4 methods to copy Linux hard drive
Whether you are running a Linux operating system doesn't mean you won't have problems over time. Always having a backup plan is a good thing, especially in case something goes wrong, such as a rare Linux virus that will attack your computer or you become the target of ransomware scammers. .
When your Linux installation fails, you want to upgrade your hard drive to a new hard drive with larger capacity, or your HDD is faulty, no matter what the problem is, if you have a backup Installing your Linux - or even the entire drive - back up and restart will be relatively simple.
Whether you use the functions built into the Linux operating system or you install third-party tools, it doesn't take long for you to back up and run your system.
4 methods to copy Linux hard drive
- 1. dd, built-in cloning tool in Linux
- 2. Partimage, partition backup tool
- 3. Partclone, software for image partitioning and duplication
- 4. Clonezilla, a common troubleshooting solution
1. dd, built-in cloning tool in Linux
Perhaps the most powerful Linux tool on today's list is dd (sometimes called "disk destroyer"). It can copy the entire hard drive or disk partitions to another location. But if abused, it can delete the content in your drive.
So you should use this tool carefully. You will find dd integrated into most Linux operating systems. If not, install it from the package manager. To copy your computer's hard drive, use the command:
dd if=/dev/sdX of=/dev/sdY bs=64K conv=noerror,sync Here, sdX is the source drive, while sdY is the destination of the data. Value of 64K, corresponding to block size command , bs. The default value is 512 bytes, very small, so it is best to include 64K or 128K conditions . However, even though the larger block size makes data transfer faster, the smaller block size makes the process more reliable.
If you just want to copy a partition on your drive, use:
dd if=/dev/sda1 of=/dev/sdb1 bs=64K conv=noerror,sync As you can see, the sda1 partition - sda1 partition (that is, partition 1 on sda device) will be cloned to sdb1 (a new partition created 1 on sdb device), for example, the second hard drive External level or external drive attached to the computer.
Press Enter to run the command. How long it takes to complete depends on the size of the drive or partition. Just make sure the destination drive is large enough to store!
2. Partimage, partition backup tool
If you have trouble trying to avoid all the instructions for the dd tool or want to avoid accidentally deleting your hard drive due to a typo, the partimage tool is also available for most distributions and not Bring any risk like 'disk destroyer'!
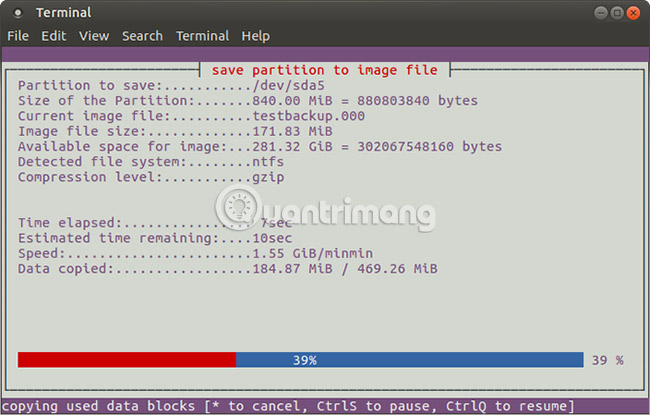
However, partimage does not support ext4 file system, so avoid using it to replicate the drive or partition of that type. However, if necessary, it can be used to copy Windows drive formats (FAT32 or NTFS, although this is only a test) as well as a more widely used Linux file system such as ext3. and older alternatives.
Before starting, make sure that the partition you want to copy is removed (using the umount command). If not, you will need to exit partimage to do so before continuing the process. You can exit at any time with the F6 key .
For Ubuntu, install with:
sudo apt-get install partimage Then you should launch from the command line with:
sudo partimage This is a mouse-controlled application, requiring you to select the partition to be cloned first.
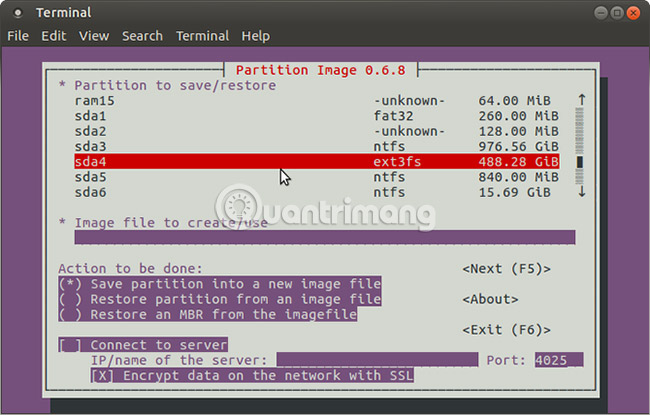
Touch the right arrow key to move to the next section, the Image file to create / use and name it (or enter the file name of the restored image).
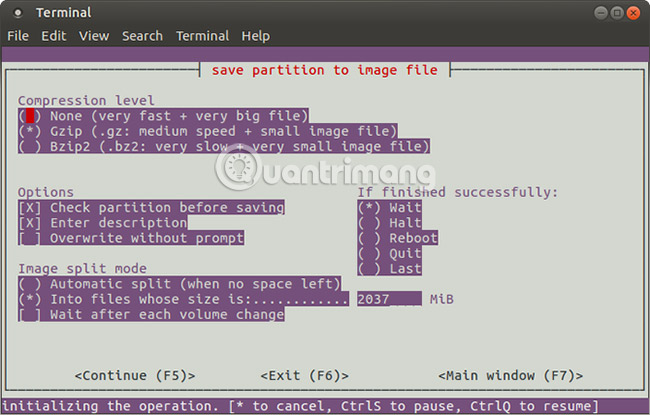
You can then select the correct Action to perform (make sure the selected option has an asterisk) and press F5 to continue. In the next screen, select Compression Level and your preferred Options . There is also the option to set an image splitting mode, and set up a guide for what will happen, after the backup process is done.
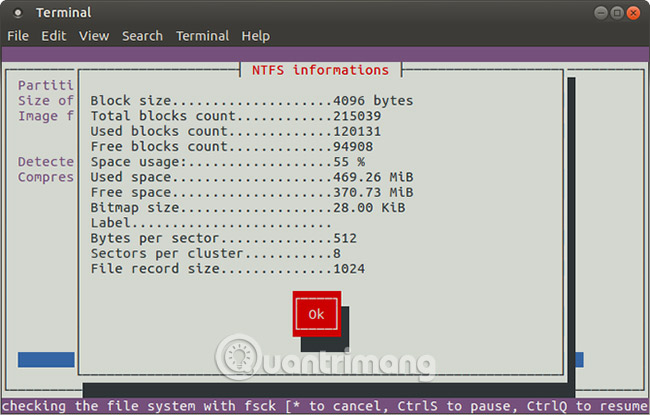
Press F5 to continue, confirm details, then click OK to start the process. The speed of this process will depend on the performance of the computer.
If you are looking for a fast and safe disk mirroring solution for Linux, partimage is the best option.
3. Partclone, software for image partitioning and duplication
If you are looking for a better alternative to dd (backup support of ext4 file system), you can consider partclone. Partclone is easy to use, but requires commands, instead of keyboard or mouse navigation. Installation with command:
sudo apt-get install partclone . and launch with the command:
partclone.[fstype] In which [fstype] is the file system type of the partition you want to copy.
The following command will create an image for the hda1 drive (hard drive 1, partition 1) called hda1.img:
partclone.ext3 -c -d -s /dev/hda1 -o hda1.img You may want to restore the image, so use:
partclone.extfs -r -d -s hda1.img -o /dev/hda1 You can find more details on how to use it on partclone.org.
4. Clonezilla, a common troubleshooting solution
If you're looking for a more flexible solution, why don't you try Clonezilla.org? This troubleshooting software is based on Partclone and is suitable for a variety of disk mirroring tasks. All common file systems are supported, on Linux, Windows and macOS (and more).
However, unlike dd and partclone, Clonezilla is a bootable ISO, which you can burn to DVD or USB. Using Clonezilla is very simple. The menus are controlled by keyboard, instead of commands, which means anyone can capture it.
You can also use Clonezilla in many other cases, such as to quickly handle many similar PC settings in the same operating system.
Although you may only want to synchronize your important data with the cloud, you should back up the entire drive so it can be recovered quickly in case of a system failure. However, remember to use these tools carefully because they can easily make you accidentally lose your data.
How do you copy your Linux hard drive? Do you use the tools in this article or have another utility that people don't know? Do you like backing up individual files? Let us know in the comment section below!
See more:
- Transfer Ubuntu to a new hard drive disk
- 5 Linux tools to recover data from damaged drives
- Use external USB hard drive for backup in Linux