How to Install Gradle on Debian 10
Install Gradle on Debian 10
- System update
- Install Java SE
- Download Gradle binaries
- Extract the Gradle file
- Set environment variables
The first step is to open a Terminal (shell) window or connect to your Debian system's console using SSH.
You're learning how to install Gradle on Debian 10 via Terminal, which can be launched by searching for it in the Activities search bar . The newly opened Terminal window is shown below:
 A new Terminal window opens
A new Terminal window opens
System update
Before continuing to install Gradle on Debian 10, update the system using the command below, then press the Enter key :
sudo apt updateThis is also shown in the following image:
 System update command
System update command
Once your Debian 10 system has updated all the required packages, you should be able to see the following screen on the Terminal window:
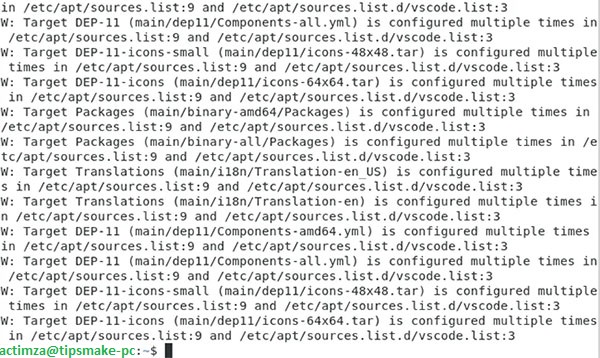 System update
System update
Install Java SE
Now, you need to have Java Standard Edition (SE) on your Debian 10 system. This can be done by entering the following command in Terminal and then pressing the Enter key :
sudo apt install default-jdkDuring the process of handling this command, your Debian 10 system needs to be sure that you are really ready to install the command. You can type 'Y' and then press the Enter key if you are sure to continue with the Java SE installation:
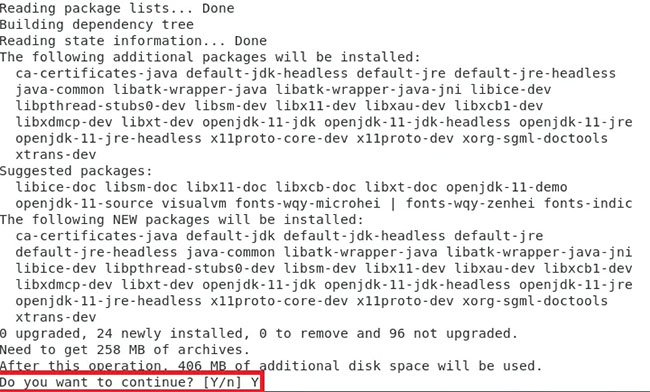 Confirm the installation of Java SE
Confirm the installation of Java SE
This entire process will take a few minutes to complete, after which you should be able to see the results displayed in Terminal:
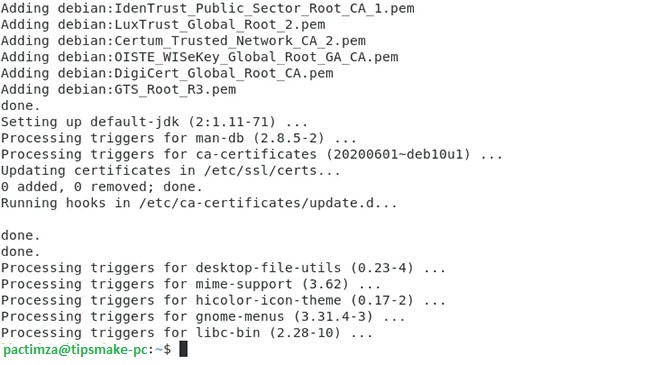 The results show up in Terminal
The results show up in Terminal
Up to now, Java SE has been successfully installed on your Debian 10 system. If you want to verify that it is actually installed, then you can do so with the help of the following command:
java -versionSuccessful execution of this command will result in the Java SE version displayed.
Download Gradle binaries
The next step is to download Gradle binaries on a Debian 10 system. This can be done by entering the following command in Terminal and then pressing the Enter key :
wget https://services.gradle.org/distributions/gradle-6.3-bin.zip -P /tmpIf you get the error message running this command, then the wget command is most likely not activated on a Debian 10 system. Wget can be activated by typing the following command and pressing the Enter key :
sudo apt-get install wgetOnce the wget command is successfully installed, you can conveniently run the above command. Once Gradle has been successfully downloaded on a Debian 10 system, you should see the results displayed in the Terminal:
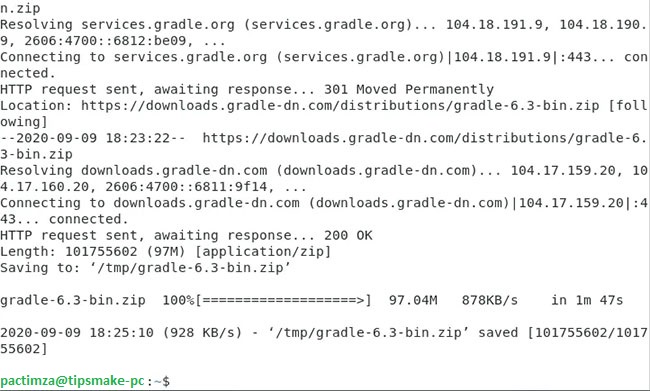 Gradle has been successfully downloaded on a Debian 10 system
Gradle has been successfully downloaded on a Debian 10 system
Extract the Gradle file
Since the Gradle file you just downloaded is in binary format, the next thing to do is unzip it. This can be done simply with the help of the following command:
sudo unzip –d /opt/gradle /tmp/gradle-*.zipRunning this command will extract the files from the tmp directory and save them in the opt directory . Now the Debian 10 system will do some processing, then the Terminal window will look like this:
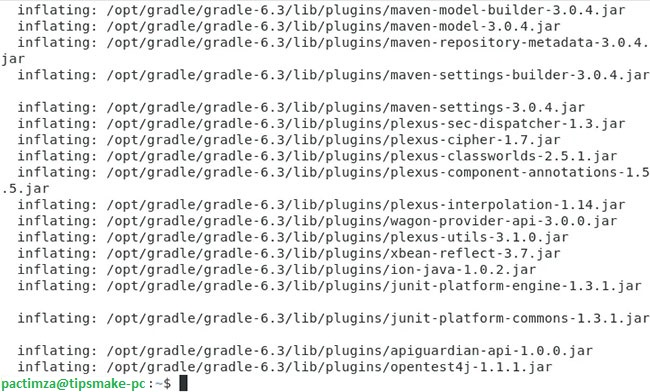 Extract the Gradle file
Extract the Gradle file
To verify if the extraction was performed successfully, you can try to display the contents of the extracted folder with the help of the following command:
ls /opt/gradle/gradle-*If the Gradle files have been successfully extracted, you should be able to see them in Terminal.
Set environment variables
Now, you need to set the environment variables by creating a new file called gradle.sh with the help of the following command:
sudo nano /etc/profile.d/gradle.shAfter creating this file, add the content shown in the following image to the newly created file. Then save the file and close it.
Now, you need to make this newly created file executable by running the following command:
sudo chmod +x /etc/profile.d/gradle.shNext, run the following command in Terminal to load the newly set environment variables:
source /etc/profile.d/gradle.shGradle has now been successfully installed on your Debian 10 system.
To verify that, simply enter the following command in Terminal, then press the Enter key :
gradle -vGradle has been successfully installed on your Debian 10 system!