How to Open Apps as Root on Mac
On the admin account

Know about risks. Most graphical applications are not designed with high-level access in mind. Limit yourself to specific tasks you understand well, otherwise you'll leave data inaccessible, applications crashing, or open security vulnerabilities.
Open Terminal. Log in to your administrator account on the computer. Go to Applications → Utilities and launch Terminal.
The administrator account must have a non-empty password, otherwise Terminal will not allow you root access.

Try a faster way. The sudo command allows us to launch applications with root access, but this requires a path to the executable file in the application package. Most Mac apps, along with many third-party programs, have a similar way of organizing their content in packages, so you should try this:
Type sudo " file path from hard drive to application .app/Contents/MacOS/ application name ".
For example, to open iTunes, you type sudo "/Applications/iTunes.app/Contents/MacOS/iTunes" and press ⏎ Return.
Enter the administrator account password that you usually log in to. Press ⏎ Return.
If the command works, the app will open with root access. If Terminal says "command not found", continue to the next step.

Open the contents of the application package. If quick opening doesn't work, search for the app in Finder. Right-click (or tap Controland click) on the application icon and select Show Package Contents from the drop-down menu.
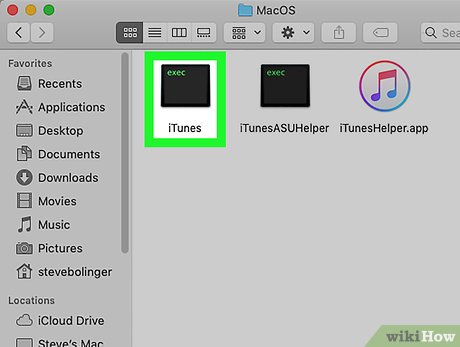
Find the executable file. You will see one or more folders inside the application. Look for the executable file in the directory. This file is usually located in the /Contents/MacOS path.
The executable file usually has the same name as the application, but can also have a different name, such as "run.sh."
Executable files usually have a black square icon with a small "exec" inside.

Enter the sudo command into Terminal. Type sudo followed by a space. Don't enter right away.

Drag the executable file and drop it into the Terminal command line. The path to the executable file will be inserted automatically.
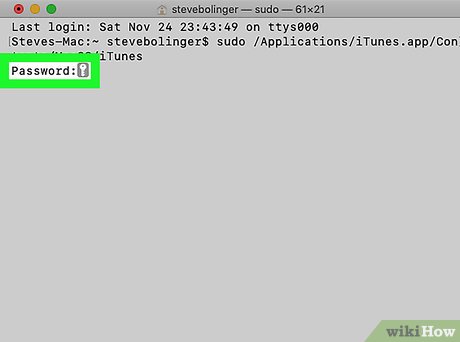
Confirm command with password. Press ⏎ Return. Enter the administrator account password you used to log in, click ⏎ Returnagain. The application will launch with advanced access.
On a non-admin account
Open Terminal with a non-admin account. Many administrators prefer to work on regular user accounts to limit the possibility of errors or malware attacks. This method still requires an administrator password, but allows you to gain temporary super access without switching accounts. To get started, open a Terminal window.
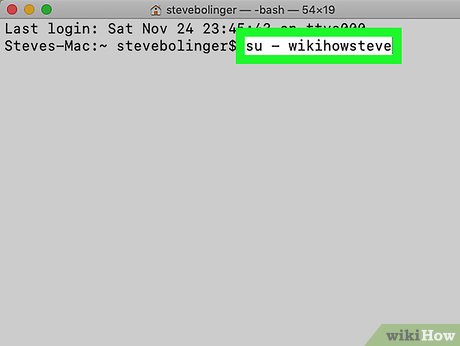
Switch to administrator rights on Terminal. Enter the command su - followed by a space and the computer's administrator account username. Enter the password of this administrator account. So you will act as that user.
Hyphens in commands are optional, but recommended. It sets the environment and directory variables for this admin user and will limit the possibility of accidentally causing errors.
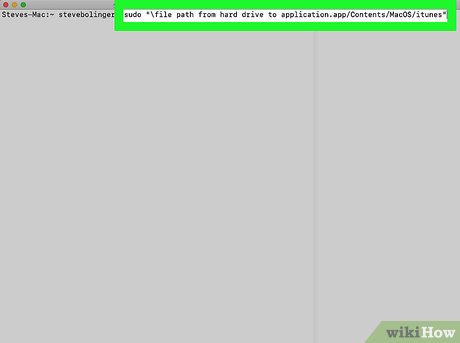
Open the application using the sudo command. The most common way to do this is to type sudo " file path from hard drive to application .app/Contents/MacOS/ application name ". If this doesn't work, or you need more guidance, see the instructions for using an administrator account above.
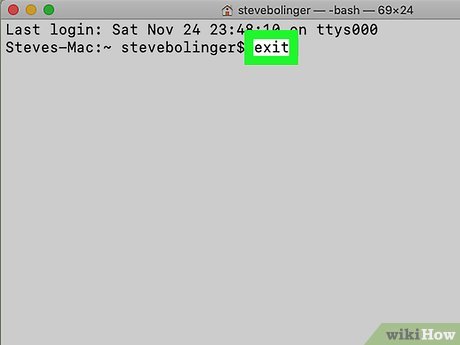
Return to your account. After you complete the tasks that require root access, enter exit on Terminal. This command will exit the administrator account and return to your regular account.
Resovle problem
Disable System Integrity Protection (SIP). This feature (introduced in Mac OS 10.11 El Capitan) will limit access to important data even for advanced users. If you can't make the changes you want, disable SIP. Note that the risks for this method are very high. You should only apply this if you feel confident in your abilities and remember that if an error occurs, the computer will be wiped clean, or even unable to function:
Restart the computer. Hold down ⌘ Command+ Rafter you hear the startup sound to access Recovery Mode.
Select Utilities from the top menu, then Terminal.
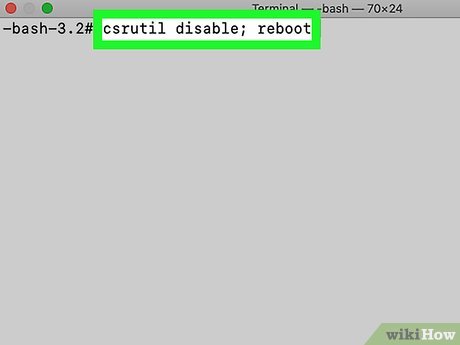
Type csrutil disable; reboot into Terminal.
Let the computer restart as usual. Now you can apply the above steps to open any application with root permissions. Once completed, consider re-executing these instructions with the enable command instead of disable to restore SIP.
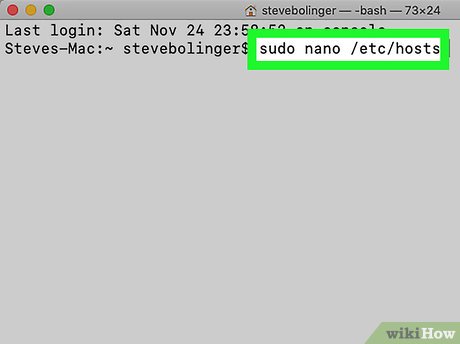
Use nano instead of a graphical text editor. This option will be more secure and reliable in editing configuration files with a text editor right on Terminal. Nano is the simple option available by default. To use this feature with root access, simply type sudo nano, followed by a space and the path to the text document. You can then edit documents right in Terminal. When finished editing, press Control+ Oto save and then press Control+ Xto exit nano.
For example, the command sudo nano /etc/hosts will open the hosts file with root access.
You should create a backup before editing any configuration files. To do this, enter sudo cp filepath_of_config_file new_filepath of backup . For example, the command sudo cp /etc/hosts /etc/hosts.backup will create a backup of the hosts file with the name hosts.backup. If you make a mistake, you can move the misconfigured file with the command sudo mv /etc/hosts /etc/hosts.bad (for example with the hosts.backup file) and restore the backup with the command sudo cp /etc/hosts.backup /etc/hosts.
 How to Eject a CD with a Mac
How to Eject a CD with a Mac How to Right Click on Mac
How to Right Click on Mac How to Right Click on a Macbook Laptop
How to Right Click on a Macbook Laptop Cách để Mở nhanh Launchpad trên máy Mac
Cách để Mở nhanh Launchpad trên máy Mac How to Force an App to Shut Down on Mac OS X
How to Force an App to Shut Down on Mac OS X How to Block and Unblock Websites on Mac
How to Block and Unblock Websites on Mac