Is it possible to run .exe files on Linux?
Can the file .exebe run on Linux?

Yes, you can run files .exeon Linux through Wine (a free software). Wine acts as an intermediary to make the operating system (Linux) and files (created for Windows) compatible. This is the only way to run the file .exewithout Windows. Because .exeit was created specifically for the Windows operating system, to run this file you must have a compatible intermediary (like Wine) or a Windows version via a Windows emulator (meaning you will no longer be using only Linux). ).
How to download Wine?

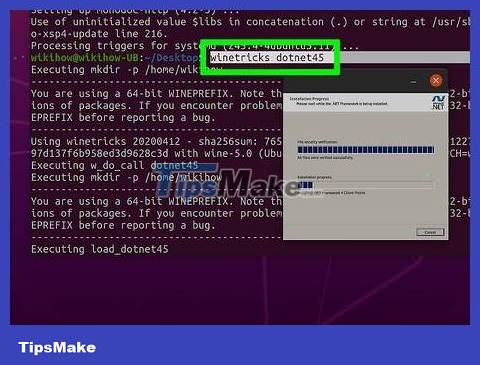
Open Terminal on Linux and type the following commands one after another. Start by updating the Linux kernel repository (where the software is collected). To do this, type sudo apt updateand press ↵ Enter. When asked, type your password and tap ↵ Enter. Then, when asked again, tap clearand press ↵ Enter. Now you are ready to enter the command line to download Wine:
Enter sudo apt-get install wineand press↵ Enter
Enter sudo apt-get install wine32and press↵ Enter
Enter sudo apt-get install libwineand press↵ Enter
Although the Terminal command line interface looks a bit intimidating, don't worry! It's unlikely that you'll mess things up, and all you need to do is copy these lines of code.
How to run files .exeon Linux?

Find the folder containing the file, then open the file with Wine. In Terminal, navigate to the folder containing the file using the command line . Then, run the file using the command line . For example: If the file is stored on your Desktop, follow this procedure:cd
Enter cd Desktop/and press↵ Enter
Enter wine example.exeand press↵ Enter
How to run Windows software on Linux?
Use Wine for single application. This is the only option to run software designed for Windows without having a copy of Windows on your computer. Wine is free, open source software that can emulate Windows to run Windows programs. As a result, you may encounter more errors and have to accept lower performance when running software through Wine.

Opt for a virtual machine for slightly better performance. A virtual machine is a program that runs a complete version of Windows in a separate window. This method is less error prone than running the application through Wine, because you will essentially be running the application in a Windows environment. The downside is that you will have to run two operating systems (Linux and Windows) at the same time, which can affect the performance of your personal computer.
Some popular virtual machines include: VirtualBox, VMware and KVM (virtual machine with Kernel kernel) built into Linux.
Because it consumes computer performance to run both Linux and Windows, this method is suitable for work applications such as Microsoft Office, but is not suitable for graphics/high-performance programs such as video games.

Use Dual-booting to run Windows games and complex applications. Dual-booting means you will reboot your computer into Windows so the application can run in the correct environment. This is the best method for games or applications that require high performance. Unfortunately, this means you'll have to restart your computer every time you want to run Windows software.
.exeWhat is the equivalent in Linux?
Linux has no direct equivalent to .exe. Windows specifies .exethat the file is executable, meaning that the operating system can run the file. On Linux, extensions are not what dictate which files can be executed. Instead, this operating system uses permissions (basic permissions are read r, write wand execute x). Permissions determine which files can be executed. Thus, Linux files can have many different extensions (like .sh) or no file extension and still be executable. Here's how to change permissions and run the file:
Type chmod +x file-name.runin the command line to change the file permissions to 'can be executed' (replace file-name with your file-name).
Type ./file-name.runto execute the file.
If you see an error, type sudo ./file-name.run. Typing sudoallows you to run the file as administrator. Be careful, because sudoit also allows you to change the entire system.
When installing software, you are often asked to type sudo.