How to check and manage disk space in Linux
An essential skill required by system administrators is to maintain the 'health' of both online and offline systems. This is especially important on production servers. Downtime or incidents can cause data loss on these servers. A common problem is that updates fail due to a lack of disk space, but there are some simple tests that users can perform when they encounter an error message, to keep critical systems smooth operation.
There are two main commands that can be used:
- df - This command reports the amount of disk space on the system.
- du - This command shows the capacity used by specific files.
Each of the above 2 commands is a different way of checking and can combine both commands at the same time if necessary. Here are some examples to illustrate the use of these commands.
How to control disk space on Linux systems
- Use the df command
- Use du command
- ncdu - Alternative to du
- Good 'cleanup' tools
- Autoremove
- Delete APT cache
- GUI-based options
- Bleachbit
Use the df command
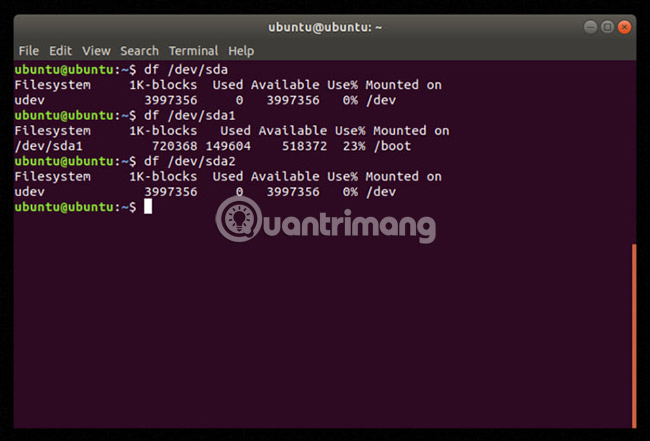
Open Terminal and type df, then press Enter. An output like the following will be displayed:

As can be seen, the results show all drives connected to the system. This result may be somewhat lengthy, so users can collapse the results by specifying the drive that is working. In the examples in this article, the main drive is reported as '/ dev / sda' - The author has also included specific partitions with '/ dev / sda1 ″ and " / dev / sda2'.
Can make df a little easier to read by typing:
df -h 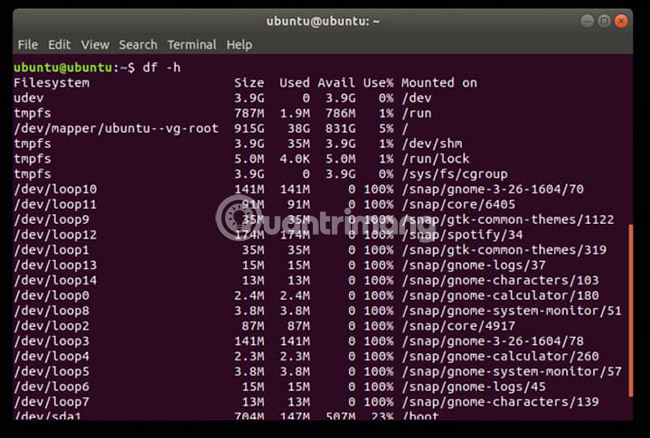
Users can collapse everything more by adding the --output flag . The parameters for this command are:
- source - The source of the device mount point
- size - Total blocks
- used - Total number of blocks used
- avail - Total number of blocks available
- Percent - Percent of used disk space
- target - Mount point for the device
In this example, the author uses only two parameters.
df --output=source,used,avail 
Use du command
Users may find that the drive is nearly full, but what causes this situation? This is the time to use the du command to display problem files. In a practical example, a user has detected a remote server with 98% disk space without any warning or real reason. Turns out, there are a lot of log files with java errors, with a total size of about 40GB. There is a lot of wasted disk space, so after using the du command , users can delete unnecessary files.
It should be warned that, if only typing du, the command will return all files and that can take a lot of time. Better define a few parameters. Let's find the 10 largest directories on the system.
du -a / | sort -n -r | head -n 10 This command will scan and create a similar type of result. Ignore warnings about rights at the present time.
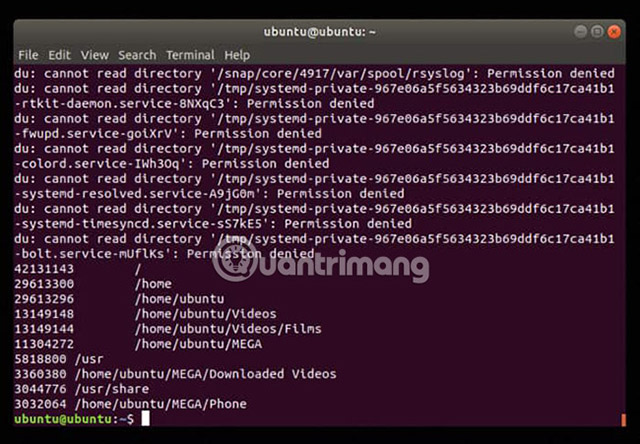
For a complete list of usable parameters, see the man page : http://linuxcommand.org/lc3_man_pages/du1.html
ncdu - Alternative to du
If you prefer a more interactive way to view hard drive information, try reviewing ncdu. Ncdu tool provides interface based on ncurses for travelers. This tool displays the same information as the travel command but in a more intuitive way. Ncdu also allows users to navigate between different folders with the arrow keys and use the Enter key to make a selection.
Users can install ncdu in Ubuntu using the command:
sudo apt install ncdu To use ncdu, enter:
ncdu /directory-to-scan Replace 'directory-to-scan' to the actual directory you want to scan. For example, to scan the entire hard drive, enter:
ncdu / 
Good 'cleanup' tools
In addition to the above commands, there are some basic things users can do to help reduce their disk usage to a minimum.
Autoremove
The most obvious way on Ubuntu-based systems is to check for outdated packages. In Terminal, users can enter:
sudo apt autoremove When the password has been entered correctly, the system will start deleting the orphaned package (the Orphaned package is a generic term, meaning that the package has no purpose on the running system). It can also remove old kernels that take up space and are mostly unnecessary.
Delete APT cache
When Ubuntu downloads packages, it keeps apt files so they can be easily reinstalled if needed. These files take up disk space and this space can be recovered with:
sudo du -sh /var/cache/apt Now, it is possible to clean these files with the following command:
sudo apt autoclean GUI-based options
What if the user feels all of the above Terminal commands are too complicated, or simply doesn't like messing things up with the command line because they can damage the system? Thankfully, Linux has a number of GUI-based tools to use.
Bleachbit
This is a program available for both Windows and Linux systems. Bleachbit works in a similar way on these two platforms. Bleachbit can be downloaded here, but most are available in system repositories. After installation, users can run the tool by selecting the checkboxes.
As the reader has seen, checking the system and the drive capacity will help prevent problems. Users also need to clean the drive regularly.
Hope you are succesful.