How to run Android on Linux using a virtual machine
TipsMake recently put together a list of top Android emulators for Linux systems and was disappointed to find that there is no suitable application that can mimic Android on a Linux distribution.
That said, there is a need to find a good way to run Android on Linux using a virtual machine that supports the Play Store. And in fact, this works better than an emulator due to the better binary translation feature and desktop-like.
Running Android on Linux using a virtual machine
Before continuing, let us briefly explain how to run Android on Linux. We will be using an open source project called Android-x86 to migrate an ARM-based Android operating system to an x86-based one. Basically, with an ISO image of Android-x86, you can boot Android on any desktop platform, be it Windows or Linux.
You can also install and run the best Android games or applications on your Linux machine. So here is the guide you must follow to install Android on Linux using a virtual machine.
Basic setup
1. First of all, download the Android 9 ISO image here. Depending on your architecture, choose a 64-bit or 32-bit ISO image. By the way, currently, Android 9 is the latest desktop-to-desktop operating system.
2. Once you've downloaded the ISO image for Android, continue to download VirtualBox. You can find setup files for all Linux distributions here. Once the download is complete, install VirtualBox on the system.
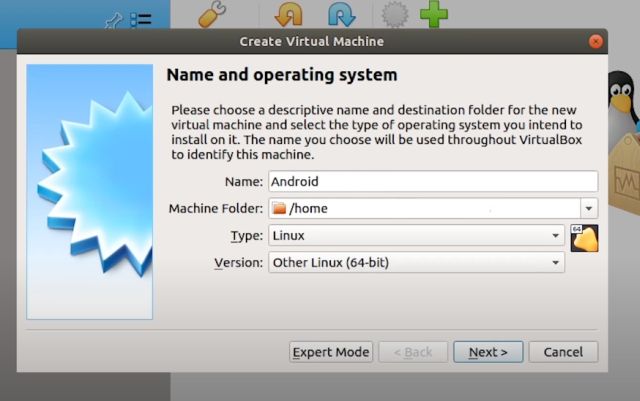
3. Here, I'm running VirtualBox on Ubuntu. Now, click New on the menu bar and give the virtual machine a name (eg ' Android '). Select Type as 'Linux' and select 'Other Linux (64-bit)' in Version. If you have a 32-bit machine, select 'Other Linux (32-bit)' . Finally, click 'Next'.
4. On next window, allocate at least 2GB RAM. If you have more RAM, increase it to 4GB for better performance when using Android.
5. Next, select 'Create a virtual hard disk now' and click 'Create'.
6. After that, select 'VDI' and click 'Next'.
7. Select 'Dynamically allocated' and click on 'Next'.
8. Here, enter the amount of storage you want to allocate to Android. The default is 8GB, but you can increase the storage to 16GB or more depending on your usage. Finally, click 'Create'.

Configure Android virtual machine on Linux
1. Now, it's time to configure a few things so that you get the best performance out of running Android on Linux. On VirtualBox, click 'System'.
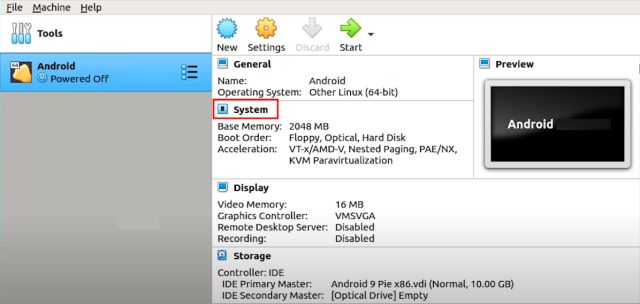
2. Move to the tab "Processor" and allocate at least 2 CPU cores. You can also increase it to 4 for better gaming performance.
3. Next, switch to the 'Acceleration' tab and select 'KVM' from the drop-down menu.
4. Once that's done, go to the 'Display' section and change the 'Graphics controller' to 'VBoxSVGA'. This is the most important step otherwise you will be stuck on a blank screen. Besides, please increase Video Memory to at least 64 - 128MB.
5. Finally, go to 'Storage' and select the 'Empty' submenu . Here, click on the disk icon and select 'Choose a disk file' .
6. Now, select the Android ISO image you downloaded in the first step. Basically, you've completed the process. Just click the 'OK' button .
Start Android in Linux
1. After basic setup and configuration, you are now ready to boot Android on Linux. Simply, select 'Android' in the left pane and then click 'Start'.

2. Here, go to "Advanced options".
3. Now, select 'Auto_Installation…' and press Enter.
4. On the next screen, select 'Yes' and press Enter.
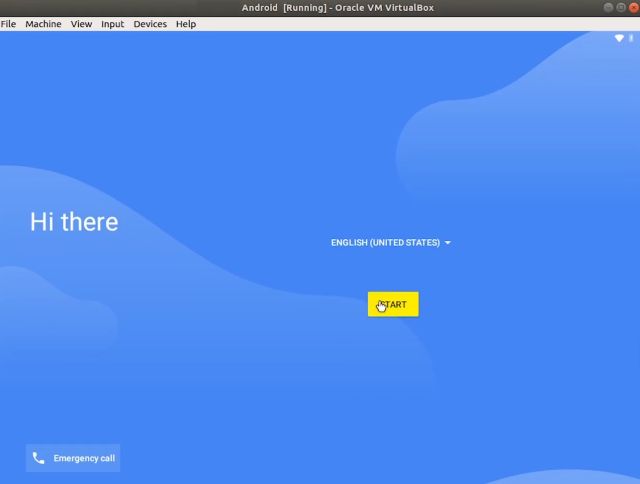
5. Finally, you will get an option to 'Run Android-x86' on your Linux machine. Press Enter and Android will start booting on your Linux machine later.
6. You can go through initial setup screen just like Android smartphone.
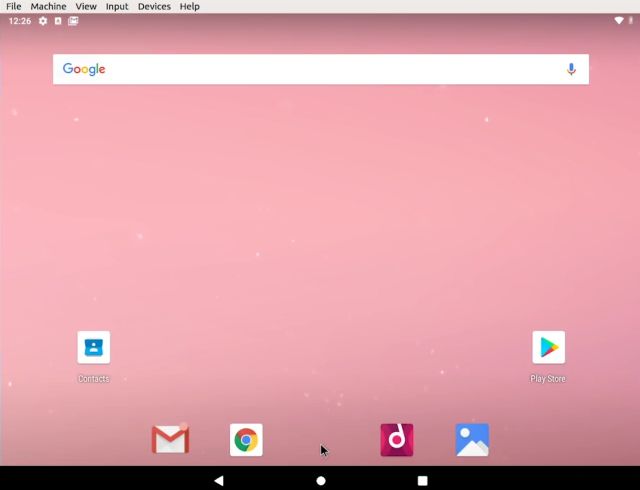
7. Finally, you've got Android 9 running on Linux with almost natively performance. That was amazing. From now on, just press the 'Start' button in VirtualBox and Android will be ready for you to use.
9. In case, you want to remove Android from Linux then simply right click on the Android virtual machine you created and select 'Remove'.
10. Next, click 'Delete all files' . It will erase the virtual hard drive and all associated files, freeing up all the space on your computer.
You should read it
- How to prevent and handle when Windows Update deletes Linux
- How to set up a Windows virtual machine in Linux
- How to Create an ARM-Based Linux Virtual Machine with Azure
- How to access Linux server from Android
- Steps to install and create virtual machine on Android Studio
- How to install Kali Linux on Android using Linux Deploy
 How to mount a Linux file system using WSL2 on Windows 10
How to mount a Linux file system using WSL2 on Windows 10 How to fix Checksum with the fsck command in Linux
How to fix Checksum with the fsck command in Linux How to install and use Microsoft Defender in Linux
How to install and use Microsoft Defender in Linux 8 commands for efficient management of Linux processes
8 commands for efficient management of Linux processes How to configure color temperature in GNOME Night Light
How to configure color temperature in GNOME Night Light How to install KDE Plasma Desktop on CentOS 8
How to install KDE Plasma Desktop on CentOS 8