Using eBox like Gateway: Firewall, Traffic Shaping, HTTP Proxy ...
TipsMake.com - eBox Platform is a server system based on Linux platform for small business models, allowing users to manage all network services such as firewall, DHCP, DNS, VPN, proxy, IDS, mail , data and printer sharing, VoIP, IM . These functions are closely linked, automatically adjusting, avoiding risks and saving time for administrators.
In the following article, TipsMake.com will show you how to use the eBox as Gateway with the ability to set up, customize the network, load balance between 2 Internet and Wan connections, rules multigateway for routes , traffic shaping, DHCP and DNS cache for LANs, HTTP proxies with many filters, anti-virus.
Test conditions
In this article we use the popular Gateway, application in any production or business environment such as a high school or a company with a maximum number of users of 250, equipped with the required application filter. Various Internet connections. Specifically in this article will detail, specifically how to set up two Internet routers with network cards for each individual. If it is necessary to increase bandwidth traffic, adding multiple routers is as easy as adding a new gateway, in which case all of these components are connected to the same surface using the IP address and parameters. subnet.
Our server system will have 3 network infrastructures, eth0 (192.168.2.254/24) and eth2 (192.168.1.254/24) as well as WAN (external) surface connecting to the same ADSL1 router (192.168.2.1/ 24) and ADSL2 (192.168.1.254/24), eth1 will take on several LAN roles (192.168.100.254/24).
Setting
The eBox Platform works on the x86 hardware platform, and make sure Ubuntu supports your server system. The installation process can proceed according to two different methods:
Using the eBox Platform Installer - this is the recommended method for users. The installation and application process is as simple and independent as when installing an application from a CD, some features have been set by default during the installation process.
Based on an existing Ubuntu LTS Server Edition platform. In this way, users must add the PPA repositories eBox Platform to the source list and install the necessary packages through it. You can review the details here and download more Virtual Machine image files.
Configure and set up the network
The first thing to do is set up the network. Open Network -> Interfaces , in this case we will set the static IP address and netmark parameters. For peripheral systems (eth0 and eth2), remember to check WAN options:
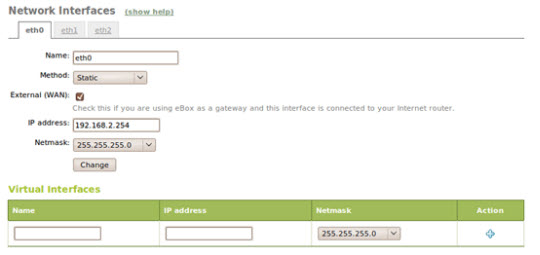
Then, edit eBox to use internal DNS at Network -> DNS :
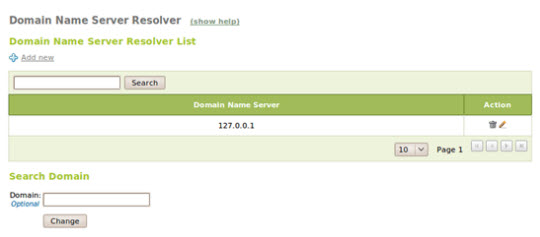
Next, check through the gateway. Open Network -> Gateways and proceed with creating two gateways, naming and memorizing the created Weight parameters to store bandwidth capacity information for each connection. In this example, both have the same speed, so we assign value 1 to them:
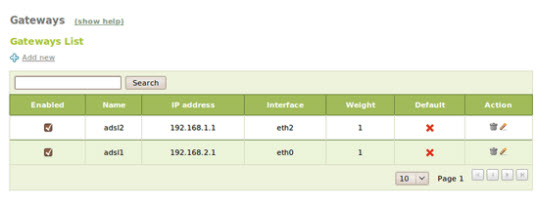
Firewall
In the default mode, the eBox will apply strict rules to surfaces, external connections and allow output connection signals from the LAN and from the eBox server itself.
Firewall mode allows users to install policies in a complex way, and each module must follow these rules. This feature is really useful for system administrators who are in charge of managing rules without making any mistakes.
These rules are divided into 5 classes, including all data traffic that can be found at Firewall -> Packet Filter :
Filtering rules từ nội bộ các mạng đến eBox
Filtering rules for internal networks
Filtering rules for traffic coming out from eBox
Cấu hình chế độ từ bên ngoài sang eBox
Cấu hình chế độ từ các mạng bên ngoài để nội bộ mạng
And here is the sample rule in this example:
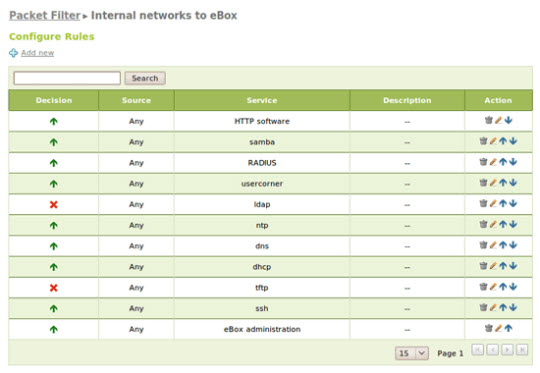
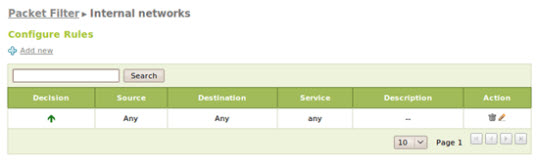
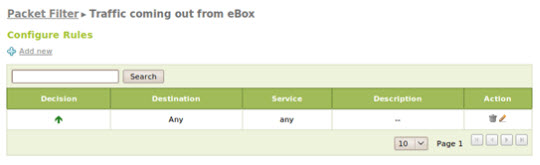
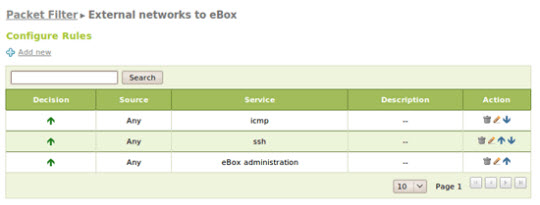
Set up Multigateway
Next, we need to enable balance between the two gateways. Open Network -> Balance Traffic and check the Balance Traffic box:
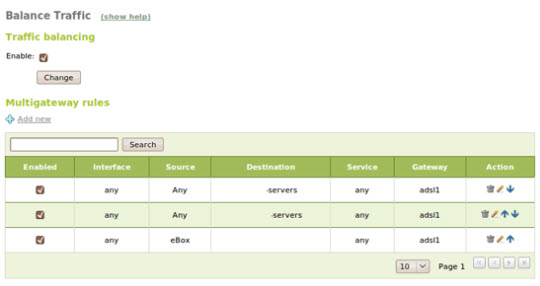
In addition, rules applicable to multigateway can define, initialize to follow connections that pass through one of the two gateways based on source, destination or port.
Along with the WAN failover feature, users can set the following set of functions: ping, DNS query or HTTP request to check if the gateway and Internet connection are working properly. If the percentage of success is below the allowed level, the gateway will automatically turn off and we will have to start over.
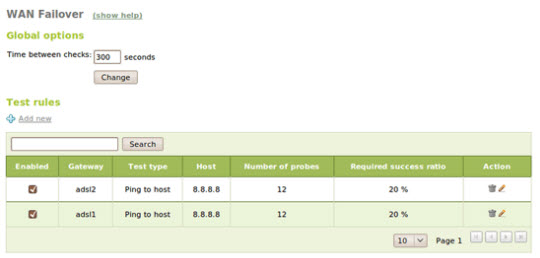
The multigateway rules for this phenomenon will not work, and the system will use the default device. When the gateway comes back, these rules will automatically set and adjust.
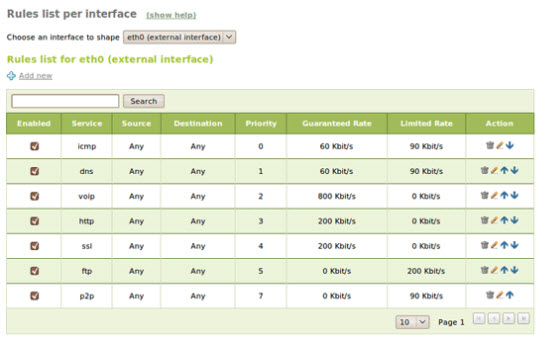
Traffic shaping
Traffic shaping, also known as Quality of Service (QoS), is very important in setting priorities between external data streams, enhancing priority for interactive services such as ICMP, DNS. or VoIP, and vice versa for other processes such as file transfer or P2P protocol. eBox well supports rules for traffic shaping based on source, destination, communication port and application layers (Layer 7).
DHCP, DNS cache and NTP
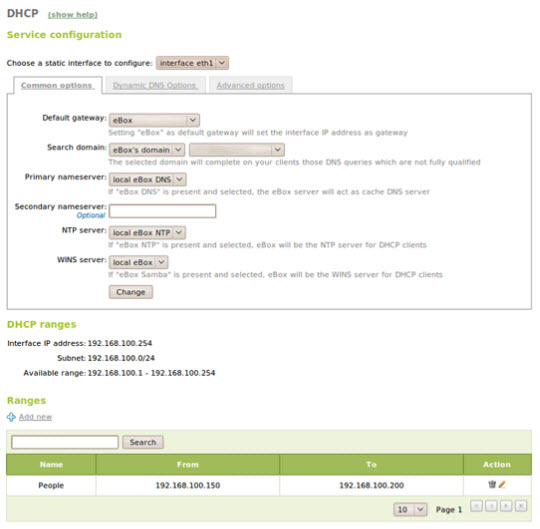
To set up all computers on the LAN easily, we need a DHCP server, DNS server and NTP server.
DNS caching server and NTP server will work outside the system when we enable the above module. To adjust DHCP, go to the DHCP menu, where we set up eBox as the default gateway value, DNS, NTP and other advanced options, network network for DHCP pool. Static components based on MAC and other features such as dynamic DNS or PXE are available.
HTTP Proxy
The last module to set up in the order of making a Gateway system is an HTTP proxy. eBox uses Squid and Dansguardian to do this. The HTTP proxy module uses different objects in the network to apply rules, such as Firewall or Traffic Shaping.
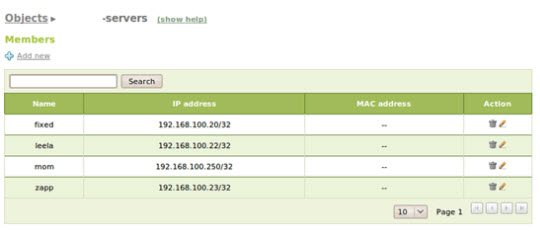
Here, we will proceed to apply two rules, and besides we need to create an object called spread for the entire LAN system and another object for non-LAN servers, where data streams are not subject to rules or filters. Select the Objects menu and create a new object, name it lan with a component with subnet 192.168.100.0/24, and another object is -servers with the address stream outside the server:
General settings
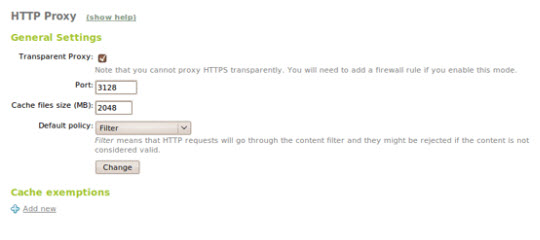
We can set the default policies, and the domain will not be stored on Squid's cache at HTTP Proxy -> General Configuration -> Default policy :
Always allow : allow, accept all requests
Filter : filter all requirements
Always deny : prevents all requests, except for those defined at the highest allowable level
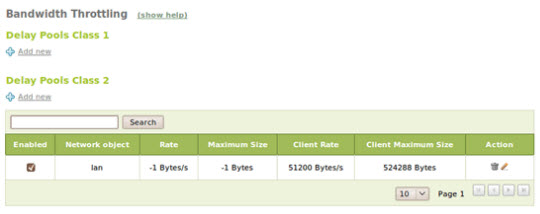
Bandwidth throttling
This feature ( HTTP Proxy -> Bandwidth Throttling ) is used to control download requests in large numbers. When conducting a download of any file, after defining the file size, the proxy speed drops to the allowable level. This policy can be applied to the entire LAN system using the Pools Class 1 Delay feature or each client using the Pools Class 2 Delay. In this example, we do not limit download speeds on each subnet but gender. term on each client: each file with a capacity of less than 50KB will be downloaded at maximum speed, larger files will be limited to 512 Kbps from the first 50KB:
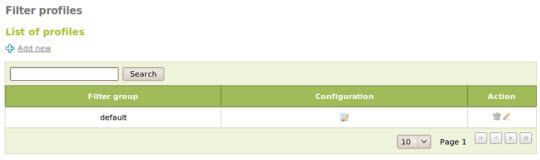
Filtering profiles
At the HTTP Proxy -> Filter Profiles section we can define, create different filtering conditions. By default, these profiles will be applied to all objects. And with these profiles, we can apply virus analysis on download files, dynamic filters based on keywords, extension files and MIME file policies. Besides, users can also define blacklist, whitelist, block unknown addresses, download URL data or other categories.
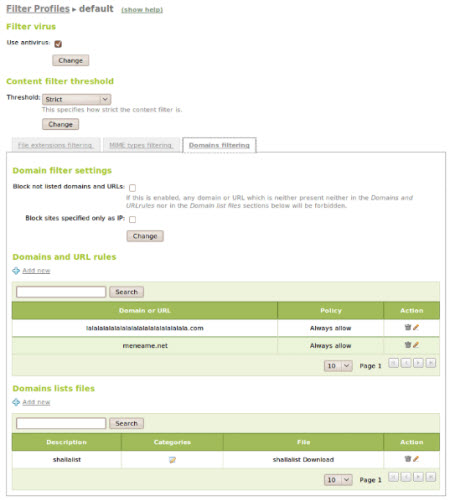
Once validated, different policies can be applied to groups of objects using Transparent Proxy, to objects in the network. Besides, you can also apply the default policy Always allow or Always deny to each group or object:
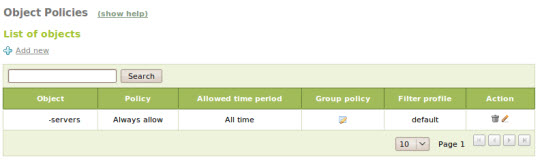
Logs and warnings
The use of the Logs module is used to query and revolve around all the log files of the service in the system. The only query pattern is available to filter and 'understand' all the events recorded in the log file without knowing its format.
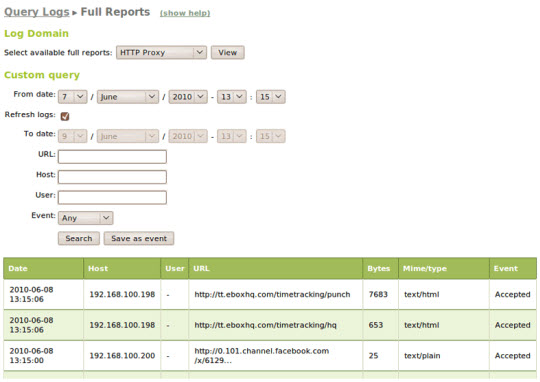
The unification of records shows information about a period of time allowing a thorough view of service operations:
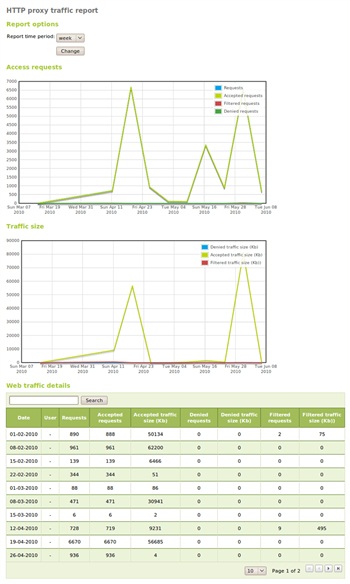
These logs allow users to create events and alert the status of the server system to the administrator.
eBox Platform is an open source alternative to Windows Small Business Server. In addition, eBox Technologies is the company that sponsors the development of the eBox Platform project in the form of GPL2 licensing, which is equipped to meet the needs of small and medium-sized businesses and organizations. handy, affordable and cost-effective management tool set. eBox Technologies is a branch of the parent company, providing to all eBox partners, customers, IT services, comprehensive solution providers of basic services of eBox, and providing thorough support. arts and skills training.
Good luck!