4 Wi-Fi Router Features for the Best Performance
1. Wi-Fi Band
There are three Wi-Fi bands: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz. The Wi-Fi band you use has an impact on your network speed. The second fastest of the three is 5.0 GHz. The benefit of this frequency is that it is twice as fast as the 2.4 GHz band. If you are using a lot of resource-intensive programs, this frequency is best. The problem is that 5.0 GHz does not travel well. If you have a large home and only have one access point, it is possible that the Wi-Fi signal will not reach the farthest corners of your home. If this is the case, you may want to switch to 2.4 GHz.
There are three Wi-Fi bands: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz. The Wi-Fi band you use affects your network speed and range.
- 2.4 GHz is the slowest band but has the best range
- 5 GHz is twice as fast as 2.4 GHz, but its range is significantly reduced
- 6 GHz has similar range to 5 GHz, but is almost twice as fast
If you're using data-hungry programs or services, it's best to use the 5 GHz Wi-Fi band. However, if your device is further away from the router, you'll need to use the 2.4 GHz band to ensure a good connection.
The latest Wi-Fi frequency is 6 GHz. This frequency offers twice the number of gigabits per second as the 5.0 GHz band. However, while most routers allow users to choose between 2.4 and 5.0 GHz, only the newest routers offer 6 GHz.
2. Quality of Service (QoS)
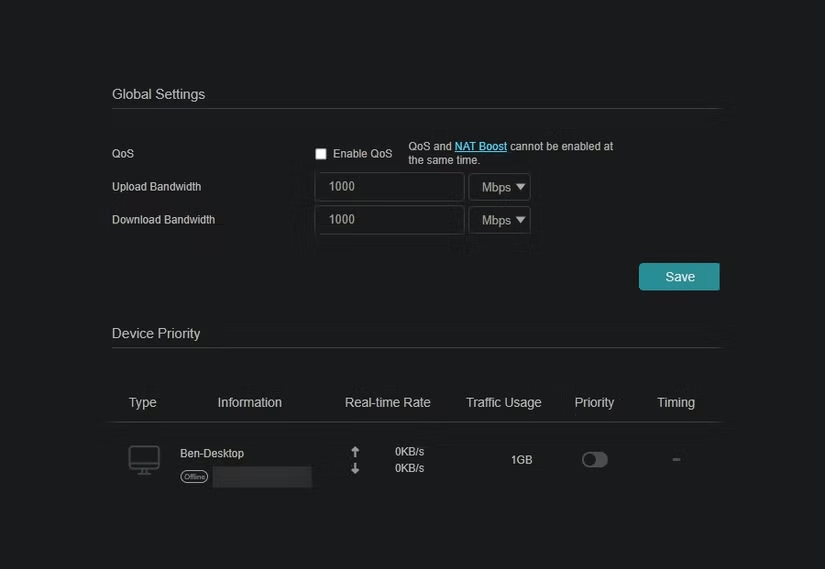
What if you could prioritize data sent to certain devices? For example, let's say whenever you stream a movie on your Roku TV, it experiences a lot of interference. If that's the case, you can go into your router settings and configure the QoS settings to prioritize traffic sent to your Roku TV.
The home is like a small office, with many devices using resources at the same time. This can cause traffic to spike, similar to peak hours. Prioritizing certain devices over others is like line cutting, ensuring that one device's needs are met before another's.
3. Wi-Fi Channel
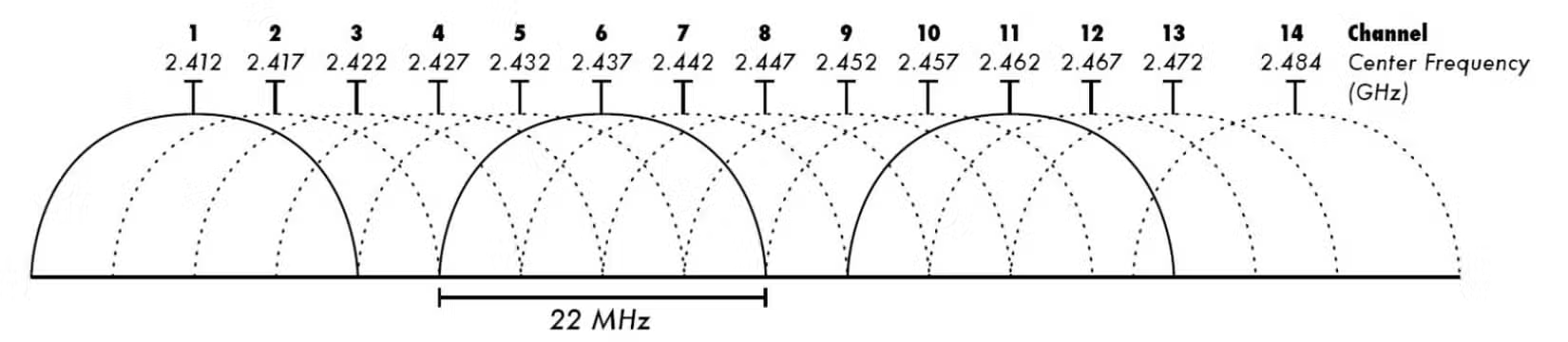
A Wi-Fi channel is the frequency band on which a router transmits its signal. The 2.4 GHz band uses 14 channels, the 5.0 GHz band has 34 channels, and the 6.0 GHz band has 59 channels. Routers transmit their signals using radio waves, just like radio stations. However, routers must use different channels, otherwise they can cause interference.
The same thing happens with Wi-Fi when you're surrounded by other routers using the same channel you're using. If you live in an apartment building or a crowded residential area, you may be sharing a congested channel. To find a less congested channel, use a tool like a Wi-Fi analyzer.
4. Update your router's firmware
Updating the apps and operating systems on your smartphones, computers, laptops, etc. is a given. But when was the last time you updated your router's firmware? Firmware is a type of software that interacts with hardware and allows the hardware to communicate with the software.
Your router should automatically check for and run firmware updates. If it doesn't, you'll need to check for and run updates manually. Firmware updates aren't as common as app updates. Make sure to check for firmware updates every 6 months or so. If your device needs a software update, it's either because it has a vulnerability or bug that needs to be fixed, or because performance can be improved. Regardless of the reason, if you receive a notification about a software update, you should accept it.
While these are all technical tweaks, perhaps the easiest and most effective change is to move your router closer to your devices. Given how much time we spend online, slow connections can be a pain, but using these features to speed up your home internet can make a big difference!
 What is Mesh WiFi? How does Mesh WiFi work?
What is Mesh WiFi? How does Mesh WiFi work? 5 best WiFi routers in 2024
5 best WiFi routers in 2024 Users may have to upgrade to Windows 11 24H2 to use Wi-Fi 7
Users may have to upgrade to Windows 11 24H2 to use Wi-Fi 7 How to block wifi users, see who is using temple wifi and disconnect
How to block wifi users, see who is using temple wifi and disconnect 12 How to change Wifi password, change Wifi Pass on computer and phone
12 How to change Wifi password, change Wifi Pass on computer and phone How to get the wifi password next door is extremely simple
How to get the wifi password next door is extremely simple