How to Configure Firewall on Debian Using UFW
Securing a Debian system is essential and an important step in achieving this is configuring the firewall. Firewalls are not complicated. UFW provides a user-friendly way to control incoming and outgoing traffic, strengthening your system's defenses against unauthorized access and potential threats.
Here's everything you need to know about effectively installing, configuring, and managing a firewall using UFW on a Debian system.
What is UFW?
UFW or Uncomplicated Firewall is a user-friendly front-end for iptables and one of the best firewalls for Linux. You can easily install this firewall management tool on different Linux distributions, including Debian.
UFW simplifies the complex iptables configuration process by providing simplified interfaces and commands. This firewall allows you to define rules for handling network traffic. This ensures that only authorized connections are allowed and prevents potential security risks.
Note : Firewalls are very different from antivirus software.
How to Install UFW on Debian
Before moving on to the UFW configuration, install it on your Debian machine. To do that, first open a terminal and update the packages with:
sudo apt updateInstall UFW on Debian with:
sudo apt install ufw -y 
Once UFW is installed, you can enable it with:
sudo ufw enable 
Defining UFW Rules on Debian
You can control the network traffic of a Debian system by defining some UFW rules. For example, here's a description of some of the UFW rules:
- allow : Grants access to any traffic to specified services, ports, or services
- deny : Stops access to any traffic to specified services, ports or IP addresses
- Ports can be identified by numbers, such as 22, or by their names, such as
- Specify a single IP address or use the any option to allow all IP addresses
- UFW by default blocks all computer IP addresses
Configure Default UFW Rules on Debian
To configure default firewall rules on Debian, see the examples given.
1. Allow all outgoing connections
By default, UFW blocks or denies all outgoing connections. However, you can allow them with:
sudo ufw default allow outgoing 
2. Block or deny all incoming connections
Execute the following command to block all incoming connections:
sudo ufw default deny incoming 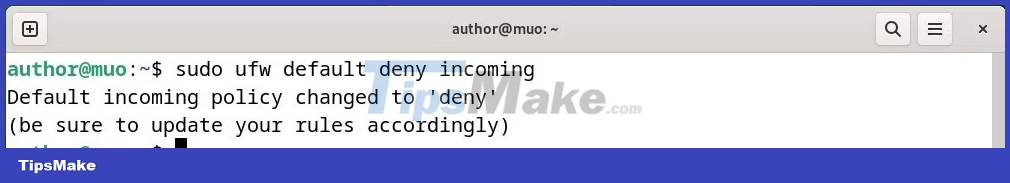
3. Allow a specific port
To allow network traffic on a port identified with UFW, add the port number to the whitelist:
sudo ufw allow 22 
Or port name:
sudo ufw allow ssh 
4. Deny a specific port
Similarly, deny network traffic on any given port using the deny method with the port number or name:
sudo ufw deny 443 
5. Allow IP addresses
To allow traffic from a specific IP address, run:
sudo ufw allow from 192.168.9.12 
6. Reject IP address
You can also deny traffic from an IP address with:
sudo ufw deny from 192.168.9.12 
7. Restart UFW
After defining the desired rules, simply restart UFW to apply all the changes:
sudo systemctl restart ufw8. UFW . status display
Display the status of UFW and its operating rules with:
sudo ufw status verbose 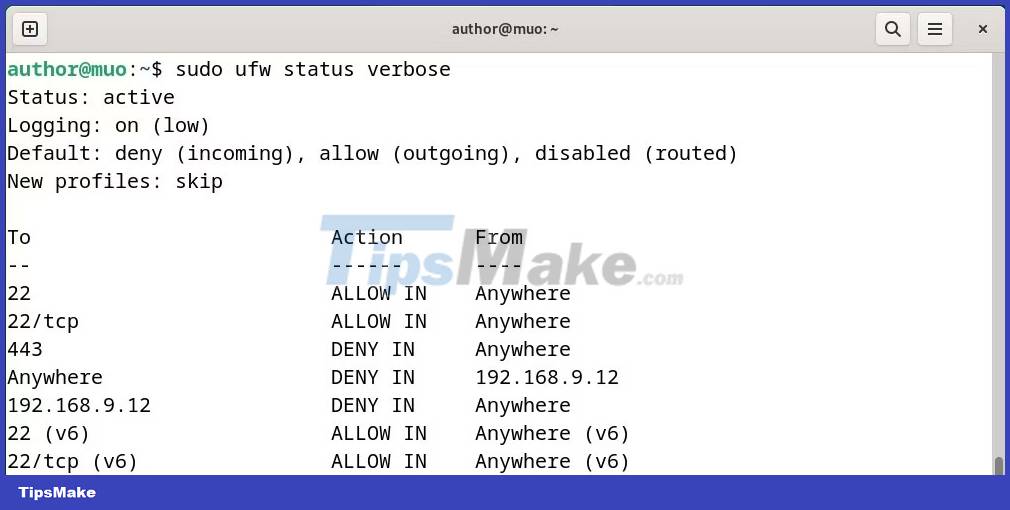
9. Reset UFW . rules
To reset all UFW rules to default, run:
sudo ufw reset 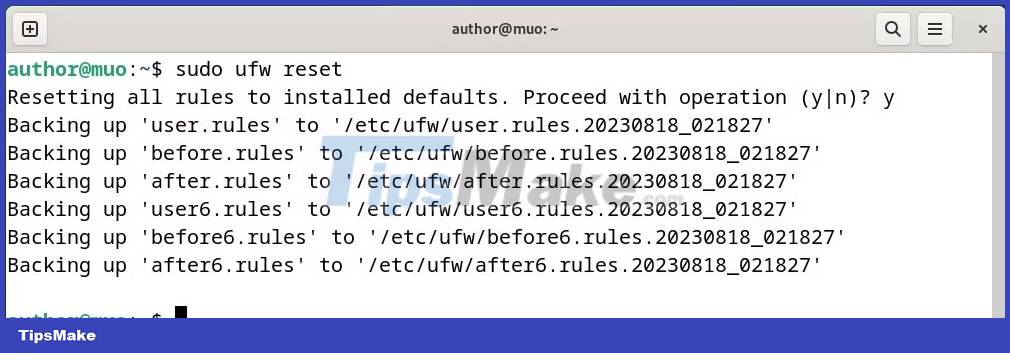
How to Uninstall UFW on Debian
You can easily uninstall UFW on Debian with:
sudo apt purge ufw gufw -y 
You should read it
- ★ How to configure the router as an IoT firewall
- ★ Install and configure email handling solutions on TMG 2010 Firewall - Part 2: E-Mail Policy
- ★ Install and configure email handling solutions on TMG 2010 Firewall - Part 5
- ★ Configure advanced firewall in Windows Server 2008 using the MMC snap-in
- ★ Configure advanced firewall in Windows 2008 using NETSH CLI