GAMMALN.PRECISE function - The function returns the natural logarithm of the gamma function, Γ (x) in Excel
The following article introduces you to the GAMMALN.PRECISE function - one of the functions in the statistical function group is very popular in Excel.

Description: The function returns the natural logarithm of the gamma function, Γ (x). The function is not different from the GAMMALN function, but the function only supports versions from Excel 2013 onwards.
Syntax: GAMMALN.PRECISE (x)
Inside:
- x: The value you want to calculate the natural logarithm of the gamma function, Γ (x). .
Attention:
- If the function's x value is not numeric -> the function returns the #VALUE! Error value
- If x ≤ 0 the function returns the #NUM! Error value
- The exponent e of GAMMALN.PRECISE (i), i is an integer, returns the same result as (i - 1) !.
- The function is calculated as follows:
[GAMMALN.PRECISE = LNleft ({Gamma left (x right)} right)]
Inside:
(fleft (x right) = left {{begin {array} {* {20} {c}}
{0 ,,,,,,, {rm {if}}, x <0}
{x ,,,, { rm {if}}, 0 le x le 1}
{1 ,,,,,,,, {rm {if}}, x> 1}
end {array}} right.,)
For example:
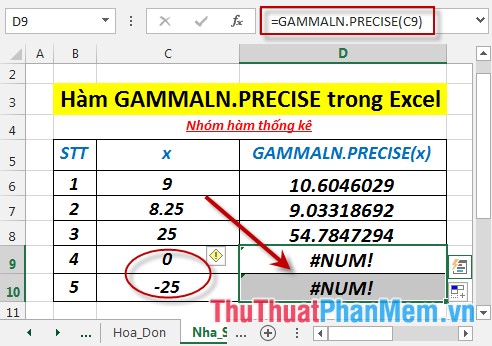
Calculate the natural logarithm value of the gamma function, Γ (x) of the values in the following data table:
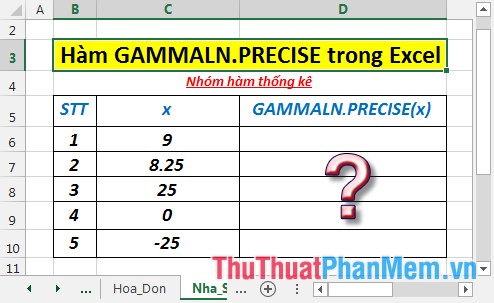
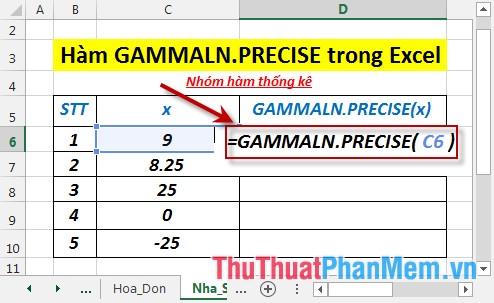
- In the cell to calculate enter the formula : = GAMMALN.PRECISE (C6)
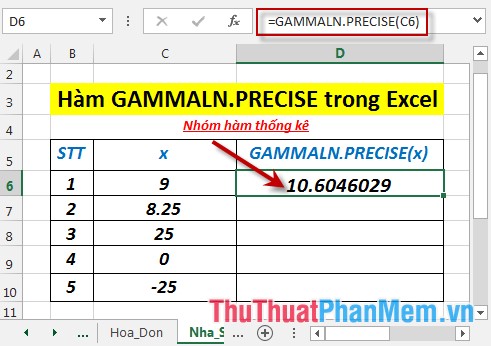
- Press Enter -> the natural logarithmic value of the gamma function, Γ (x) is:
- Similarly copying the formula for the remaining values results:
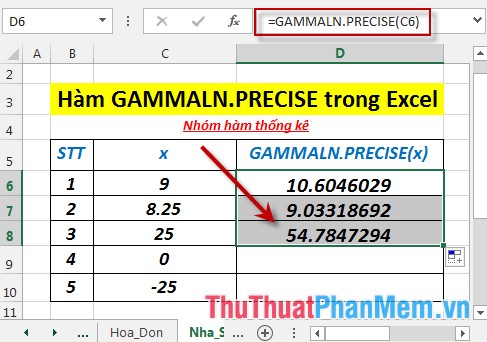
- Where x ≤ 0 -> the function returns the #NUM! Error value
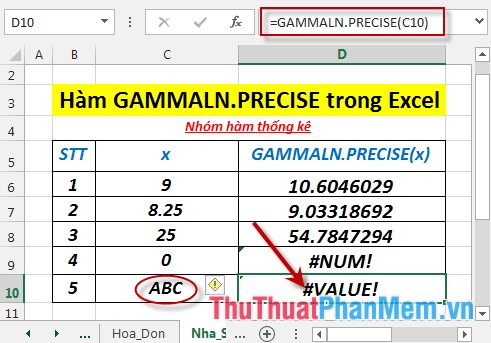
- Where x is not a number -> the function returns the error value #VALUE!
Above are instructions and some specific examples when using the GAMMALN.PRECISE function in Excel.
Good luck!
You should read it
- ★ GAMMA.INV function - The function returns the inverse of the gamma distribution in Excel
- ★ GAMMA.DIST function - The function returns the gamma distribution in Excel
- ★ How to use the IFS function in Excel 2016
- ★ How to use the IF function in Excel
- ★ OR function in Excel, how to use the OR function, and examples