COUPNUM function - The function returns the number of interest payments on a security in Excel
In the process of investing in securities, paying special interest is very important. It helps you calculate and plan a reasonable calculation and investment. The following article details the COUPNUM function - The function returns the number of interest payments of securities in excel.
Description: The function returns the number of interest payments from the settlement to maturity date. If the value is returned as a decimal, the function automatically rounds that value.
Syntax: COUPNUM (settlement, maturity, frequency, [basis]) .
Inside:
- settlement : The settlement date of a security or the date securities are sold to buyers after the issue date, which is a required parameter.
- maturity : The maturity date or the expiry date of a security, is a required parameter.
- frequency : The number of annual interest payments, is a required parameter, with the following values:
+ frequency = 1 => Pay interest 1 time per year.
+ frequency = 2 => Pay interest twice a year.
+ frequency = 4 => Quarterly interest payment.
- basis : Is the basis used to determine counting the number of days, is an arbitrary parameter. The following values are available:
+ basis = 0 or skip: Calculate the number of days based on US standards: The number of days per month is 30 / number of days per year is 360.
+ basis = 1: The actual number of days per month / The number of actual days per year.
+ basis = 2: The actual number of days per month / the number of actual days per year is 360 days.
+ basis = 3: The actual number of days per month / The number of days of the year is 365 days.
+ basis = 4: Number of days per month is 30 days / 360 days per year according to European standards.
Attention:
- If the return value of the function is a decimal, the function automatically rounds that value.
- Use the Date function (year, moth, day) to enter monthly values, avoid unnecessary confusion.
- If the parameter value is decimal => the function will take the integer value of that parameter.
- The function returns the error value #NUM! In the following cases:
+ If the settlement date and securities expiry date are invalid.
+ If the basis value is outside the set {0, 1, 2, 3, 4}.
+ If the settlement value is outside the values {1, 2, 4}.
+ If the settlement date is greater than the securities expiry date.
For example:
Calculating the number of interest payment times from the settlement date of securities to the expiry date of the securities knows the number of expiry dates, settlement and some facts as follows:
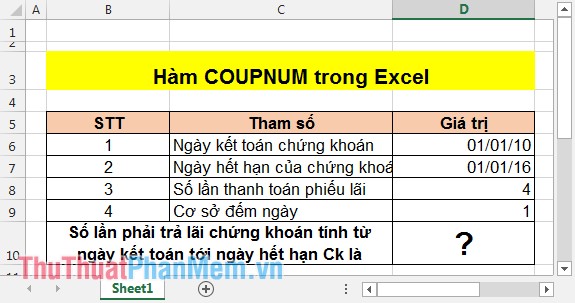
In the cell to calculate enter the following formula: = COUPNUM (D6, D7, D8, D9) .
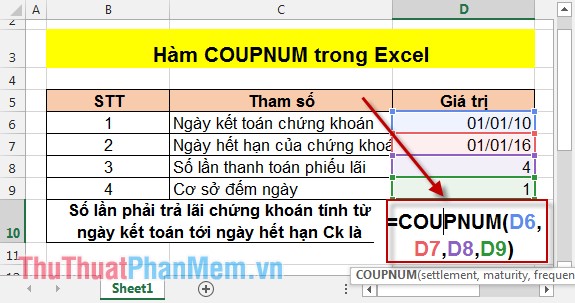
Results after calculation:
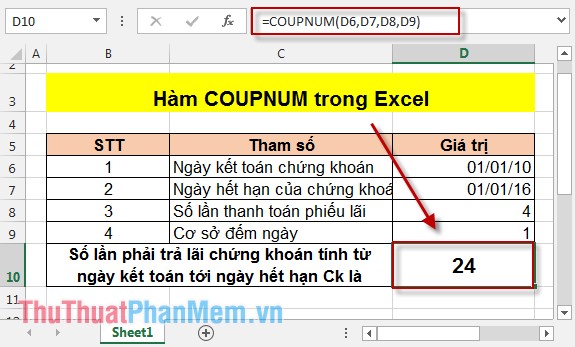
Thus, from the settlement date of securities to the expiry date, securities have to pay interest 24 times.
The above is a detailed guide on how to use the COUPNUM function to help you when deciding to invest in the securities sector.
Good luck!
You should read it
- ★ RANK.AVG function - The function returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers in Excel
- ★ PERMUT function - The function returns the number of permutations of a given number of objects in Excel
- ★ The DAYS function - The function returns the number of days between 2 dates in Excel
- ★ GAMMA function - The function returns the gamma function value in Excel
- ★ FVSCHEDULE function - Returns the future value of an investment that has variable or adjustable interest in period in Excel