How to Open Applications Using Terminal on Mac
Part 1 of 2:
Opening an Application
-
 Launch Terminal. Look for Terminal in Applications → Utilities → Terminal. You can also open Terminal by using spotlight in the right hand top corner.
Launch Terminal. Look for Terminal in Applications → Utilities → Terminal. You can also open Terminal by using spotlight in the right hand top corner. -
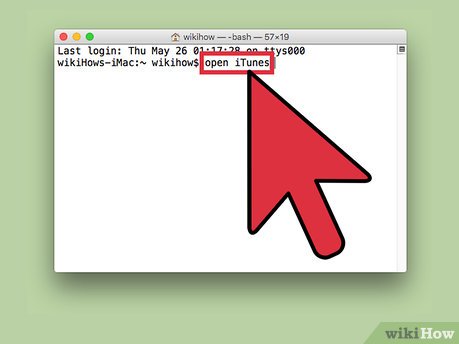
 Open an application from anywhere. The open command normally requires you to input the full file path from your current directory. However, adding -a followed by the name of an application instructs Terminal to open that Application, no matter where it is located. For example:
Open an application from anywhere. The open command normally requires you to input the full file path from your current directory. However, adding -a followed by the name of an application instructs Terminal to open that Application, no matter where it is located. For example:- To open iTunes:
open -a iTunes - Use quotation marks if the application has a space in its name:
open -a "App Store"
- To open iTunes:
-
 Open a file with a specific application. You can also use this command to override the default application for a file type. Just type in the file path followed by -a and the application name. If you're not sure how to enter file paths, see the Troubleshooting section below.
Open a file with a specific application. You can also use this command to override the default application for a file type. Just type in the file path followed by -a and the application name. If you're not sure how to enter file paths, see the Troubleshooting section below.- For example, you can open a .doc file with TextEdit:
open Downloads/Instructions.doc -a TextEdit
- For example, you can open a .doc file with TextEdit:
-
 Include additional options. Enter info open to see a full list of options for modifying the open command. (When you are finished, press Control+C to return to the command line.) Here are a couple basic examples:
Include additional options. Enter info open to see a full list of options for modifying the open command. (When you are finished, press Control+C to return to the command line.) Here are a couple basic examples:- Use -e to specify TextEdit, or -t to specify your default text editor:
open Downloads/Instructions.doc -e - Add -g to keep the application in the background, so you remain centered in Terminal:
open -g -a iTunes
- Use -e to specify TextEdit, or -t to specify your default text editor:
-
 Add -F to open a "fresh" copy of the application. This will destroy your unsaved changes, but may help if a document is causing the application to crash when opened:
Add -F to open a "fresh" copy of the application. This will destroy your unsaved changes, but may help if a document is causing the application to crash when opened:- open -F -a TextEdit
-
 Open multiple instances of the same application with -n. This may be useful if you are comparing different access levels, or if the application only allows one window. For example, enter this command repeatedly to open multiple instances of an alarm clock program:
Open multiple instances of the same application with -n. This may be useful if you are comparing different access levels, or if the application only allows one window. For example, enter this command repeatedly to open multiple instances of an alarm clock program:- open -n -a "Wake Up Time" (Note: this is not a default OS X program.)
- This may cause unexpected behavior in other applications that interact with the duplicate application.
-
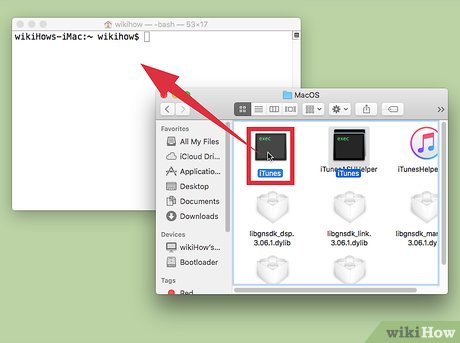
 Run an application inside Terminal. Instead of just opening an application normally, Terminal can host it. This is useful for debugging, as error messages and other console outputs will appear in that Terminal window. Here's how to do this:[1]
Run an application inside Terminal. Instead of just opening an application normally, Terminal can host it. This is useful for debugging, as error messages and other console outputs will appear in that Terminal window. Here's how to do this:[1]- Locate the application in Finder.
- Right-click the application and select "Show Package Contents."
- Locate the executable file. Typically, this is in Contents → MacOS, and has the same name as the application.
- Drag that file onto your blank Terminal command line. Hit Enter to launch that program.
- Leave your Terminal window open while you use the application. Quit the application to return to regular Terminal operations.
Part 2 of 2:
Troubleshooting
-
 Find the application name. If Terminal displays the error message "Unable to find application named...," find the exact name of the application by browsing an alphabetical list:[2]
Find the application name. If Terminal displays the error message "Unable to find application named...," find the exact name of the application by browsing an alphabetical list:[2]- Click the apple symbol in the top left corner of your screen.
- Hold down ⌥ Option and click System Information in the drop-down menu.
- In the System Information window's left sidebar, click Software → Applications. It may take a couple minutes to load the list.
-
 Understand absolute file paths. If Terminal displays "the file ... does not exist," you did not type the correct file path. An easy way to avoid mistakes is to drag and drop the file from Finder directly into your Terminal command line (after typing "open," but before hitting Enter.) This will enter the absolute file path, which will always point to that file.
Understand absolute file paths. If Terminal displays "the file ... does not exist," you did not type the correct file path. An easy way to avoid mistakes is to drag and drop the file from Finder directly into your Terminal command line (after typing "open," but before hitting Enter.) This will enter the absolute file path, which will always point to that file.- An absolute file path always begins with the symbol /. It describes the file path in relation to the root directory (usually "Macintosh HD").
-
 Understands relative file paths. The start of your Terminal command line always displays the current directory you are located in. By default, this is your Home directory, named after your username. A relative file path begins with ./ or with no special characters, and describes the file's location in relation to your current directory.[3] If you're having trouble figuring this out, follow these steps:
Understands relative file paths. The start of your Terminal command line always displays the current directory you are located in. By default, this is your Home directory, named after your username. A relative file path begins with ./ or with no special characters, and describes the file's location in relation to your current directory.[3] If you're having trouble figuring this out, follow these steps:- Enter pwd to check your current directory. The file you are trying to open must be within this directory, not at a higher level.
- Find your current directory in Finder. Open a series of folder until you reach the file you'd like to open.
- Type in the names of the folders you opened in order, separated by / symbols, then end with the file name. For example, open Documents/Writing/Novel/ch3.pdf. (You may start with ./ in front of Documents for the same result.)
-
 Switch directories. You can return to your Home directory with cd ~/, or switch to a lower-level directory with cd followed by the folder name — for example, cd Documents/Finances. Remember, the file you are trying to open must be inside your current directory, but you may use any application to open it regardless of location.
Switch directories. You can return to your Home directory with cd ~/, or switch to a lower-level directory with cd followed by the folder name — for example, cd Documents/Finances. Remember, the file you are trying to open must be inside your current directory, but you may use any application to open it regardless of location. -
 Find the correct file name. Your file name must include the extension at the end of its name. If the extension is hidden, use any of these methods to find it:
Find the correct file name. Your file name must include the extension at the end of its name. If the extension is hidden, use any of these methods to find it:- Select the file in Finder. Press ⌘ Command+I. In the Info window, look for "file name & extension" to see the whole name.
- Or switch directories to the folder that contains the file. Enter ls into your Terminal command line to list all files in your directory.
- Or drag and drop the file into your Terminal window.
Share by
David Pac
Update 04 March 2020