GROWTH function - The function calculates the exponential growth value using existing data in Excel
The following article introduces you to the GROWTH function - one of the functions in the statistical function group is very popular in Excel.

Description: The function calculates the exponential growth value using existing data.
Syntax: GROWTH (known_y's, [known_x's], [new_x's], [const])
Inside:
- known_y's : The set of known y values in the relationship y = b * m ^ x, is a required parameter.
+ If known_y's is in a single column or row -> each known_y's column or row is interpreted as a separate variable.
- known_x's: The set of known x values in the relationship y = b * m ^ x, is a required parameter.
+ known_x's may include 1 or more sets of variables.
+ If known_x's is omitted -> it is assumed to be an array of the same size as known_y's
- new_x's: Are the new x values that you want the function to return the values corresponding to the values of y.
+ new_x's must include a column (row) for each independent variable.
+ If new_x's is omitted -> it is assumed to be the same as known_x's.
+ If known_x's and new_x's are omitted -> it is assumed to be the same as known_y's size .
- const: The logical value determining the value of the constant b, is an optional value including the following values:
+ const = True or ignore -> b is calculated normally.
+ const = False or ignore -> b = 1 and m are adjusted such that: y = m ^ x.
Attention:
- The value of the returned formulas has the array formula type -> the function must be entered as an array formula.
- When entering values for an argument with the following convention:
+ Use commas to separate values in the same row.
+ Use semicolons separating between rows together.
For example:
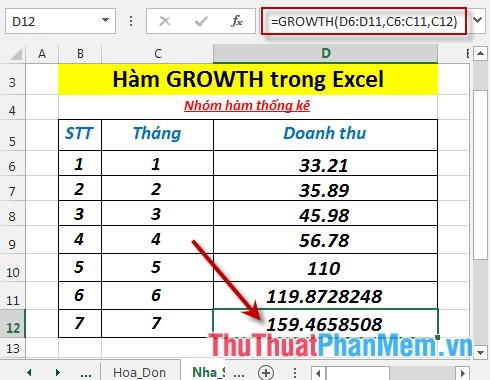
Calculate the estimated revenue for the 6th and 7th months based on the previous sales month in the data table below:
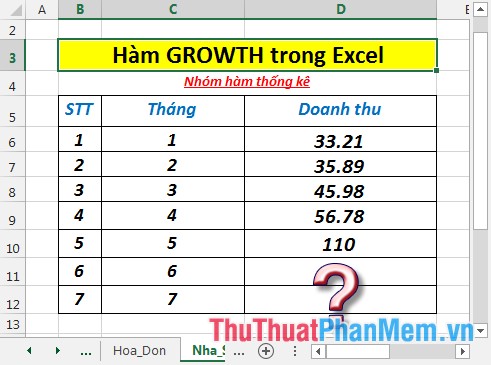
- Calculate the expected revenue of the 6th month. In the cell to calculate enter the formula : = GROWTH (D6: D10, C6: C10, C11: C12)
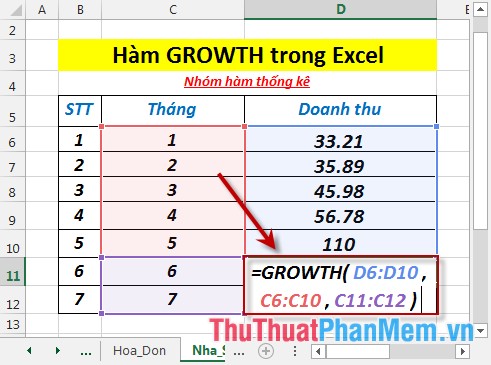
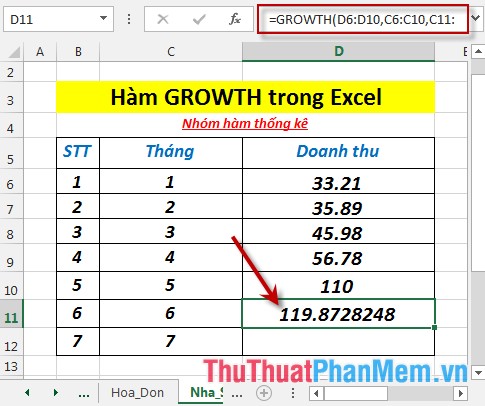
- Press Enter -> predicted revenue of the 6th month is:
- Calculate the predicted revenue of the 7th month. In the cell to enter the formula : = GROWTH (D6: D11, C6: C11, C12)
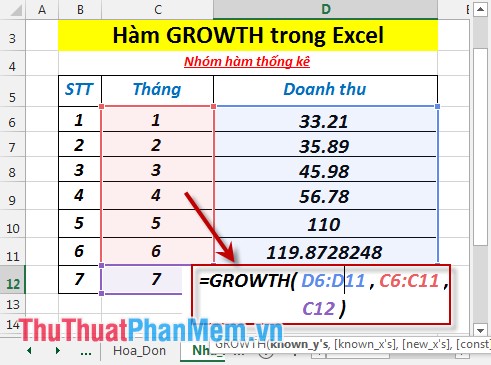
- Press Enter -> predicted revenue of the 7th month is:
Above are instructions and some specific examples when using GROWTH function in Excel.
Good luck!
You should read it
- ★ GEOMEAN function - The function returns the average of a positive array or range of data in Excel
- ★ The EXPON.DIST function - The function returns the exponential distribution in Excel
- ★ How to create growth charts in Excel
- ★ How to use Hlookup function on Excel
- ★ Growth Hacking growth strategy - Part 1