Install and configure email handling solutions on TMG 2010 Firewall - Part 2: E-Mail Policy
Network Administration - In Part 2 of the Install and configure email handling solution on this TMG 2010 Firewall, we will show you how to configure email protection policies.
 Install and configure the solution to handle email on TMG 2010 Firewall - Part 1: Installation
Install and configure the solution to handle email on TMG 2010 Firewall - Part 1: Installation
In part 1 of this series of email handling solutions on this TMG firewall, I showed you the installation process needed to create the gateway email for the TMG firewall. So far, when the email gateway components are installed, we can learn more about how to configure email protection policies. Start by activating E-Mail Policy. That means we will enable basic E-Mail protection features included in the TMG Email Gateway solution. After activating email protection methods, you will have an anti-spam and anti-malware solution right away. However, as you will see in the later sections of this series, you will have quite a few options for customizing your email policy to get a level of protection that meets the organization's requirements. mine.
Again, TMG uses a " one-to-two " approach to email protection:
- Forefront Protection for Exchange 2010 - FPE is an anti-spam and anti-malware application, and also allows content filtering.
- Exchange Edge Server - The Exchange Edge Server can perform connection filtering and anti-spam tasks.
The combination of Exchange Edge Server and Forefront Protection for Exchange makes TMG firewall a powerful weapon in your arsenal, helping you fight spam and malware production.
Let's begin! There are many issues that we need to introduce to you here.
Enable email protection
Open the TMG firewall interface, click on the computer name in the left pane of the console. Here you will see a new node not included in previous versions of the firewall - that's the E-Mail Policy button. Click this E-Mail Policy button as shown in Figure 1.
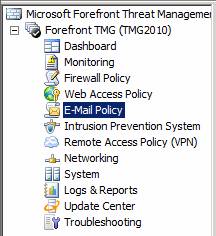
Figure 1
After clicking the E-Mail Policy button, you will see three tabs in the middle panel.
- E-Mail Policy. Configure settings tab to enable email protection.
- Spam Filtering . The tab configures anti-spam settings after email protection is enabled.
- Virus and Content Filtering . The tab configures anti-malware settings and content filtering to protect email.
Let's start with email protection by clicking the Configure E-Mail Policy link as shown in Figure 2 below.
Figure 2
You will then see the Welcome to the E-Mail Policy Wizard page shown in Figure 3. Click Next .
Figure 3
The next page is the Internal Mail Server Configuration shown in Figure 4. Here you need to configure the TMG firewall components such as the name, IP address of the internal SMTP server, which is the SMTP server on the internal network of you, this server is configured to accept incoming email from the Internet. It is also an internal SMTP server that will send email from within the organization to the outside Internet.
Click the Add button next to the Internal mail servers section . You will see the Computer dialog box appear. Enter the name of the SMTP server and the server's IP address. Alternatively, you can use the Browse button to find the device, the IP address and the name that will be entered. Note that there may be multiple mail servers in the internal network to accept incoming mail.
Click OK .
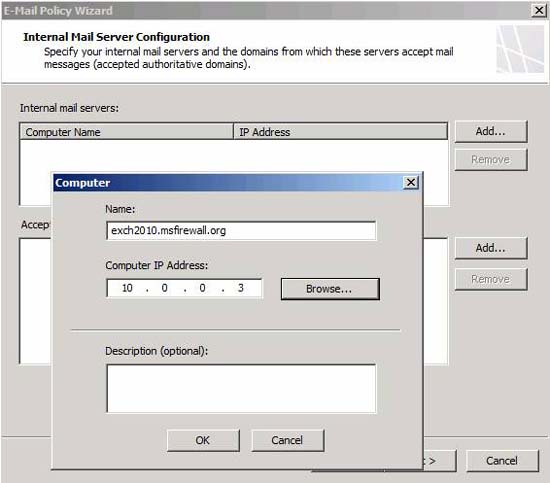
Figure 4
Now click the Add button, this is the button next to Accepted authoritative domains . You'll see the Add Authoritative Domain dialog box appear, as shown in Figure 5 below. Enter the domain name you want to accept incoming email. If there are multiple email domains to receive email, you can click the Add button again to add other domains.
Note : Emails sent to your organization through the TMG firewall without the destination email domain in the list will be removed. This is to prevent your organization from working as an SMTP relay exploited by the spammer.
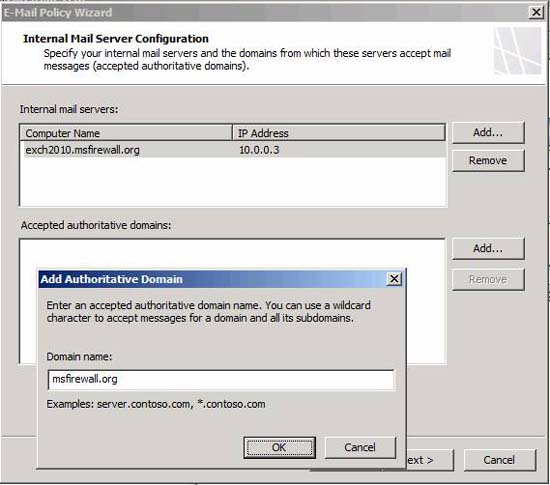
Figure 5
Click Next on the Internal Mail Server Configuration page , as shown in Figure 6.
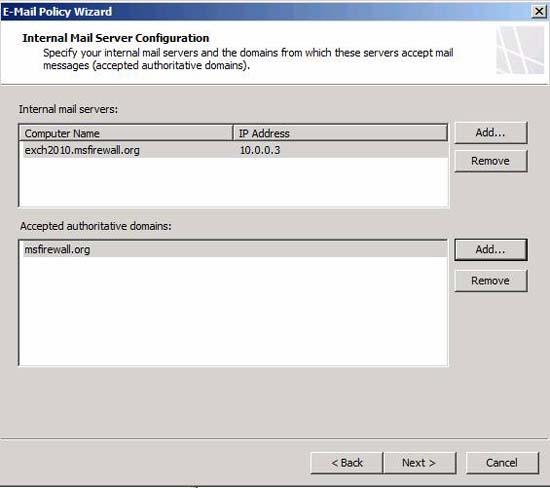
Figure 6
On the Internal E-Mail Listener Configuration page , as shown in Figure 7, select the network from which you want to send the email. If there are multiple IP addresses on that NIC, you can click the Select Addresses button and select a certain IP address to accept mail sent from the internal SMTP server.
Click Next .
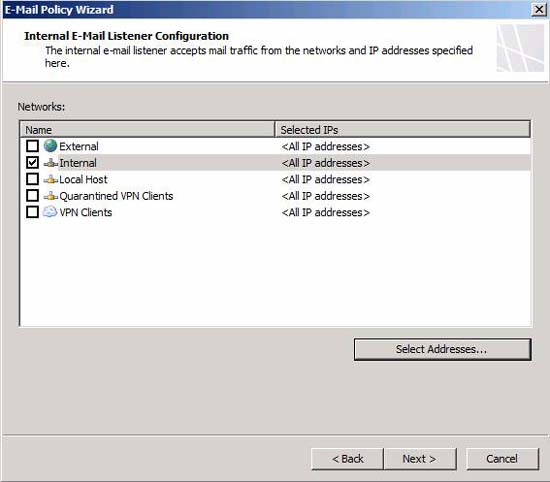
Figure 7
In the External E-Mail Listener Configuration page , shown in Figure 8, check the checkbox for the network on which you want to accept incoming email. In most cases, it will be the External network. If there are multiple IP addresses on that interface, you can click the Select Addresses button and select an IP address that is the address you want to accept the outgoing mail. In the FQDN or IP address box on this page, enter Fully Qualified Domain Name that you want the TMG firewall to use as a response to the SMTP session initialization messages, such as HELO or EHLO. Make sure that the reverse DNS record for this name resolves the IP address correctly, which is the address receiving the incoming mail.
Click Next .
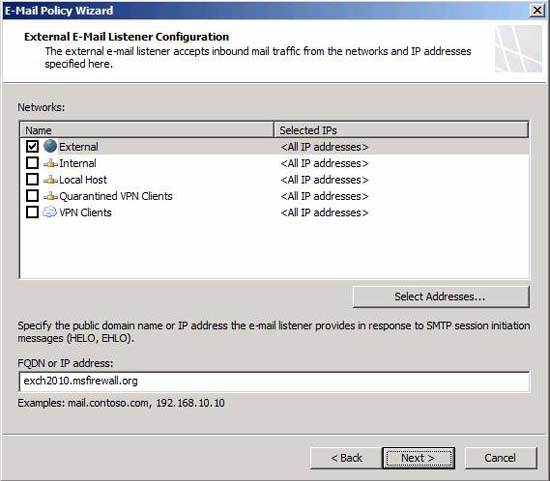
Figure 8
Email policy options
On the E-Mail Policy Configuration page , shown in Figure 9, you can activate the following options:
- Spam filtering: This option will enable Forefront Protection for Exchange's antispam technique and use many antispam filtering methods to protect your organization from spam. It also takes advantage of the anti-spam technique available in Exchange Edge Server.
- Virus and content filtering: This option activates Forefront Protection for Exchange's anti-virus protection mode and uses many anti-virus engines to protect you from malware-producing emails; In addition, it can perform content filtering to block inappropriate content.
- Connectivityfor EdgeSync traffic: You can register Exchange Edge components on the TMG firewall with your Exchange organization. This allows you to perform mail recipient filtering, addresses addressed to people not in the organization will be removed at the gateway email.
For the strongest protection, check the check boxes and click Next .
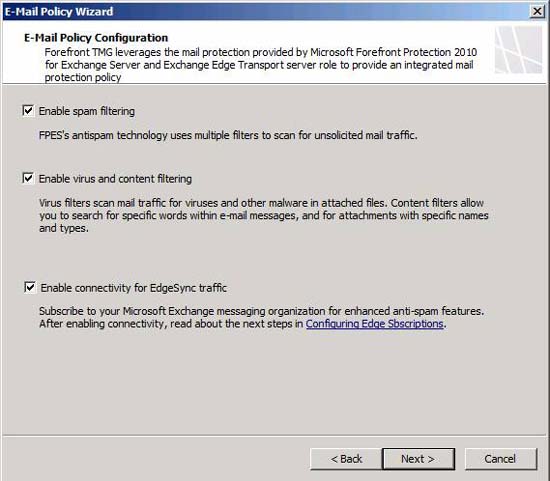
Figure 9
If you select Enable connectivity for EdgeSync traffic , you will have many other things to do. There are two steps you need to take here and we will see how to perform those steps in this article. Help entries for two steps - To create an Edge Subscription file and Using the Exchange Management Console to import the Edge Subscription file - shown in Figure 10 and 11 below.

Figure 10

Figure 11
Click Finish in the last page of the Completing the E-Mail Policy Wizard, as shown in Figure 12.
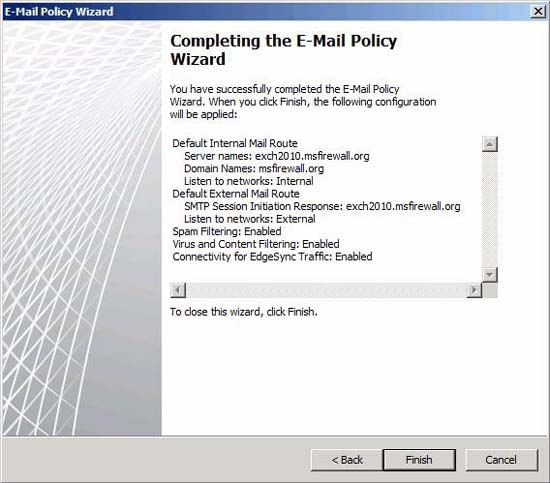
Figure 12
The Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway dialog box, like the one shown in Figure 13, will appear, asking you to enable the System Policy Rules needed for receiving and forwarding SMTP traffic. We will do that, so click Yes .
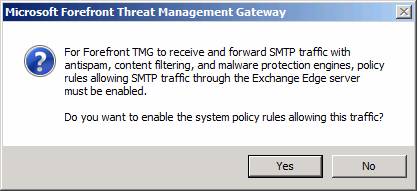
Figure 13
Configure email policy
At this point, we are ready to study and configure email policy. Now you can click the Apply button to save your configuration, or you can wait until it's done. It will save for you. I prefer to click Apply rather than not, because I myself don't want to lose the configuration changes I made when something went wrong, such as the console crashing. Although there is no problem with the TMG firewall console during my work, I will never know when such bad things can happen - and the best way to prevent that. is the way I chose.
You can see, in the middle pane of the interface in the E-Mail Policy tab, the following settings:
- Email Policy : Enabled
- Spam Filtering: Enabled
- Virus and Content Filtering: Enabled
- Edge Subscription: Enabled
- Protection Manager Integration: Disabled
- E-Mail Policy Integration Mode: Enabled
Note that Forefront Protection Manager (formerly known as 'Stirling') cannot be configured at this time because Forefront Protection Manger remains in a state of change. We will mention this when FPM is more stable and the product group has a better idea of how to end it.
At this point, double-click the External_Mail_Servers section, as shown in Figure 14 below:
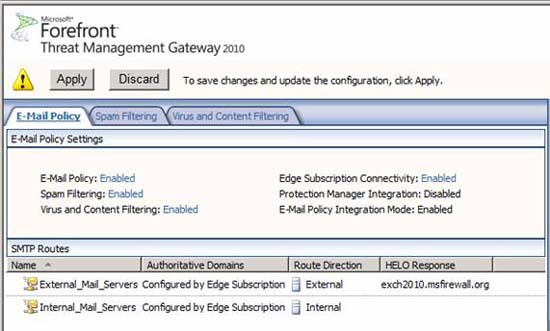
Figure 14
You will then see the External_Mail_Servers Properties dialog box, as shown in Figure 15, where we can upgrade the External Mail Server settings. On the Listener tab, you can see the Networks and FQDN settings that you set in the wizard.
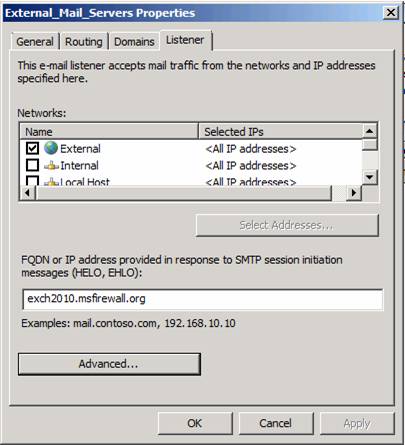
Figure 15
If you click on the E-Mail Policy link at the top of the middle pane (('Enabled' in Figure 14), the E-Mail Policy dialog box appears as shown in Figure 16. Here you can enable or disable security. and Email Policy We will also see the same options for other links in the upper part of the middle pane when accessing the E-Mail Policy tab.
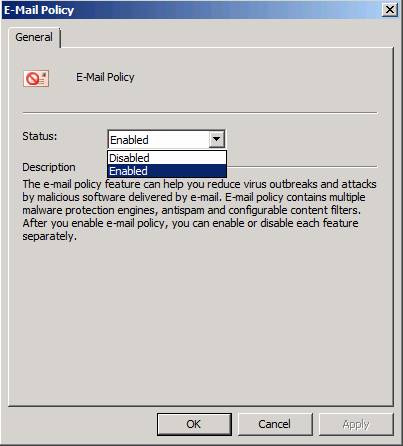
Figure 16
Here, you have a working configuration and you can now configure your MX records to send mail to the external interface of the TMG firewall. The default settings will work well and will provide a high level of protection. However, as I mentioned above, you can customize the configuration to a large scale and we'll take a look at those customization options later in this series.
Troubleshoot
If it detects that incoming mail doesn't reach the TMG firewall after making changes to the MX record, consider some of the following issues to fix the problem:
- Checking the TTL on the MX record, check the A record that the MX record is pointing to - this allows you to know how quickly your changes will be "popular" on the Internet.
- If you have a firewall or NAT device in front of the TMG firewall, make sure that it forwards incoming messages in TCP port 25 to the IP address you configured when running the wizard as the incoming IP address.
- If you encounter problems with outgoing mail, make sure you have configured your SMTP server to use the TMG firewall as a 'smart host' or have configured Exchange 2007/2010 servers to Use the firewall for outgoing connections.
- Check the Services section of the TMG firewall to ensure that all TMG firewall services, such as Exchange and Forefront Protection for Exchange services work.
Conclude
In the second part of this article series, we went over some of the necessary procedures for the Email Protection components to work. We have configured the incoming SMTP listener listener, which is used to accept incoming mail, and configure the outgoing SMTP listener, used to send mail. In addition, we have enabled Forefront Protection for Exchange components and Exchange Edge to enable anti-spam and anti-virus protection.
In the next part of this article series, I will show you more details about the spam filtering configuration on the TMG firewall. Some configuration options we will cover in those sections, including anti-spam features such as allowed IP addresses, authorized providers, blocked IP lists, locked providers. , filter content, filter recipients, filter outgoing mail, configure sender ID and configure recipient reputation, .
You should read it
- ★ Install and configure the solution to handle email on TMG 2010 Firewall - Part 1: Installation
- ★ What is a firewall? General knowledge about Firewall
- ★ Install and configure email handling solutions on TMG 2010 Firewall - Part 4
- ★ Learn about firewalls, Windows Firewall on Windows Server 2012
- ★ How to set up a firewall in Linux