DURATION function - The function returns the periodic periodic interest payments in Excel
The following article details how to use the DURATION function to determine the period of periodic interest payment.
Description: The function that returns the validity of a bond is a weighted average of the current value of the cash flow.
Syntax: DURATION (settlement, maturity, coupon, yld, frequency, [basis]) .
Inside:
- settlement : The settlement date of a security is the date securities are sold to buyers after the issuance date, which is a required parameter.
- maturity : The expiry date of the stock, or the maturity date, is a required parameter.
- Coupon : The annual coupon rate of the security, is a required parameter.
- yld : Annual profit of the securities, is a mandatory parameter.
- frequency : Number of interest payment times per year, a required parameter.
- basis : The basis determined to calculate the number of days, is an optional parameter. The following values are available:
+ basis = 0: Calculates the number of days according to US standards, the number of days / year is 30/360.
+ basis = 1: The number of days / year is the actual number of days on the month / number of actual days per year.
+ basis = 2: The number of days / year is the actual number of days on the month / days on the year is 360.
+ basis = 3: The number of days / year is the actual number of days on the month / days on the year is 365.
+ basis = 4: Calculating the number of days according to European standards, the number of days / year is 30/360.
Attention:
- If the input parameters are decimal numbers => the function takes an integer part of the parameters.
- If the settlement date and expiry date of the CK are invalid => The function returns the error value #VALUE !.
- If coupon The function returns the #NUM error value.
- If frequency is outside the value set {1, 2, 4} => returns the #NUM! Error value
- If basis is outside the value set {0, 1, 2, 3, 4} => returns the #NUM! Error value
- If the expiration date is less than the settlement date => the function returns the #NUM! Error value.
For example:
With the following table, calculate the period of time to pay interest annually.
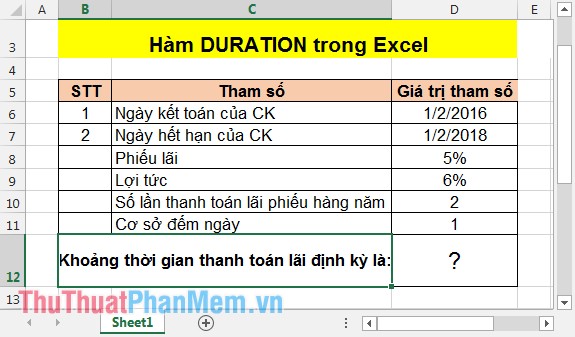
In the cell to calculate enter the following formula: = DURATION (D6, D7, D8, D9, D10, D11) .

After pressing Enter the result is:
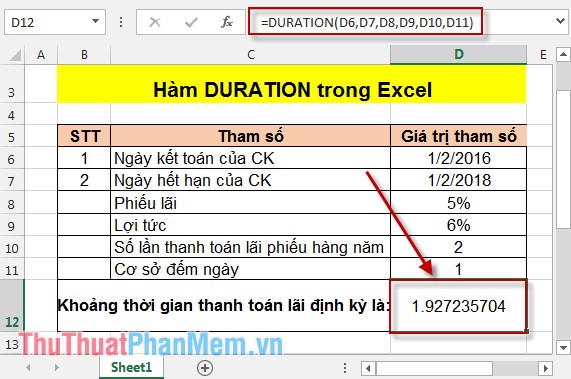
Thus, the term of bonds with the above terms is 1,927235704.
Above is the instruction for using the DURATION function.
Good luck!
You should read it
- ★ Enable / disable Periodic Scanning feature on Windows 10
- ★ FVSCHEDULE function - Returns the future value of an investment that has variable or adjustable interest in period in Excel
- ★ PMT function in Excel - Usage and examples
- ★ How to use the IF function in Excel
- ★ GEOMEAN function - The function returns the average of a positive array or range of data in Excel