Instructions on DD-WRT - Part 1: Static DHCP
Network Administrator - DD-WRT , a free, open source software program that is coded and distributed by 'BrainSlayer', stands out as one of the leading, powerful and user-friendly alternatives. Best for Linksys WRT54G series routers . DD-WRT can support to increase the range of external WRT54G routers, including Asus, Belkin, Buffalo Devices, Motorola and Siemens models.
During the upgrade of the router sometimes there are some unexpected problems. However, in this article we ignore that problem and assume that you have successfully installed DD-WRT, this is what we can exploit in this tool to help our network.
When you first observe the new features from an open-source router software in detail, you will find it interesting to see that the features of the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) it provides.
Static DHCP
After the software is installed, most routers and computers are designed to dynamically manage their IP addresses. Computers, whether wired or wireless, require an IP address and related network parameters from the router using the DHCP protocol. The router will take an unused address from the available address store and give it to the client.
This process results in what we call 'dynamic IP addresses' - each time the PC connects to the router, it is assigned a new IP address. This router can assign the same address it assigned in the previous session. Or maybe not. You will not know and usually do not care about that.
However, there are many cases where you want your client to receive a consistent or predictable IP address. The most commonly used script is when you run a server on your client. Suppose you run a website on a home computer and need to access its server from somewhere - such as work, school, etc. The router will 'hide' your server with that. The outside world, this is a way to secure. That's why people invented port forwarding (Port Forwarding).
The router will allow you to forward the intended traffic to a specific port to a specific machine. In its simplest form, you can configure the router to forward incoming traffic intended for port 80 - the default port for web traffic - to an IP address of the computer running the web server.
What is the IP address of your web server? If it receives the address automatically from the router - you don't know for sure. It may change, and your port forwarding will become unreliable.
One solution to that is to manually assign your web server an IP address and network parameters, rather than using DHCP. Although this method can limit the ability to easily connect that computer to other networks - a common problem for laptops. If your ISP sometimes changes servers, it will also ruin the network configuration you set yourself.
Set up step by step
Fortunately, DD-WRT allows you to easily create static DHCP addresses for your network. Combining what's best in both worlds, a static DHCP address will allow your clients to continue to receive their network parameters automatically, but you know exactly which IP address will be assign.
- Open the browser and connect to the router's admin page. The default address for DD-WRT is http://192.168.1.1, but it may be different if you have reconfigured it.
- Go to Setup / Basic Settings menu . The router may require you to log in with an administrator password. (default is root / admin). Find the 'Network Address Server Settings (DHCP) section.'
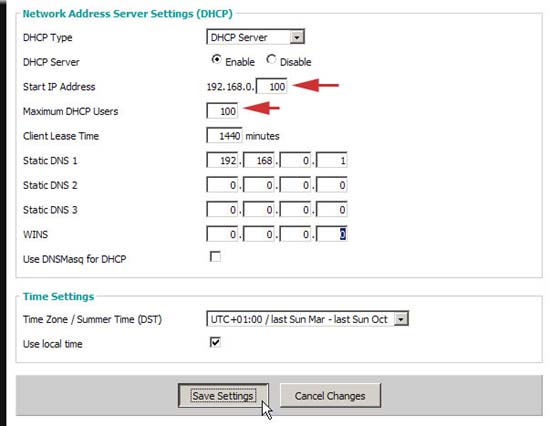
- Create a note about the address store that the router uses when assigning dynamic IPs. Here we see a repository of 100 addresses, starting from 192.168.0.100 to 192.168.0.200. Later your static DHCP address needs to be outside the above address range. (If you make any changes here, you need to save your settings.)
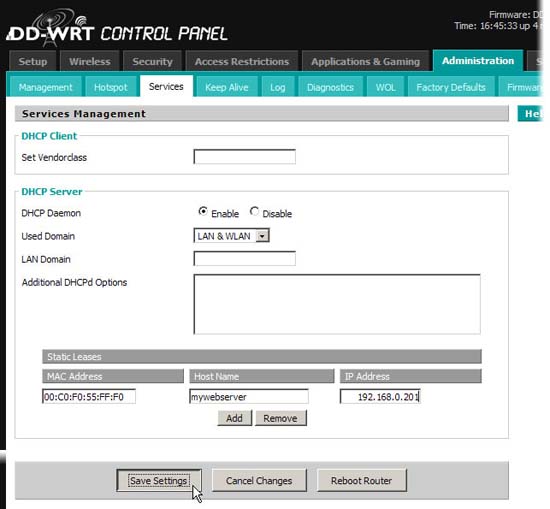
- Go to the Administration / Services page. This is where the action takes place. Under the 'Static Leases' heading, click the 'Add' button to create a new DHCP input field.
- Enter three values: the MAC address of the network adapter of the machine, the hostname for the machine, and the IP address you want it to be assigned. Choose any hostname you like, such as 'webserver' or 'gameserver'. Select an IP address according to the same pattern as the addresses in your DHCP address range (in our example 192.168.0.x). Select some x that is outside the address range we saw in step 3. (in the example we chose to be 201).
You can see the MAC address for the network adapter in Windows XP or Mac OS X with a few clicks.
Windows XP
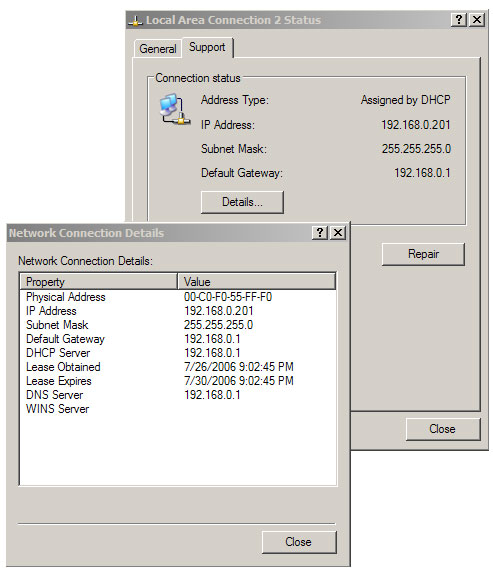
Click Start / Settings / Control Panel / Network Connections and click the name of the network connection. Wired connections are usually named 'Local Area Connection,' and wireless connections are often called 'Wireless Connection'. In the status window, click Support , in that window, click Details . Your MAC address is a series of hexa pairs labeled 'Physical Address'. Use colons ':' instead of '/' to separate pairs in the DD-WRT interface.
Mac OS X
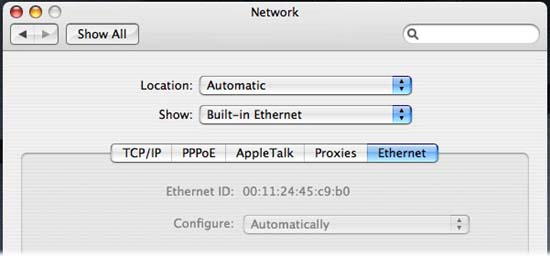
Go to Dock / System Preferences / Network . Click the Ethernet tab. Your MAC address is labeled 'Ethernet ID'.
- When the MAC address, host name and selected IP address are entered into DD-WRT, click the Save Settings button at the bottom of the page. If you want to add a static DHCP entry, you must save the previous settings, then click Add to create a new entry.
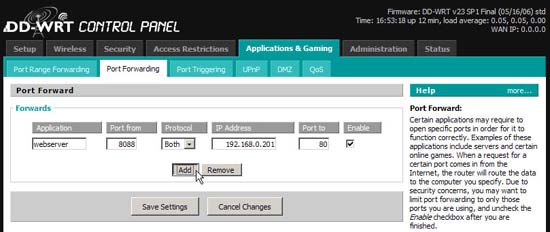
- If you like, add a port forwarding entry for the new static DHCP address. In the example, we have set up a Web server on a client. The web server listens to the traffic on the default port 80. However, the ISP blocks the traffic sent to port 80, because they do not want us to use the Web server (the use of the experiment here is completely personal). Go to Applications & Gaming / Port Forwarding in the DD-WRT menu. Click Add to create a new forwarding entry. We enter something that identifies it into the 'Application' field, in this case, 'webserver'. The router will listen for traffic on port 8088, so we can connect from outside without being locked by the ISP. Our destination IP address is a static DHCP created in step 5, our destination port is where the Web server is listening, port 80. Be sure to check this definition to take effect. And obviously, you need to save the settings, Save Settings.