TIMEVALUE function - The function returns the decimal number of time expressed as a text string in Excel
The following article introduces you to the TIMEVALUE function - one of the functions in the date and time group is very popular in Excel.

Description: The function returns the decimal number of time indicated by a text string. The decimal number that the function returns is from 0 to 0.99988426, which corresponds to the time from 0:00:00 (12:00:00 AM) to 23:59:59 (11:59:59 PM).
Syntax: TIMEVALUE (time_text)
Where: time_text is the time value expressed in the text to be expressed in decimal.
Attention:
- Date information in time_text is ignored.
- The time value is part of the date value and is expressed as a decimal.
For example:
Find the decimal value corresponding to the time value below:

- In the cell to calculate, enter the formula: = TIMEVALUE ("2:35:59").

- Press Enter -> corresponding values are:
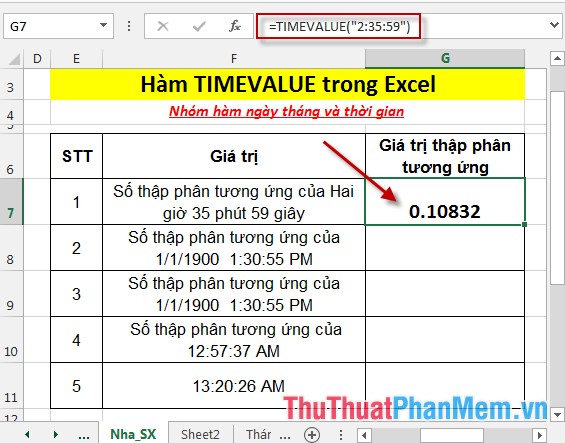
- Similarly, enter the formula for the remaining values:

- Where two values with the same time but different dates -> the function returns the same result -> the date value in the TIMEVALUE function is ignored:
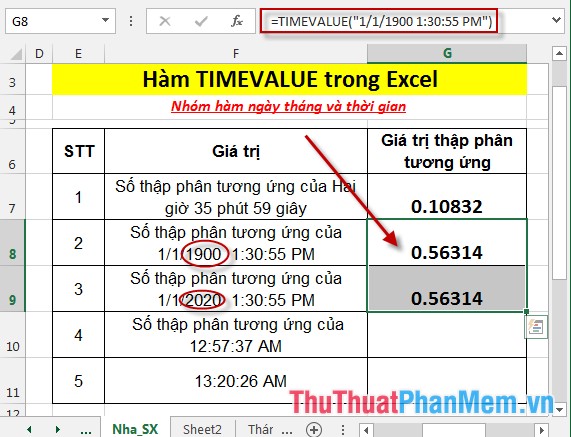
- In case you enter the formula as the reference value to cell F11:
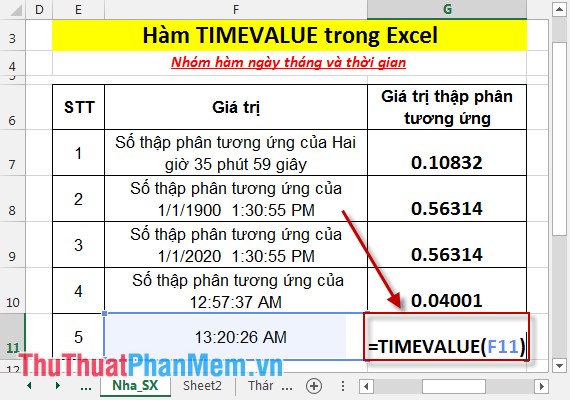
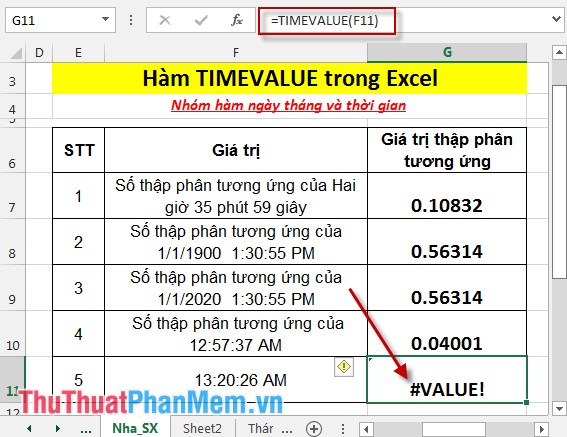
- Press Enter -> function returns the #VALUE! Error value So you should enter the time_text value as a text string when working with TIMEVALUE:
Above are instructions and some specific examples when using TIMEVALUE function in Excel.
Good luck!
You should read it
- ★ Instructions on how to count words in cells in Excel
- ★ LEN () and LENB () functions in Excel
- ★ ENCODEURL function - The function returns a query string with URL code in Excel
- ★ Save time with these text formatting functions in Microsoft Excel
- ★ The MID function in Excel, how to use the MID function, and examples