Configure file-level antivirus software in Exchange Server 2007
By definition, antivirus software checks files when the operating system performs operations on them, such activities as opening, creating, and closing a file. To create a secure environment, each Exchange administrator must understand the environment security issue. In terms of antivirus software, we have two types of antivirus for Exchange Server :
Exchange Server level antivirus software
This software runs in Exchange Server. Exchange Server 2007 supports Virus Scanning API (VSAPI), and also supports virus scanning at the transmission level. Transmission-level antivirus is installed in Exchange Server roles (Hub Transport and Edge Transport) and it gives transport agents the ability to handle incoming traffic before these messages reach the machine. mailbox owner. We can see an example of transport agent antivirus software through the Get-TransportAgent cmdlet, see Figure 1.
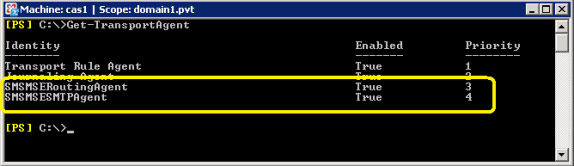
Figure 1: Antivirus software uses Transport Agents to protect
Exchange Server environment at the transport layer
File level virus scanning software
It is really unclear to Exchange Server but can protect the server against viruses located in the operating system file system. File-level antivirus does not protect against email viruses, they will not clean your mailbox if you receive a virus notification from a certain software. The best implementation is to use file-level antivirus software on all servers and client operating systems, create a procedure to make all antivirus software signatures up-to-date across the organization.
Before starting with the topic of this article, we need to keep in mind that Exchange Server 2007 is a new architecture. This new architecture is required to use x64 bit servers. Verify with your antivirus software vendor if there is any version for x64 bit so you can take advantage of this operating system architecture.
Note :
Some file-level antivirus software vendors only have 32-bit versions. We can install them on x64 computers, but software running x64 bit will take advantage of this x64 architecture to give higher performance.
In file-level virus scanners, there are two options: Memory-resident and On-demand; The first thing that allows anti-virus software to reside in memory and it checks all files no matter what file, memory or file level, the second option allows scanning the process to run during a cycle. Specifically.
The best method is to use both: antivirus software for Exchange Server and file-level antivirus software on the operating system. We also encourage you to use file-level antivirus on client workstations.
Configure file-level antivirus software
Now let's configure Exchange Servers to use for file-level antivirus. Before we get started, we need to pay attention to every Exchange Server role (Mailbox, CAS, Hub Transport, Edge Transport and Unified Messaging) have different requirements defined by antivirus software. file level.
To properly configure file-level antivirus software for each specific role we need to configure the following:
- Prevent directory
- Stop the process
- Prevent file expansion
Note :
You must verify what options are available for your antivirus software vendor.
Configure directory blocking list
We will see how to configure the directory blocking list of antivirus software on the Exchange Server Role:
Client Access Server (CAS)
We must ensure that the following directories are prevented by antivirus software:
- Folder compressed Internet Information Services (IIS) 6.0
Default value:% systemroot% IIS Temporary Compressed Files - IIS system files
Default value:% SystemRoot% System32Inetsrv folder - Interner-related files are used by CAS
Default value:% Program Files% MicrosoftExchange ServerClientAccess - The temporary directory of the server performs the main situation
Default value: C: WindowsTemp
To collect information: Right-click the My Computer icon, Properties, click Advanced, then the Environment Variables button, you can see in Figure 2.

Figure 2: Server TEMP directory
Mailbox server
In Mailbox servers, we must ensure that the database, log files and test standard files are prevented by file-level antivirus software. The following Cmdlets will show the directory of this component:
- Mailbox database directory (Figure 3)
Get-MailboxDatabase –server | fl * path * - Directory of Public Folder databases (Figure 4)
Get-PublicFolderDatabase –server | fl * path * - Message Tracking and Log Path for Folder management folders (Figure 5)
Get-MailboxServer | select * path * - Storage Group folder (Figure 6)
Get-StrorageGroup –Server | fl * path *

Figure 3: Folders used by LCR file and Mailbox database (if applicable)
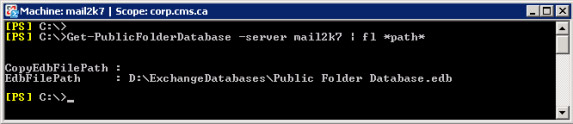
Figure 4: Directory used by the Public Folder database

Figure 5: Mailbox server settings must be in the anti-virus directory list.

Figure 6: Folders used by Storage Groups
- Offline Address Book files
% Program Files% MicrosoftExchange ServerExchangeOAB folder - Temporary directory of mailbox database
% Program Files% MicrosoftExchange ServerMailboxMDBTEMP - Compressed folder of Internet Information Services (IIS) 6.0
Default value:% systemroot% IIS Temporary Compressed Files - IIS system files
Default value:% SystemRoot% System32Inetsrv folder - Indicators of data content. We can get the Index directory with the following script :
getSearchIndexForDatabase.ps1 –all, see Figure 7.
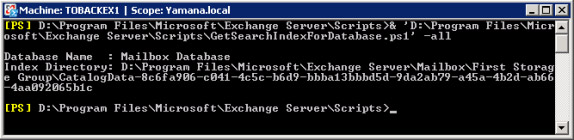
Figure 7: Use the GetSearchIndexForDatabase.ps1 script to validate the Index directory
- The default system TEMP directory is used to implement the main situations (Figure 2).
- Directory is used for OLE situations
% Program Files% MicrosoftExchange ServerWorkingOleConvertor folder - If you use any Exchange maintenance utility (eseutil, isinteg, .), make sure that the temporary folder is in the file-level antivirus software prevention list.
Edge Transport Server and Hub Transport
In the Hub Transport Server we must prevent all directories used by Message Tracking, message folders, etc. Use the cmdlet Get-TransportServer | select * path * to validate directories, see Figure 8.
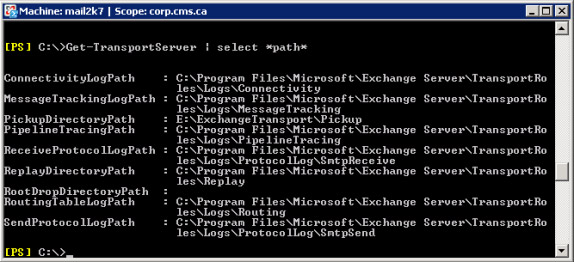
Figure 8: Information of directory used by Transport components
We also have to prevent queue-related folders and IP filtering, which are the directories listed in the EdgeTransport.exe.config file, see Figure 9.

Figure 9: Queue database settings and IP address filtering
- TEMP directory of the server (Figure 2)
- The folders OLE % Program Files% MicrosoftExchange ServerWorkingOleConvertor .
- The Sender Reputation database file can be found under the following directory
% Program Files% MicrosoftExchange ServerTransportRolesDataSenderReputation - ADAM database log files (specific to Edge Transport) : The default path is % Program Files% MicrosoftExchange ServerTransportRolesDataAdam, but you can change or virtualize it via the ConfigureAdam.ps1 script.
Unified Messaging
Unified Messaging
Unified Messaging roles require some directories to be prevented by file-level antivirus software:
- Grammar Files
% Program Files% MicrosoftExchange ServerUnifiedMessaginggrammars - Voice Prompts
% Program Files% MicrosoftExchange ServerUnifiedMessagingPrompts - Voice mail
% Program Files% MicrosoftExchange ServerUnifiedMessagingvoicemail - Bad Voicemail
% Program Files% MicrosoftExchange ServerUnifiedMessagingbadvoicemail
Prevent the public folder for all Exchange roles
Usually there is an antivirus software of Exchange Server installed in Exchange Servers, and we have to exclude the Quarantine folder and any applications that the antivirus software vendor specified in the product's installation instructions.
Extension steps when using the Mailbox Server group
Exchange Server 2007 allows two types of group solutions: CCR (Cluster Continuous Replication), using a shared witness file as a delegate and the SCC (Single Copy Cluster) using a physical disk as a delegate . In both components of the delegate must be removed from the file-level antivirus software. To find out what kind of group you are using, open the Cluster Administrator and view the Cluster Group. If you see Majority Node Set, you are using CCR (Figure 10), if it is Physical Disk, that is using the SCC cluster.
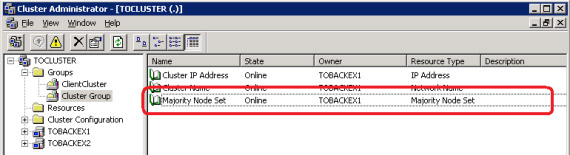
Figure 10: Majority Node Set section used by CCR cluster implementations
The % Winnt% Cluster folder must be shown in the directory blocking list of file-level antivirus software in both scenarios (CCR or SCC). Now that we know what type of group is available, let's continue configuring the antivirus software.
Cluster Continuous Replication (CCR)
In the CCR environment, our Quorum is partially contributed to remote control; We can use the cluster utility to find out where the file sharing witness is located, then configure in a listed machine, except on that directory.
The command line used to display as shown in Figure 1 has the syntax is:
Cluster res 'Majority Node Set' / priv , where ClusterName is not the name of the Exchange Cluster but the name you set during the Cluster deployment process.
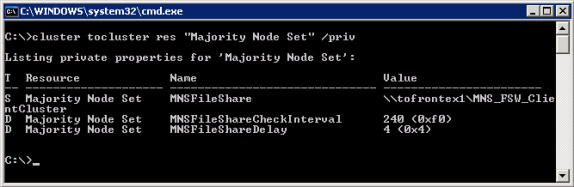
Figure 11: File sharing witness used by CCR
At this point, we know the server and the shared folder. Log in to that server and configure the directory exclusion list for that directory. In our image is a server named tofrontex1 and a physical path of the shared folder MNS_FSW_ClientCluster .
Single Copy Cluster (SCC)
Using SCC we must see which disks are being used by delegates through Cluster Administrator and configure that disk in the exceptions list. We must perform these steps in all Cluster nodes.
Configure extended file blocking list
Some antivirus software vendors allow us to prevent extended files with real-time anti-virus capabilities, the following blocking must be defined for Exchange Server 2007:
Mailbox Servers use the following blocking:
- .chk
- .log
- .edb
- .jrs
- .que
Unified Messaging blocks
- .cfg
- .grxml
Application-related blocking
- .config
- .dia
- .wsb
Offline Address Book blocking can be found in Mailbox servers:
- .lzx
Containment related to Content Index
- .ci
- .dir
- .wid
- .000
- .001
- .002
Process to configure blocking list
Some antivirus software vendors allow blocking processes from file-level antivirus software. We can use the following table to prevent the process listed for each server role.
Process
Server Role
Cdb.exe
common
Cidaemon.exe
Common
Cluster.exe
Mailbox
Dsamain.exe
Edge
Edgecredentialsvc.exe
Edge
Edgetransport.exe
Edge
Galgrammargenerator.exe
Unified Messaging
Inetinfo.exe
Mailbox and CAS
Mad.exe
Mailbox
Microsoft.Exchange.Antispamupdatesvc.exe
Hub, Edge
Microsoft.Exchange.Contentfilter.Wrapper.exe
Microsoft.Exchange.Cluster.Replayservice.exe
Mailbox
Microsoft.Exchange.Edgesyncsvc.exe
Hub
Microsoft.Exchange.Imap4.exe
CAS
Microsoft.Exchange.Imap4service.exe
CAS
Microsoft.Exchange.Infoworker.Assistants.exe
Mailbox
Microsoft.Exchange.Monitoring.exe
All Roles
Microsoft.Exchange.Pop3.exe
CAS
Microsoft.Exchange.Pop3service.exe
CAS
Microsoft.Exchange.Search.Exsearch.exe
Mailbox
Microsoft.Exchange.Servicehost.exe
CAS and Mailbox
Msexchangeadtopologyservice.exe
Mailbox, Hub, CAS, Unified Messaging
Msexchangefds.exe
CAS and Unified Messaging
Msexchangemailboxassistants.exe
Mailbox
Msexchangemailsubmission.exe
Mailbox
Msexchangetransport.exe
Hub Transport and Edge
Msexchangetransportlogsearch.exe
Mailbox, Hub Transport and Edge
Msftefd.exe
Mailbox Cluster
Msftesql.exe
Mailbox
Oleconverter.exe
Mailbox, Hub Transport
Powershell.exe
General
Sesworker.exe
Speechservice.exe
Unified Messaging
Store.exe
Mailbox
Transcodingservice.exe
Umservice.exe
Unified Messaging
Umworkerprocess.exe
Unified Messaging
W3wp.exe
The IIS Service used by CAS and Mailbox
Conclude
In this tutorial, we introduced how to deploy file-level antivirus software on Exchange Server 2007 independently of the file-level antivirus software installed. We also see which folders must be prevented from file-level antivirus software, specifying extensions and services running in memory.
You should read it
- ★ Top 7 best free antivirus software for Linux
- ★ Top free antivirus software, no bloatware and requires upgrade to free of distractions
- ★ Free 6-month license for McAfee AntiVirus Plus 2018 antivirus software, priced at $ 55
- ★ Microsoft claims Windows Defender is the best antivirus software
- ★ Should you choose free or paid antivirus software?