also ideal for activities that require faster speeds, like gaming, streaming HD video, or transferring large files.
How to set preferred band in Windows
By default, the network adapter will automatically select the band with the best signal based on your distance from the router and other factors.
However, if you've determined which band suits your needs and the layout of your home or office, you can easily switch to your preferred band on Windows in just a few steps:
- Right-click the Start button and select Device Manager .
- Expand the Network adapters category and locate your network adapter.
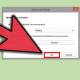
- Right-click on your network adapter and select Properties .
- In the Properties window , go to the Advanced tab .
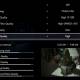
- Look for an option labeled Preferred Band or Band in the Property list.
- In the Value drop-down list , you can see the option is set to No Preference .
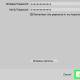
- Select the desired band, 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz , based on your needs, click OK and reboot the device to apply the changes.

Keep your band set to No Preference if you frequently move your laptop between rooms and each band works better in different areas.
No band is perfect for every situation. You should try both bands to find the one that best suits your situation and needs. This will keep you from constantly switching bands. However, when you need faster speeds or a more stable connection, switching to a specific band will give you better performance.
Switching bands can improve both connection stability and speed, but tweaking other Wi-Fi settings is just as important for getting the best performance.
You should read it
- Optimize Windows 10: +24 tips to increase performance (Update 2020)
- 26 Tips optimize Win 10 - Speed up Windows 10 comprehensively
- How to optimize Win 10 to play the smoothest game
- Optimize Windows 10 for maximum performance when operating
- How to optimize RAM to use Chrome on a Laptop
- How to speed up Windows 10, optimize Windows 10 for maximum performance
- How to optimize Windows 11 PC graphics and performance in seconds very simply
- How to free up computer RAM memory, optimize RAM on Win 7/8/10
May be interested
- What is PAI on Mi Band 5? How to use PAI?
 since mi band 5, xiaomi has added a pai body index measurement feature. so what is this index? how to use it?
since mi band 5, xiaomi has added a pai body index measurement feature. so what is this index? how to use it? - How to optimize video game graphics settings
 the following article is a guide for you, if you are worried whether you have made the correct changes to these settings or just wonder why the game runs at less than 30fps when placing the game at ultra preset.
the following article is a guide for you, if you are worried whether you have made the correct changes to these settings or just wonder why the game runs at less than 30fps when placing the game at ultra preset. - How to optimize Win 10 to play the smoothest game
 how to optimize win 10 to play the smoothest game. windows 10 is the preferred operating system for gamers today because of its high security, smooth operation along with support features for gamers such as gaming mode (game mode), screen recording. screen (screen record), live stream (broadcast).
how to optimize win 10 to play the smoothest game. windows 10 is the preferred operating system for gamers today because of its high security, smooth operation along with support features for gamers such as gaming mode (game mode), screen recording. screen (screen record), live stream (broadcast). - 5 Settings to Optimize Storage on Windows
 optimizing storage helps your windows computer run smoother and more efficiently, while making space for important files.
optimizing storage helps your windows computer run smoother and more efficiently, while making space for important files. - Realme Band launched: Color screen, 10-day battery, heart rate monitor, VND 475,000
 despite having many attractive features, realme band has a retail price of less than 500,000 vnd, which is a formidable competitor to xiaomi's mi band 4.
despite having many attractive features, realme band has a retail price of less than 500,000 vnd, which is a formidable competitor to xiaomi's mi band 4. - Realme Band: 10-day battery life, no-charge battery charger
 the realme band is equipped with a 0.96-inch screen with a resolution of 160x80 pixels, capable of displaying about 64 letters and supports touch operations.
the realme band is equipped with a 0.96-inch screen with a resolution of 160x80 pixels, capable of displaying about 64 letters and supports touch operations. - How to Optimize Windows 8
 one of the best methods to improve the performance of your pc is to optimize the drive. windows 8 has features that allow you to optimize the drives in pcs. the system automatically determines the best optimization for you. the...
one of the best methods to improve the performance of your pc is to optimize the drive. windows 8 has features that allow you to optimize the drives in pcs. the system automatically determines the best optimization for you. the... - How to fix Mi Band 4 error when the battery is low
 how to fix mi band 4 error when the battery is low. because of its large and colored screen, the mi band 4 has problems with its battery when first connected and used. in this article, the software tips will guide you on how to fix mi band 4 error when the battery drops quickly when used.
how to fix mi band 4 error when the battery is low. because of its large and colored screen, the mi band 4 has problems with its battery when first connected and used. in this article, the software tips will guide you on how to fix mi band 4 error when the battery drops quickly when used. - How to Check WiFi Band on iPhone
 are you wondering whether your iphone is connected to a router with a 2.4ghz or 5ghz band? although the iphone does not have a built-in feature to determine the network connection band, you can still apply some simple ways to determine the ghz number of the router in your home. this article will help you know how to check the wi-fi band on iphone and a simple way to connect to the band you want.
are you wondering whether your iphone is connected to a router with a 2.4ghz or 5ghz band? although the iphone does not have a built-in feature to determine the network connection band, you can still apply some simple ways to determine the ghz number of the router in your home. this article will help you know how to check the wi-fi band on iphone and a simple way to connect to the band you want. - Review Honor Band 6 Smart Watch
 the honor band 6 is not a smartwatch, although at this point the gap between wearables isn't really clear anymore.
the honor band 6 is not a smartwatch, although at this point the gap between wearables isn't really clear anymore.






 7 must-have features on a WiFi router
7 must-have features on a WiFi router 4 Wi-Fi Router Features for the Best Performance
4 Wi-Fi Router Features for the Best Performance What is Mesh WiFi? How does Mesh WiFi work?
What is Mesh WiFi? How does Mesh WiFi work? 5 best WiFi routers in 2024
5 best WiFi routers in 2024 Users may have to upgrade to Windows 11 24H2 to use Wi-Fi 7
Users may have to upgrade to Windows 11 24H2 to use Wi-Fi 7 How to block wifi users, see who is using temple wifi and disconnect
How to block wifi users, see who is using temple wifi and disconnect