How to use ncdu to check disk space in Ubuntu
If so, you'll want to see how the ncdu command can help solve this problem.
Here's how to use ncdu to check disk space usage on Ubuntu and make disk space management an easy task.
Prerequisites: Install ncdu on Ubuntu
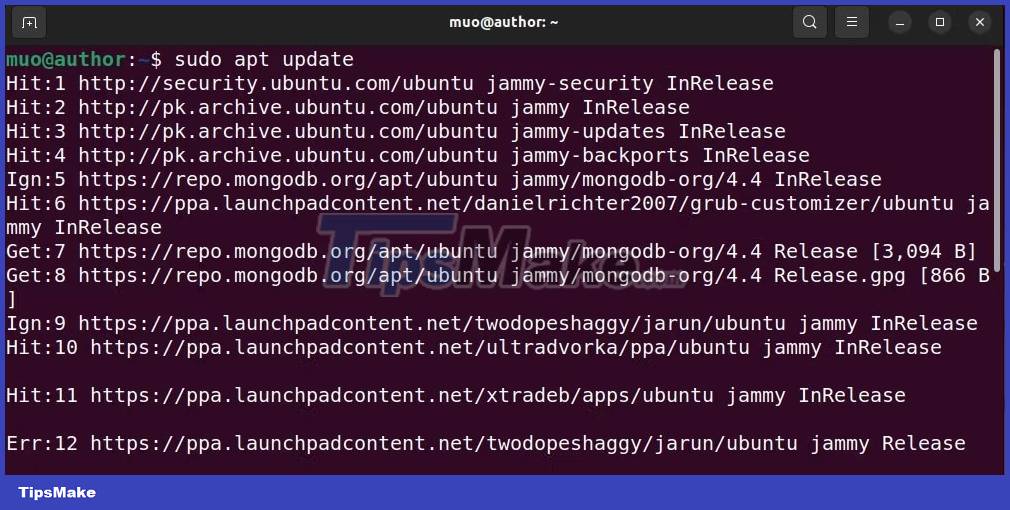
First, open terminal and update your system package information:
sudo apt update
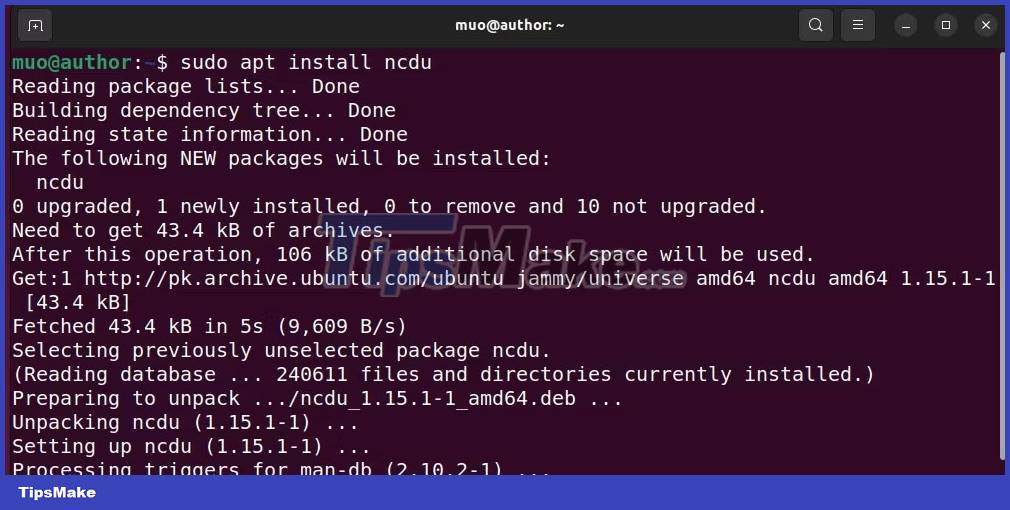
Next, install ncdu on your Ubuntu system:
sudo apt install ncdu
To check if you can now run ncdu, just display its version:
ncdu -version

How to use ncdu on Ubuntu
ncdu is a modern replacement for the classic du command. This utility helps you analyze the disk usage of any folder.
Let's explore some practical use cases of the ncdu command.
1. Check the disk usage of the current folder
Running ncdu without any options displays the current directory's drive usage:
ncdu

2. Display subfolder details
To select a subfolder, you can use the up and down arrow keys. Then, press the i key to check the information of that subfolder such as Name, Path, Type, Disk usage and Apparent size:

3. Navigate to a specific subfolder
To navigate to the selected subfolder, simply press the right arrow key:

View relevant drive usage details and press the left arrow key to switch back to the parent folder.
4. Check the disk space of the root directory
To check the disk usage of the root directory, use the -x option with a forward slash /.
sudo ncdu -x /
The -x option instructs ncdu to only include files on the same file system:

The ongoing scan will take a few seconds to complete and then display the results:

5. Check the disk usage of a specific folder
To visualize the disk usage of any given folder, specify the relative or absolute path, just like you did with the root folder. For example:
ncdu ~/snap

By mastering ncdu, you can easily test and manage your memory, which makes your Ubuntu experience more efficient. So, take control of your system's efficiency and organization, and implement these tips to enjoy an optimized Ubuntu experience like never before.