How is GPT and MBR different when partitioning a drive?
GPT is a new standard and this standard is gradually replacing the MBR standard. The GPT standard has many advantages and advantages over the MBR standard. However, MBR standards are highly compatible and in some cases this standard is extremely important and necessary.
Not only Windows operating system but Mac OS X or Linux and some other operating systems can also use GPT standard.
When setting up a new drive on Windows 8.x or Windows 10, you will be asked to use the MBR standard or GPT standard.
1. What do GPT and MBR do?
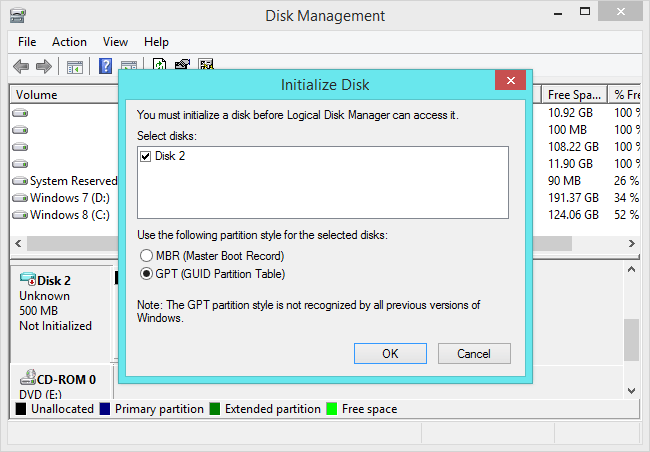
You will have to proceed with the drive partition before you can use these standards. MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (GUID Partition Table) are two different ways to store partition information on a drive.
This information includes the Start and Begin partitions, so the operating system will identify the areas of each partition and the boot partition.
This is why you must select MBR or GPT before creating partitions on the drive.
2. Limitations of MBR

MBR stands for Master Boot Record. The MBR standard was introduced with IBM PC DOS 2.0 in 1983.
It is called a Master Boot Record because the MBR is a special boot area located at the top of a drive. This area has a Boot loader installed on the operating system and information about the Logical partition of the drive.
On the Boot loader, you can understand that it is a pre-programmed system boot and operating system and placed in ROM.
Broadly speaking, the Boot loader is a small piece of code that is executed before the operating system starts running and it allows the device manufacturer to decide which features users are allowed to use or restricted.
If Windows operating system is installed, the initial bits of Windows Boot Loader will reside here - that is why you must repair the MBR if it is overwritten and Windows will not be able to boot. If the Linux operating system is installed, the Boot Loader GRUB will usually be in the MBR.
MBR works with drives up to 2 TB in size, but it cannot handle drives larger than 2 TB.
In addition, MBR only supports 4 main partitions. If you want more partitions, you have to convert 1 of the primary partitions into "extended partition" and create a Logical partition inside that partition.
3. Advantages of GPT
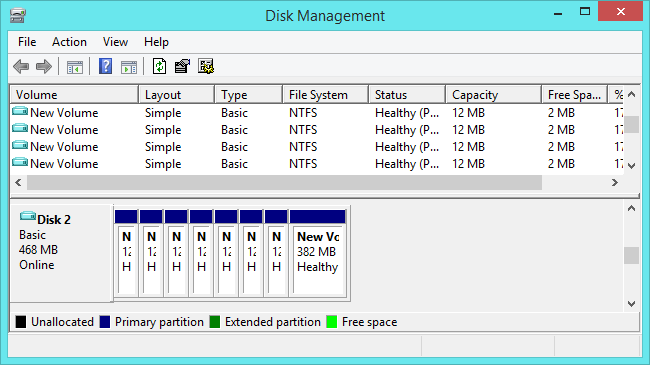
GPT stands for GUID Partition Table. This is a new standard, gradually replacing the MBR standard.
GPT is related to UEFI - UEFI replaces BIOS, UEFI has more modern interface and features, and GPT also replaces ancient MBR partition systems with more modern features and interfaces.
The reason is called a GUID Partition Table because each partition on your drive has a "globally unique identifier," or GUID.
This system is not limited to MBR. The drive may be more, much larger and the size limit will depend on its operating system and file system.
GPT allows an unlimited number of partitions, and this limit will be your operating system - Windows allows up to 128 partitions on a GPT drive, and you do not need to create Extended partition (partition extend).
On MBR drives, partition data and boot data are stored in one location. If this data is overwritten or corrupted, then you will encounter problems. In contrast, GPT stores multiple copies of these data on disk, so you can restore the data if these data fail.
GPT also stores Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) values to check whether the data is intact. If this data fails, GPT will detect the problem and try to recover the damaged data from another location on the drive.
MBR has no way of knowing its data has been corrupted. You can only identify problems when the boot process fails or your drive partition disappears.
4. Compatibility
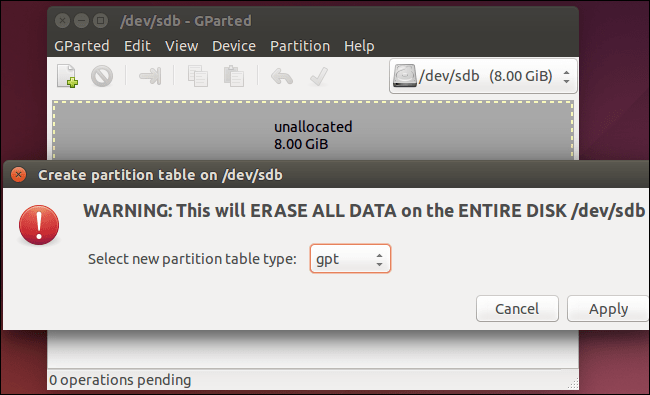
The GPT drive includes a "protective MBR." If you try to manage a GPT disk with an old tool that can only read MBRs, this tool will see a single partition that spans the entire drive.
The MBR ensures that the old tools are not confused with the GPT drive for an unpartitioned disk and overwrite its GPT data with a new MBR. In other words, MBR protects the GPT data from being overwritten.
Windows can boot from GPT on UEFI - based on the computer running the 64-bit version of Windows 8.1, 8, 7, Vista, and the corresponding server versions. All versions of Windows 8.1, 8, 7, and Vista can read GPT drives and use them to store data.
In addition, other modern operating systems can use GPT. Linux has built GPT support. Apple Intel Mac no longer uses the Apple APT program (Apple Partition Table) but uses GPT instead.
Refer to some of the following articles:
- How to recover data from "Ghost" hard drive (or image) error / mistake
- 3 ways to hide recovery partition (Recovery) on Windows 10 / 8.1 / 7
- How to recover lost files after repartitioning the hard drive?
Good luck!
You should read it
- ★ Aomei Partition Assistant standard Edition - Software for managing computer partition information
- ★ What is the MIL-STD 810 durability standard? Is this an important factor to buy a smartphone or laptop?
- ★ New USB 4 standard specifications: 8 times the speed of USB 3.0, 5GB / s data transfer
- ★ Officially has DisplayPort 1.3 standard to support 5K screen
- ★ How to create and extract Ghost in UEFI standard and standard GPT hard drive