How to use the IFS function in Excel 2016
What is the IFS function?
The IFS function in Excel is a logical function introduced in Excel 2016. This function is a function that replaces the nested IF function and is much easier to use. The IFS function checks one or more conditions and returns a value that meets the first TRUE condition.
Recipe
= IFS (logical_test1, Value1 [logical_test2, Value2] ., [logical_test127, Value127])
Inside:
- Logical_test1 checks the logic condition first. It is a required argument and is a condition used by Excel to evaluate either TRUE or FALSE.
- Value1 is the result when logical_test1 is TRUE. If necessary, you can set it blank.
The rest of the logical_test and Value arguments are optional. The function allows users to use logical_test 127 arguments.
How to use the IFS function in Excel
This is a built-in function that can be used as a function in an Excel worksheet. Let's take an example:
Suppose we want to classify points A, B, C, D, E, and F according to the student scores achieved, we use the IFS function as follows:
= IFS (A2> 80, "A", A2> 70, "B", A2> 60, "C", A2> 50, "D", A2> 40, "E", A2> 30, "F" )
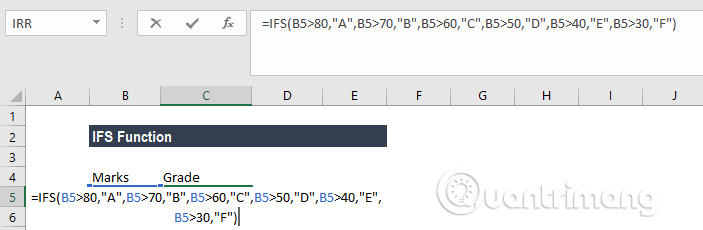
Specifically in this function set if A2 is greater than 80, the result returned is point A, if A2 is greater than 70 the result is returned as B, and so on to point F.
Using this formula we will have the following result:
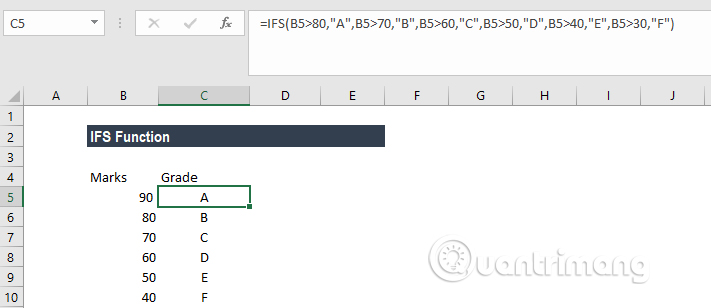
Example of IFS function in Excel
To understand how to use this function, let's look at a few examples:
Example 1 - Using IFS with ELSE
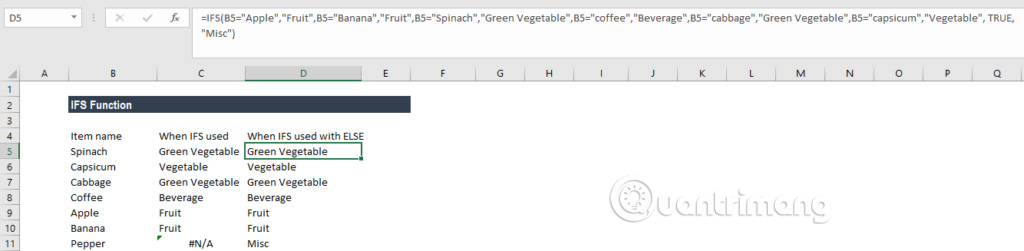
Suppose there is a list of items and need to classify them into groups of plates: Vegetable, Fruit, Green Vegetable and Beverage. When using the IFS function, you will have the following formula:
= IFS (A2 = "Apple", "Fruit", A2 = "Banana", "Fruit", A2 = "Spinach", "Green Vegetable", A2 = "coffee", "Beverage", A2 = "cabbage", "Green Vegetable", A2 = "capsicum", "Vegetable")
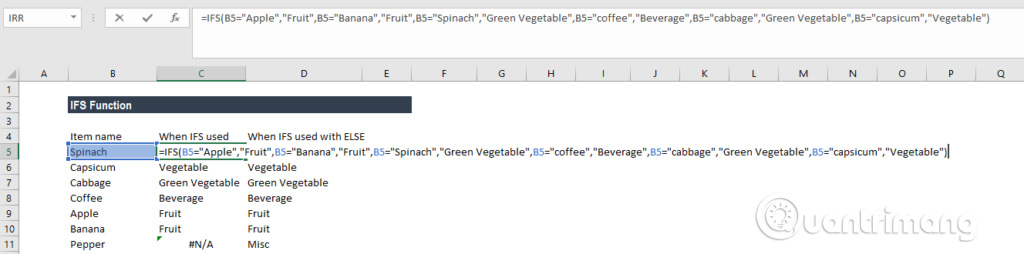
After that, we will get the following result:

In this example, we have set the logic condition in the IFS function. When a logical condition evaluates to TRUE, the corresponding value will be returned. However, if there is no logical condition evaluated as TRUE, IFS function will issue a # N / A error. As in this example is Pepper in cell B8.
To prevent the # N / A error from appearing, we can use the ELSE function. Therefore we can set the final logic condition in the formula to TRUE and then set a return value.
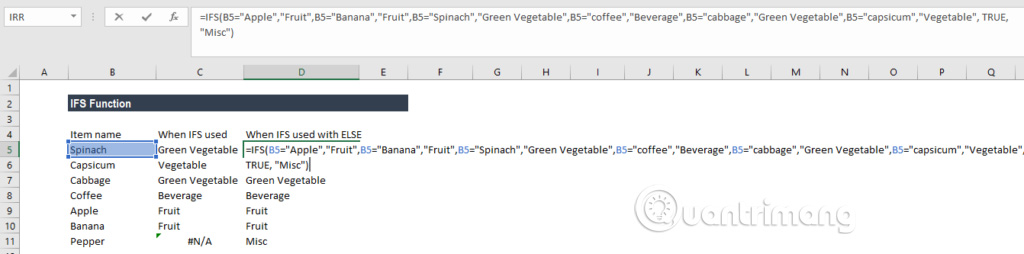
Here, we have added TRUE, "Misc", to ensure that Excel returns the "Misc" value in case no previous logical condition in the IFS function is evaluated as TRUE.
Now the result will be as follows:
Example 2 - IFS vs IF nested function
Before IFS functions, we often use nested IF functions. Let's see how IFS function is more efficient than nested IF function. Suppose a store makes a discount for customers based on their total purchase bill. Therefore, customers will receive a 5% discount for bills from USD 100 to USD 500, a 10% discount for bills from USD 500 to USD 750, a 20% discount for the total amount of USD 750 to USD 1,000 and a 30% discount when customers buy over 1000 USD.
Here is the formula when using the nested IF function:
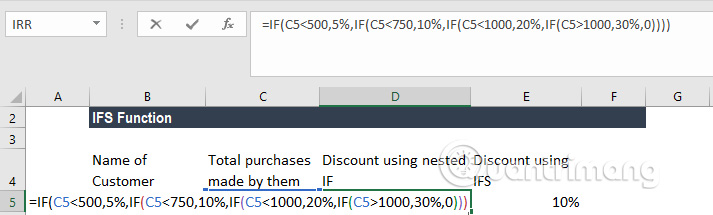
Now let's see what happens if IFS uses the function:

As you can see, the IFS function is easier to use because you only have to use a single function to enter a variety of logical conditions, while the nested IF function must use multiple logical conditions and is easy to confuse while write function.
Some errors occur when using the IFS function
1. Error # N / A occurs when no TRUE condition is found in the IFS function.
2. #VALUE! Error occurs when the logical_test argument processes into a value other than TRUE or FALSE.
3. Error message "You've entered too few arguments for this function" appears when you provide argument logical_test without the corresponding value.
I wish you all success!
See more:
- How to use the SWITCH function in Excel 2016
- How to use the TEXTJOIN function in Excel 2016
- These are the most basic functions in Excel that you need to understand