What is a firewall? General knowledge about Firewall
Although the Internet is a valuable information and social communication mine, it's not always friendly. Instead, there are many bad guys stalking online with intrigue to hack into computers connected to the Internet.
After a series of large-scale network attacks recently, security on the computer has become hotter than ever. Besides the anti-virus software and communication ports in the system, you also need to pay attention to one more factor: firewall - firewall.
The first line of defense against intruders is a firewall: a set of specialized tricks that can help prevent malicious intent from entering your computer and limit what goes out of your computer. Windows also includes a separate firewall and the router (which helps connect computers to the Internet) also has its own router.
So what is a firewall or what is a firewall ? How does the firewall work? Is it safe to use only the built-in firewall? You will get answers to all the firewall issues in this article.

Overview of the firewall
- What is Firewall Firewall?
- How does the firewall work?
- Is Windows Firewall enough?
- Firewall deployment options
- Firewall is stateful (Stateful firewall)
- Next-generation firewall (Next-generation firewalls - NGFW)
- Proxy-based firewall (Proxy-based firewall)
- Web application firewall (Web application firewall - WAF)
- Hardware firewall
- Firewall software
- Check status
- Kill the virus
- Intrusion prevention system (Intrusion Prevention Systems - IPS)
- Deep analysis of packages (DPI)
- Check SSL
- Sandboxing
- Epilogue
What is Firewall Firewall?
A firewall is a network security system that can be based on hardware or software, using rules to control incoming and outgoing traffic. The firewall acts as a barrier between a secure network and an unsecured network. It controls access to network resources through an active control model. That is, only the traffic in accordance with the policy defined in the firewall can access the network, all other traffic are denied.
Any computer connected to the Internet also needs a firewall, which helps manage what is allowed on the network and what is allowed out of the network. It is important to have such a 'gatekeeper' to monitor everything that happens because of two reasons:
First, any computer connected to the network often connects permanently to the Internet. Secondly, each online computer has its own digital signature, called the Internet Protocol address (also known as an IP address): If there is no firewall support, it is no different from turning on all lights. up and open the door to steal into.
A correctly configured firewall will prevent this from happening and help your computer 'hide' effectively, allowing users to comfortably enjoy what the online world has to offer. Firewall is not the same as an antivirus program. Instead, it works with these tools to ensure that computers are protected from most common malicious attacks.
Windows XP, Vista and 7 include a firewall, called Windows Firewall, that is enabled by default. Check your firewall by: XP users should click Start → Control Panel , then click on the Switch to Classic View link before double-clicking on the Windows Firewall icon: check if the On button has been activated. or not
Windows Vista or Windows 7 users will have to click Start → Control Panel → System and Security (or Security in Windows Vista). Then, find the Windows Firewall line and click on it (in Vista) or click on Check firewall status (for Windows 7).
How does the firewall work?
The work of a firewall is quite difficult, because there is a lot of legal data that needs to be licensed to or to a computer connected to the network. For example, when we visit TipsMake.com, read news, new technology tips, the information and data of the website needs to be transmitted from and to the computer via the network to complete this process.
A firewall needs to know the difference between legitimate traffic like this and other types of harmful data.
Firewall uses rules or exceptions to work with good connections and eliminate bad connections. In general, this process is done offline, users cannot see or need to interact at all.
To see how Windows XP does, click Start → Control Panel and double-click the Windows Firewall icon. When a dialog box appears, click the Exceptions tab at the top to see what software is allowed to connect to - it's like including antivirus and online storage, such as Dropbox. .
Windows Vista and Windows 7 users will have to click Start → Control Panel → System and Security (or Security in Vista) → Windows Firewall . When a window appears, click the link Allow a program or feature through Windows Firewall in the list on the left ( Allow a program through Windows Firewall ) to see what software is allowed to communicate via the firewall.
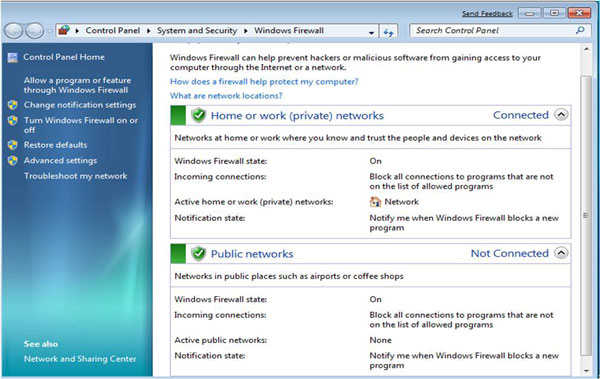
In general, Windows automatically keeps track of these rules and exceptions, but this is where you need it when you want to change something.
- How does the firewall work?
Is Windows Firewall enough?
For XP users, Windows Firewall may still be inadequate because it does not block external connections. So, if some malware finds a way to get into the computer, there's no way to stop its vandalism. We recommend users to download some free firewall software and install it to use in parallel with the Windows XP firewall.
Windows Vista and Windows 7 firewalls do not suffer from the same problems. Even so, we still recommend that users enable the hardware firewall built into the router - the device is used to connect to the Internet. The hardware firewall is designed to isolate external threats and protect all devices and computers connected to the home network.
Depending on the type of router, most of them are managed via a web-based configuration screen. Find the address by checking the manual. For example, with BT Infinity Home Hub, type http:///bthomehub.home into the address bar of the browser, or use the IP address like http://192.168.1.1 ).
Log in to the router's management panel with the name and password you created at the first setup. Next, refer to the router's support file to find the firewall settings: for a BT Home Hub, under Settings → Advanced Settings → Port Forwarding .
In our sample, the hardware firewall is set up to allow connections to come out and block all incoming traffic. Click Supported Applications will display it automatically set up to manage software and games that need Internet access to work.
Firewall deployment options
Advances in firewall technology have created firewall deployment options over the past decade. There are many options for end users, they include the following options:
Firewall is stateful (Stateful firewall)
When the firewall is created for the first time, they have no state, meaning that the hardware that the traffic goes through while being monitored will track each packet of private network traffic and block or allow it.
Beginning in the mid to late 1990s, the first advances in firewalls were born. The firewall has a traffic inspection state, related to the operating state and network connection characteristics to provide a more comprehensive firewall. Maintaining this state allows the firewall to give certain traffic access to specific users while blocking similar traffic to other users.
Next-generation firewall (Next-generation firewalls - NGFW)
Over the years the firewall has added a wealth of new features, including deep Packet Inspection (DPI), intrusion detection, blocking and checking encrypted traffic. Next-generation firewalls refer to this integrated but advanced feature firewall.
Proxy-based firewall (Proxy-based firewall)
These firewalls act as a gateway between end users who request data and the source of that data. All traffic is filtered through this proxy before being transferred to the end user. This is to protect the client from exposure to threats by hiding the identity of the person requesting the initial information.
Web application firewall (Web application firewall - WAF)
Firewalls are used for specific applications instead of being placed on an entry or exit point of a wider network. While proxy-based firewalls often protect end-user clients, the web application firewall protects the application server.
Hardware firewall
Firewall hardware is usually a simple server that can act as a router to filter traffic and run firewall software. These devices are located in the corporate network, between the router and the connection point of the Internet service provider. An enterprise can deploy dozens of physical firewalls in a data center. Users need to determine throughput they need a support firewall based on user base size and Internet connection speed.
Firewall software
Often end users deploy multiple firewall hardware endpoints and central firewall software systems to manage deployment. This central system is where policies and features are configured, where analysis and response to threats can be performed.
Check status
This is the basic firewall function in which the device blocks unwanted traffic.
Kill the virus
Thanks to the latest threat updates, the firewall can detect known viruses and vulnerabilities in network traffic, thereby protecting them from these threats.
Intrusion prevention system (Intrusion Prevention Systems - IPS)
This security layer can be deployed as a standalone product or integrated into the next generation firewall. While basic firewall technology identifies and blocks certain types of network traffic, IPS systems use many more detailed security measures such as signature tracing, unusual detection to prevent threats. Unwanted entry into the corporate network.
Deep analysis of packages (DPI)
DPI can be part or used in conjunction with an IPS system, but it becomes an important feature of next-generation firewalls because of the ability to analyze traffic in detail, especially targets. threads of packets and traffic data. DPI can also be used to track outbound traffic to ensure sensitive information does not leave the corporate network, a technology called blocking data loss (DLP).
Check SSL
Secure drive layer inspection (SSL) is used to check encrypted traffic to see if there are threats. As more and more traffic is encrypted, SSL testing becomes an important part of DPI technology being deployed in the new generation firewall. SSL checks act as a decryption buffer before it is transferred to the final location for inspection.
Sandboxing
Sandboxing is one of the new features deployed in the next generation firewall, referring to the firewall's ability to receive certain unknown traffic or code and run it in a test environment to determine if it has a problem or not.
- 7 best Sandbox apps for Windows 10
Epilogue
In general, Windows 7, 8 / 8.1, 10 and Vista users may be a bit less worried because they already have a built-in firewall that does the job. However, as mentioned above, Windows XP users are recommended to install antivirus software instead. In all cases, users should regularly check their 'defenses' to ensure they are always working well.
See more:
- 10 free firewall software is most worthwhile
- Instructions for handling and troubleshooting firewall problems in Windows 10
- How to block or unblock programs on Windows Firewall?