Network better
The help in this article is to solve the problems from wave dead spots, security issues and data transfer problems. Network systems are considered standard when they operate continuously but in reality are often "harsh". When your network printer "disappears", Skype calls, or connection to entertainment items on You-Tube are "broken", this is the time for you to hand out and strengthen the network. Here are some experiences and "tips" to deal with the problems in your network.
The most basic problem
Most of the most common network problems in this article are less common in Internet connections, printers and computers.
Connection loss : Often this problem can be solved by restarting the modem, router or computer. But if this keeps repeating over and over again, the problem may lie in setting up your router and computer.
Try extending the router's IP address (DHCP) time (this is the time the router spends an IP address for a device on the network) for about a week. You can perform this configuration through the router manager.
If a connection break occurs with a laptop (laptop), check the source of the network card. In Windows XP, go to the Network Adapter in Device Manager, find the network card, right-click and choose Properties. Under the Power Management tab, uncheck Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power. Laptop battery may be faster, but you will have a more stable connection.
Domain name system (DNS) system can also cause loss of connections. DNS server is a computer that contains data of service providers (ISPs), it is responsible for transferring personal URLs, such as www.pcworld.com.vn, into a corresponding IP address on the network. Internet. If you get a message that you can't access the website or can't receive the email, try using the DNS server at OpenDNS.com instead of the DNS servers of the ISPs you're using. First, access the manager on your router, then switch the IP address in DNS to 208.67.222.222 and 208.67.222.220. OpenDNS is a free service and has the function of locking websites that are supposed to be fraudulent (phishing).
 No printer found : If you decide to share the printer via USB, you should make sure the computer connected to the printer is not turned off. If possible, install the printer to a desktop computer (do not use a laptop) and turn it on permanently (it can save power by turning off the screen).
No printer found : If you decide to share the printer via USB, you should make sure the computer connected to the printer is not turned off. If possible, install the printer to a desktop computer (do not use a laptop) and turn it on permanently (it can save power by turning off the screen).
In Windows XP, it is also confirmed that "File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks" is installed on all network cards, so switching between wired and wireless networks does not affect sharing. In XP, go to Control Panel.Network Connections (for each network card) and right-click on the device and select Properties. If you do not see "File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks" appear in the window, select Install to add it.
Better yet, install as a print server over the network so you don't have to worry about the ability to share printers in the form attached directly to your computer. Some routers have built-in USB ports for print servers over the network to operate independently, just plug the printer into the router. If you use a multi-function device, support printing as well as image scanning, you can refer to D-Link's USB RangeBooster G Multifunction Printer Server (cost about $ 100, find.pcworld.com/56594).
No computer : In many cases, file sharing problems over the network are due to the group name (Workgroup) and PC. You have to make sure that the computers on the network don't have the same names and don't abuse easy-to-remember names like "Desktop" or "Dell" . Computer names should not have spaces in between (Windows ME and versions Previous Windows operating systems do not support whitespace) and computer names should not be more than 15 characters. On the other hand, you must also make sure all computers on the network have the same Workgroup name. The default Workgroup name in Windows XP Home is "MSHome". In previous and in Windows Vista versions, it was named "Workgroup". To change the Workgroup name and the name of the computer in Windows XP, select Start, Control Panel> System and select the Computer Name tab.
Differences in Windows Vista : Have you still not resolved the main problems in sharing information? So it's time to think about upgrading to Windows Vista. In this new OS, the "Networking and Sharing Center" section gives easy access to sharing and configuration features. Vista's Link Layer Topology Discovery function automatically checks network hardware and allows you to see their location in Network Map.
Block unauthorized access through firewalls : Vista's firewall system is smart enough to manage sharing on the network. But if the cause of the problem is due to the Vista firewall, try using a third-party tool. ZoneAlarm's Trusted Zone feature allows Workgroup computers to communicate with each other.
The messy arrangement between file sharing and printers in Vista can be solved by using an additional program called Network Magic (costing 30/40 / 50USD for 3/58 PC numbers respectively) . Like Windows Vista, Network Magic (one of the best 100 products of 2006, see www.pcworld.com/56595), put all your network shares and functions in one place, simplifying things. share folders and printers. A special mode allows protection of folders when your laptop is connected to a public Wi-Fi network that is a security concern. The free version of Network Magic allows network connections and wireless security to be repaired, but the paid version is good for printer and file sharing.
Security enhancement
The only way to ensure the security of your network is to prevent it with the outside world - no Web, no e-mail, no utility. But you don't need to use the NSA (National Security Agency) tactic to protect your data.
Put everything behind the firewall : The way to secure the home network begins with the hardware firewall system. Most routers support, but in inexpensive routers, firewalls are often based on NAT (Network Address Translation) rather than using higher-end SPI (Statefull Packet Inspection) technology with a computer-guaranteed design. Your only receive the data it requires. However, to be more certain, you must change the router's default password when installing and change it periodically later.
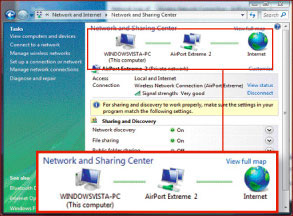
View from Vista: Network and Sharing Center visually see connections and simple configurations.
Perform a second protection round for each computer by turning on Windows auto-update mode, and installing personal anti-virus, anti-spyware and firewall. You can buy security tools (Symantec and McAfee for $ 70 or more) or use standalone tools like Web-root SpySweeper ($ 30), BitDefender antivirus ($ 30) and ZoneAlarm's firewall software. Check Point (if you use basic functions, ZoneAlarm is free).
Whatever security technology you use, don't trust Windows XP's firewall system because it can only filter incoming data. ZoneAlarm and other firewall software can filter 2-way data, protect both incoming and outgoing information. Windows Vista's firewall system also protects both ways, but you have to set it manually to filter out the information. Go to Vista's Command Promt, type wf.msc to enter the configuration screen. Vista also has Windows Defender for anti-Spyware, but no antivirus software.
Simplify use by using the same tool for all your PCs. Then install them when logging in with administrative rights or working with advanced permissions for different software (both in Windows Vista). Keeping your password secret: Remember, the security of your network is only equal to its weakest link.
Covered radio : Firewalls and security tools are not effective in protecting "stolen" packets while transmitting on Wi-Fi at a given frequency. Use the strongest encryption standard supported by Wi-Fi devices: In the strongest to weakest order are WPA2, WPA and WEP.
Available software-based intruders can decrypt WEP encryption information in just a few minutes, so this protection doesn't work unless you want to prevent "using" wireless bandwidth of In case of necessity you should buy a new device that supports WPA.To ensure the old device and the new device support maximum security, you should choose a router that supports both WPA and WPA2 standards simultaneously.
Don't worry about what you can hear like using the MAC address (Media Acccess Control - the only indicator that supports the identification of hardware devices) and turn off the SSID (Service Set Identifier - name of the Wi-Fi network) ) is able to play on a secure wireless network. Both of these components are easier to overcome than WEP, but make administration much "miserable".
For example, MAC address filtering will require you to enter the device's MAC address into the router manager to check the validity for connecting to the network, but your network snoopers can. Get a valid MAC address to connect. Similarly, specialized network detectors (sniffer) can detect SSID even if it is turned off; Therefore, turning off this playback feature only makes it difficult for valid users to connect to the network.
Safe transport : Public access points are a fertile source of infection. To be truly secure when using a public network, you should use a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt information transmitted between your computer and the intermediate server. Companies often build virtual private networks for their employees; Or you can sign up for a VPN service such as Witopia Personal VPN ($ 40 / year, find.pcworld.com/56597) or JiWire Hostpot Helper.
Next, in Wi-Fi setup, turn off Adhoc mode (pc-to-pc) and prohibit automatic connection to strange networks. In XP, you can change both of these settings by clicking on the Wi-Fi icon on the system tray (system tray) and selecting Change Advanced Setting. Under Wireless Network card select Advance according to Access Point (Infrastructure) Network. Next, uncheck Automatically connect to non-prefered networks.
In Windows Vista, turn off the Vista Network Discovery feature (this section allows other computers to see your network) when you have a hotspot. Vista will automatically turn off if you specify a connection like "public" but you can also turn it off in Task's View Network Status and Control Panel.
Increase transfer speed
If the download speed of Wi-Fi takes a long time, your network backup may have experienced problems, try some experience for this issue as follows:
Use wired connections when possible : Wired network speeds (ideally wired Ethernet) are often faster and more stable than wireless waves. There is no reason why you must put the network storage drive away from the router, plug it into an available ethernet port on the router. You can do the same for network printers.
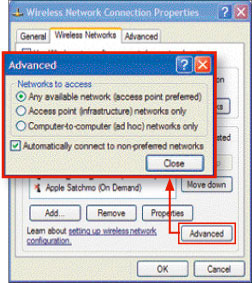
The number of network names increases when you do not automatically connect to unknown networks.
Gigabit speed : Most computers today have built-in gigabit-speed network cards, which means they can transmit data at very fast speeds - 1000Mbps. To take advantage of that, the ethernet port on the router must also support gigabit speeds. For network backup, superior speed can complete the task in a short time instead of taking a whole night. The gigabit Wi-Fi router costs about 150USD.
Buy Wi-Fi accelerator : To achieve the highest speed of the latest standard Wi-Fi-802.11n draft (draft-n), each wireless device in the network must have a draft-n network card (price about 100USD). Don't forget to update the draft-n device firmware regularly, as manufacturers are now trying to raise the first generation draft-n product to draft-n second generation, which helps both work. be together.
Channel change : The biggest obstacle to obtaining good Wi-Fi signals is no longer a distance (most MIMO and draft-n routers cover the entire building) but rather noise by the network signal. nearby, especially in the city where there are many networks. The 2.4GHz band, which is 802.11b / g standard and most of the new standard devices, only has three non-overlapping channels so the risk of interference from the neighbor network degrades your wireless network performance. It is entirely possible. In fact, the most recent draft 802.11n doesn't work at a 50% reduction in performance if your network is near another active Wi-Fi network.
To minimize noise, you can install and run the free NetStumbler tool (www.netstumbler.com/downloads) to determine the strength of the signal and channels that networks are running. Then, you can set up the router to select the channel at the farthest distance from the neighboring network's channel with the strongest signal (the auto-channel selection feature of some routers will help you do this).
Furthermore, you might consider using a dual-channel draft-n router, such as the Buffalo Nfiniti Dual Band Router ($ 299, find.pcworld.com/56599) that can work on 2.4 GHz bands and 5 GHz. This helps you allocate legacy 802.11 b / g devices on the 2.4 GHz band and use the 5GHz band (allowing up to 20 overlapping channels) for applications that require high bandwidth such as transmission. video.
Ready for Media
When you need to transmit a smooth video signal or call a voice IP phone, only the transmission speed is not enough.
Try using powerline : If you can't use ethernet, try considering using a networked device via a power line (instead of using Wi-Fi). Many network technologies pass power to nearly the speed of ethernet. In our test with high-speed video transmission, Homeplug AV was less affected by noise of other electronic devices.
The Linksys PowerLine AV Ethernet Kit ($ 180, find.pcworld.com/56600) helps transfer data over indoor power lines. Plug the controller (adapter) into the power outlet, to set up the network, start attaching the network card to the available ethernet port on the router. You can then add other devices to the network by attaching a cable end to this device and the other end to the adapter. You won't have to worry about overloading like wireless networks even with high quality image files. This is a solution that offers higher performance than wireless networks, especially for homes with large areas.
Update Wi-Fi : If you still want to use Wi-Fi for streaming media streaming, make sure you have 802.11n drafts. It is not only fast, but also has Quality of Service (QoS) technology that supports data streams, Internet telephony, online gaming and other applications. Don't forget to update firmware draft 2.0. All major vendors offer free firmware draft 2.0 updates.
Router for game : Do you play World of Warcraft at home? To play high-end games, there are routers that support the best performance for group play in the local network as well as through the Internet. This is an important issue if many people access the network simultaneously. Gamming routers have a priority QoS function that helps reduce unnecessary applications in the network and often uses faster processors. All of these highlights make the ability to meet the network faster with computers. Linksys' Wireless-N Gamming router ($ 200 finder) supports Wi-Fi draft-n, gigabit speed LAN and games.
Better backup
Often, people tend to use network drives to periodically back up data to the hard drive, but it's best not to rely solely on this. Maybe at some point, the network sharing feature has not been activated or the system needs to be backed up is turned off or in sleep mode; backup process is interrupted .
Choose network storage devices carefully : Shared storage devices over the network have two basic types: an external USB drive directly connected via an available USB port on some routers or via a network connection such as D -Link (80USD) Express EtherNetwork DNS-120 Network Storage Adapter; and network storage devices (NAS - Network Attached Storage) built into the router.
If you use a USB drive, you can remove it from the router and attach it to the computer (at another location) if you want. USB drives are easy to set up and you can use an old drive, available for storage.
In contrast, NAS is available both as a processor, operating system and can only be attached to the network. They often have many features and allow you to set them up for yourself or allow configuration to become common storage areas for the network. The leading model in PC World USA network storage testing is Infrant Ready NAS NV (about $ 900) and Maxtor Shared Storage II (about $ 750).
The best security and performance response is that NAS supports gigabit speed (of course you must have a gigabit router) and use RAID 1 or 5. Don't risk 500GB of your music collection data stored on NAS not backed up; The best way to maintain a copy of NAS is to map it using a RAID mechanism.
The problem is that you will choose which storage drive to ensure it is large enough, suitable for future development. Storage is often failed if the storage device is full. One advice is to choose a storage drive capable of 1.5 to 2 times your current need to make a backup drive; Double if you want to create a backup online.
Increasing backup capabilities: By copying only files that have changed since the last update, it will help you reduce the load on the network and save backup time. Cobian Backup (free, see find.pcworld.com/56604) can perform backups once or sequentially with the ability to compress or not compress data and can encrypt data to ensure safety. on storage devices over the network in sharing.
Keeping your PC active: The need to keep your PC running at the time of backup is obvious, but the computer's status is turned off at this time is a common cause of backup failure. Do not turn off the computer at night but switch it to hibernate. However, you must ensure that backup software is able to wake up the computer. If the software does not do this, use XP's Scheduled Tasks feature (located in Programs> Accessories> System Tools) to wake up the computer at the time of backup.
Add a Mac
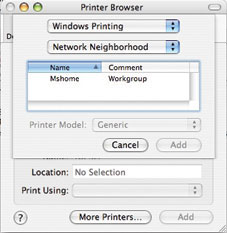
The MAC OS is ready to join the Windows network
You are already connected to your Windows machine. But now you have a Mac. How to set it up? Will it work with your printer? Can you share files the way you did with a PC?
In most cases, the Mac OS X operating system provides everything you need to connect your Mac to the Windows network and perform file and printer sharing. You can attach your Mac to the network or access the Wi-Fi router just like you would with a new PC, by selecting the SSID from the list of available Wi-Fi networks and entering the Wi-Fi encryption key. Mac OS supports WEP, WPA and WPA2.
To be able to share files and printers, Mac operating systems support built-in connectivity like PC. It uses SMB / CIFS (Server Message Block / Common Internet File System) protocol for file sharing with Windows and uses Windows group name.The default group name for any Mac is Workgroup. You can change the name, for example, to MSHOME using the Mac Directory Access tool, and it also supports Windows Active Directory (used for collaboration servers).
Next, turn on Windows Sharing in the Mac OS's Sharing Preference Pane and license each user account you want to share. The Mac will appear as a member of the network when you access the network.
After selecting your Mac and entering your account, password, you can view the information on your Mac's drive and back up or upload files using drag and drop. This task can also be performed on both XP and Vista. Similarly, you can print from a Mac via a shared printer from Windows based on the SMB protocol, although the setup process is not simple. In the Mac printer setup utility, select Add. If the printer in Windows does not display in the list of available printers, select the More Printer button to activate the Printer Browser dialog box.
Now, select Windows Printing and Network Neighborhood from the menu. Working groups on the local network will appear in the window, when you select it, you will see a list of shared printers to choose from. From then on, the printer on Windows will appear in the print dialog of the Mac.
If all this seems too complicated, you can buy the Network Magic software from Pure Networks for Mac ($ 30 for 3 machines, $ 40 for 5 machines and $ 50 for 8 Macs). The trial version is also available for download (see: find.pcworld.com/56806), which allows network operations on Macs similar to those on Windows.
Duc Quang
You should read it
- Access the home router with admin rights
- How to Monitor Network Traffic
- 5 settings need to change right on your new router
- Build a wireless network with a broadband router - Part 1: Prepare hardware
- Why should you restart the router regularly?
- Building a wireless network with a broadband router - Part 2: Configuring the router and computers on the network
 TCP / IP Troubleshooting: Structural Methods - Part 1: Introduction
TCP / IP Troubleshooting: Structural Methods - Part 1: Introduction Introduction to Network Access Protection (Part 7)
Introduction to Network Access Protection (Part 7) Troubleshooting TCP / IP: Structure method - Part 2: Troubleshooting routing tables
Troubleshooting TCP / IP: Structure method - Part 2: Troubleshooting routing tables Troubleshooting TCP / IP: Structure method - Part 3: Fix network connections
Troubleshooting TCP / IP: Structure method - Part 3: Fix network connections Troubleshooting TCP / IP: Structural Methods - Part 4: Use Netdiag.exe
Troubleshooting TCP / IP: Structural Methods - Part 4: Use Netdiag.exe Managing Windows networks using scripts - Part 7: Troubleshooting errors
Managing Windows networks using scripts - Part 7: Troubleshooting errors