What is HTTPS? and why is it needed for your site
Compare HTTP and HTTPS
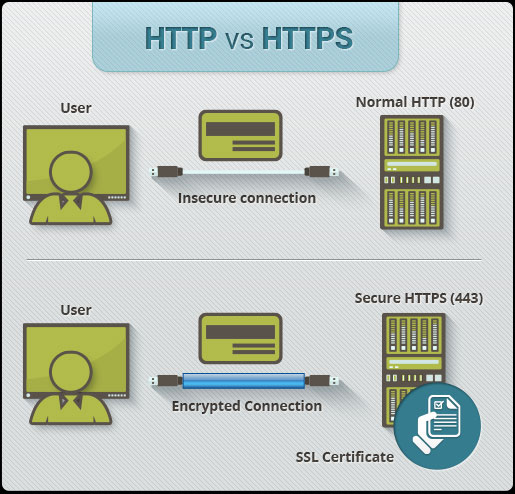
HTTPS stands for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure, a secure version of HTTP, the protocol by which data is sent between the browser and the website you are connecting to. The 'S' at the end of HTTPS stands for "Secure". It means that all communication between the browser and the website is encrypted. HTTPS is often used to protect highly secure online transactions such as banking transactions and online shopping orders.
Web browsers such as Internet Explorer, Firefox and Chrome also display the padlock icon in the address bar to indicate an HTTPS connection is valid.
- Differentiate HTTPS, SLL, Address bar
- Things you should know about HTTP / 2 protocol
How does HTTPS work?
HTTPS pages often use one of two security protocols to encrypt communications - SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security). Both TLS and SSL protocols use asymmetric Public Key Infrastructure PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) systems. An asymmetric system uses two 'keys' to encrypt communications, lock 'public' and 'private' keys. Anything encrypted with a public key can only be decrypted by a private key and vice versa.
As the name suggests, the 'private' key needs to be strictly protected and accessible only by the owner of the private key. In the case of a website, the private key is kept private on the web server. In contrast, the public key is distributed to anyone and everyone who needs to be able to decrypt the encrypted information using a private key.
- What is SSL? Is SSL important to the website?
What is HTTPS certificate?
When requesting an HTTPS connection with the website, the site first sends an SSL certificate to your browser. This certificate contains the required public key to start the security session. Based on this initial exchange, the browser and the website will start the SSL handshake protocol (handshake protocol). The SSL handshake protocol involves creating shared secrets to establish a secure connection only between you and the website.
When using a trusted SSL certificate during HTTPS connection, users will see the lock icon in the address bar of the browser. When an Extended Validation Certificate is installed on a web page, the address bar will turn green.
Why should there be an SSL certificate?
All communications sent through HTTP connections are in plain text and can be read by any hacker who can break into the connection between the browser and your website. This can be a danger if it contains contact information located in your order, credit card details or social security numbers. With HTTPS connection, all communications are securely encrypted. This means that even if someone has broken into the connection, they will not be able to decrypt any data passing between you and the site.
Benefits of HTTPS protocol
The main benefit of HTTPS certificates is:
- Customer information, such as credit card numbers, is encrypted.
- Visitors can verify you are a registered business and you own the domain name.
- Get customers' trust and complete purchases from websites that use HTTPS.